Asset Management
Asset Management helps you to see your cloud resources easily and thoroughly. You can view the relationships between your cloud resources at a glance, and find out how you can optimize your cloud resources and save costs based on our automated analysis.
Quick Start Guide
This guide provides the basics of Asset Management. First, make sure to register your cloud accounts and configure required settings in Service Portal. If you need to register your cloud accounts and configure required settings, please see Service Portal Quick Start Guide.
Dashboard
Dashboard provides graphical displays of total collected resources of your cloud services and related information. It also provides recent weekly usage and performance trends by collecting and analyzing resources. See Dashboard for more information about server, database & storage, network usage, performance, and resource information.Service Group
You can group certain resources according to your specific needs into a Service Group in Service Portal > Manage Service Group. You can view the grouped resources under each Service Group after selecting a View and Cloud Service accounts. See Service Group for details.Usage
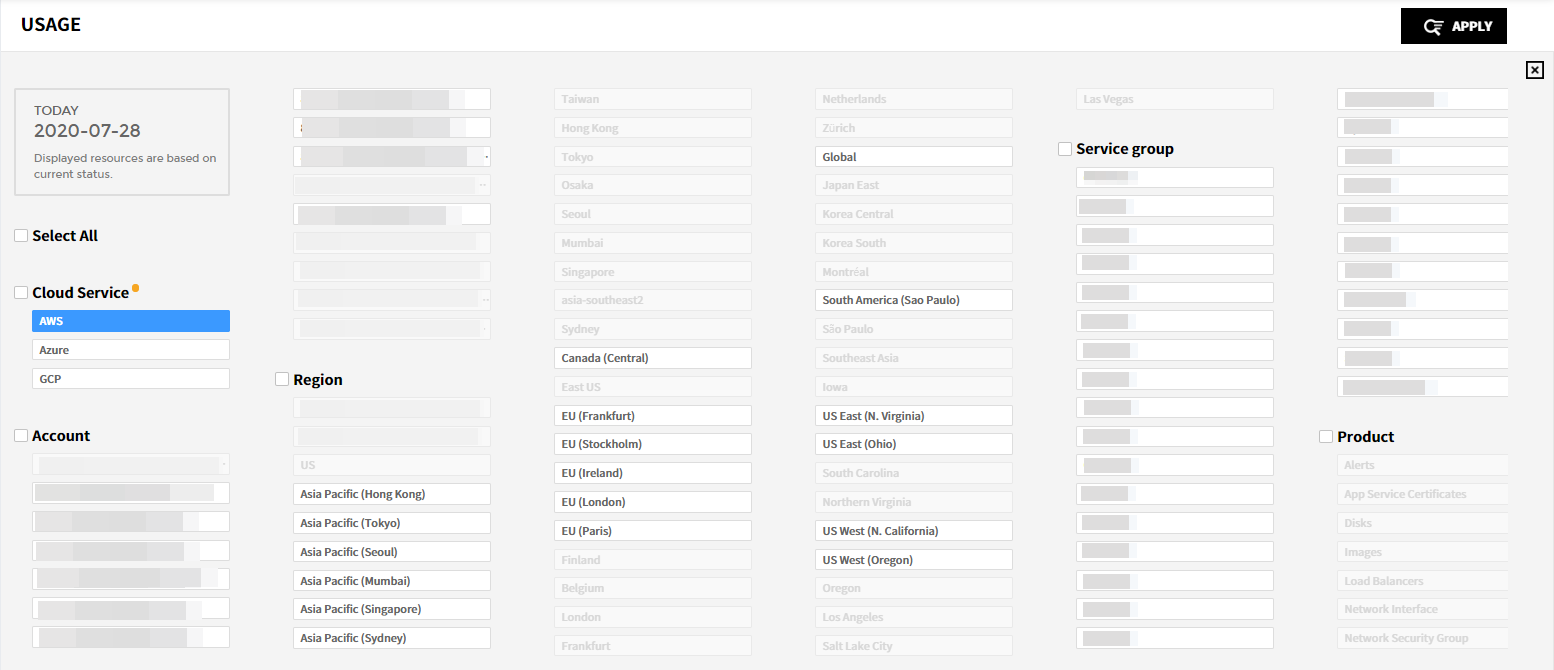
You can view your current resource usage and usage history. In Current tab, you can check the number of resources by status, regions, and types with pie charts and tables. In History tab, you can view the history of resource usage per hour. See Usage for more information.
Dashboard
Asset Management > Dashboard
From Dashboard, you can view overall summary and collected resources data in tables and charts.
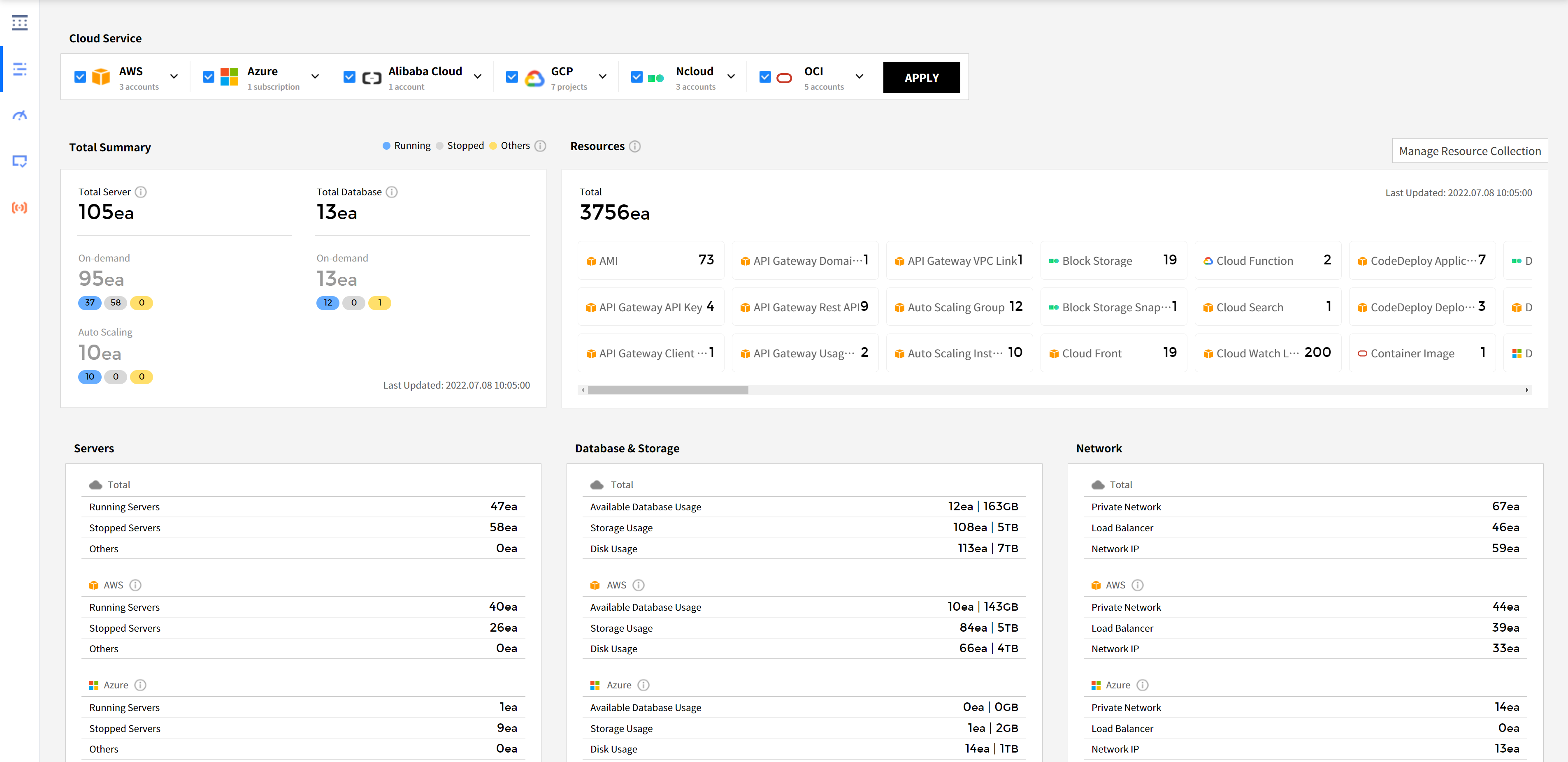
Cloud Service
The cloud service vendors currently in use and the number of accounts you registered are shown here. Select the cloud services and accounts you want to view and click the [Apply] button to see the resource status of the selected cloud resources. To view certain accounts only, click the drop-down button next to the cloud service vendor name and select accounts and click [Apply].

Total Summary
Displays the total number of servers and databases for selected cloud services and accounts. It displays the total number of On-Demand and Auto Scaling items as well as the number of each item by status. The number shown in blue is the running resources, gray is the stopped resources, and yellow is the resources that are either stopped, terminated, or Check Failed status.
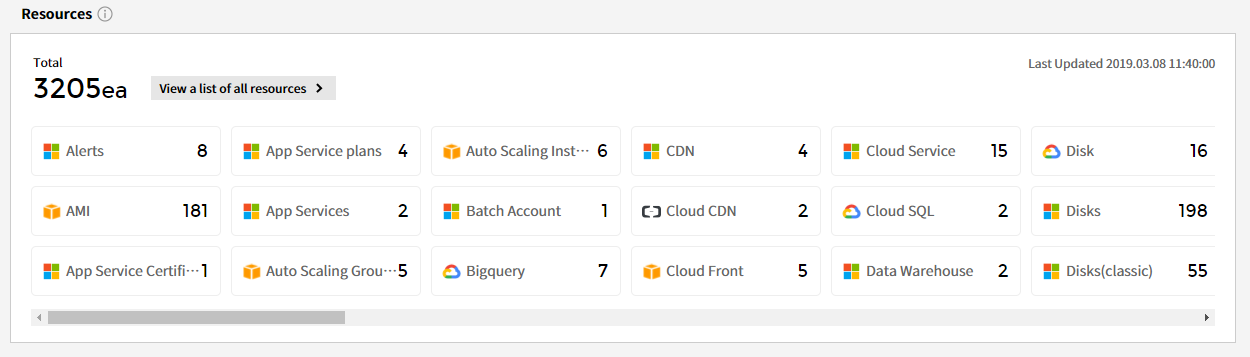
Resources
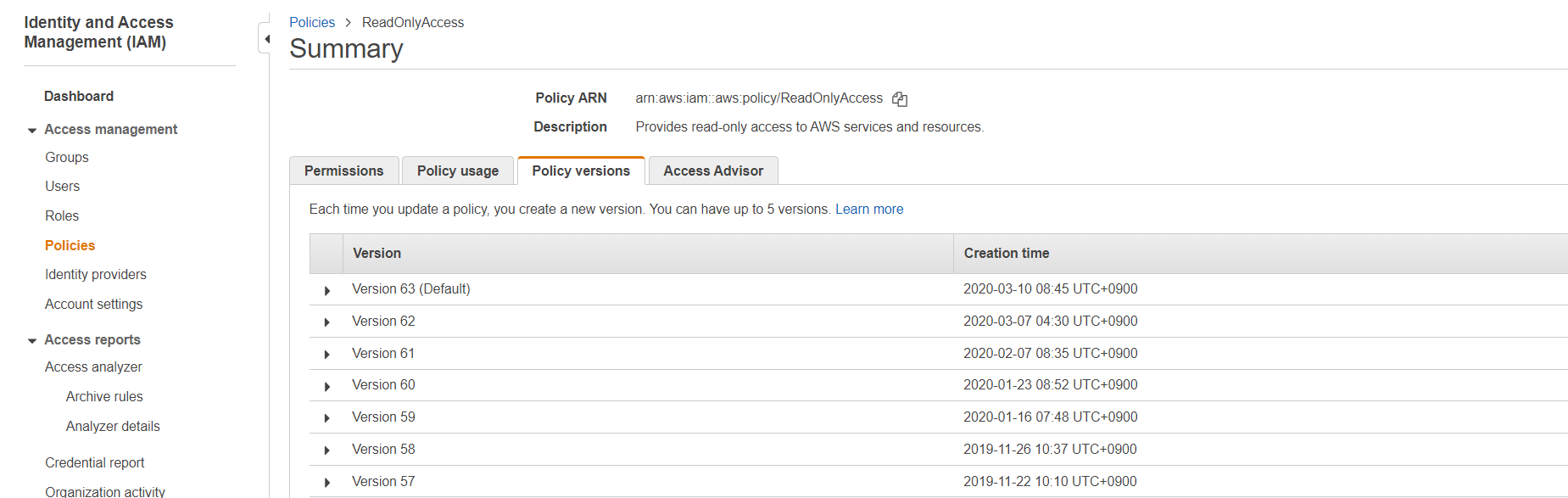
Displays a list of all the resources currently being collected and the number of each resource that are in use. Resource information is periodically updated. In order to view all resources, you need to add permissions to resources in your cloud service.
Manage Your AWS Policies to Add the Permissions
Widen your range of resources that are subjected to the resource data collection by updating your AWS IAM policies on the AWS Management Console.
⑴ Sign in to the AWS Management Console and go to the IAM menu. In the navigation pane, select Policies. In the list of policies, find the policy name of the policy attached to your cloud account. Most of them are [ReadOnlyAccess]. Search for [ReadOnlyAccess] or use the Filter feature to view the list of policies.
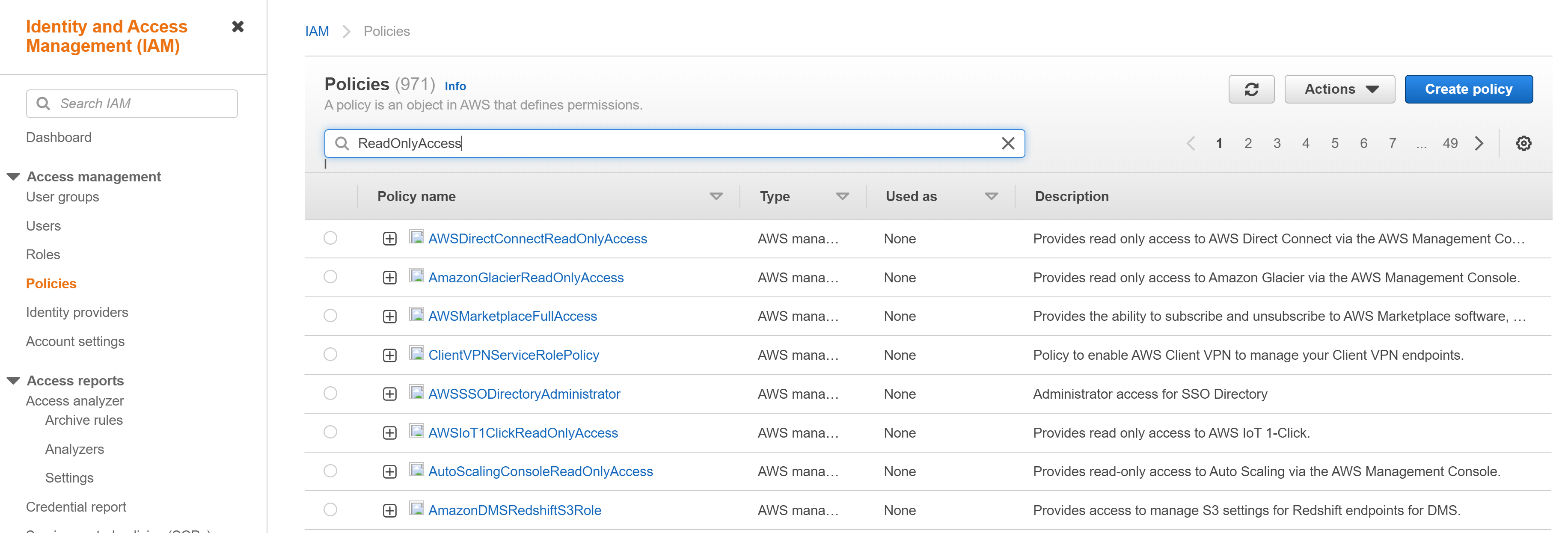
⑵ Select [ReadOnlyAccess] to see the permissions. Click [Show remaining OO] to see if there are any uncollected resources because of the lack of permission.
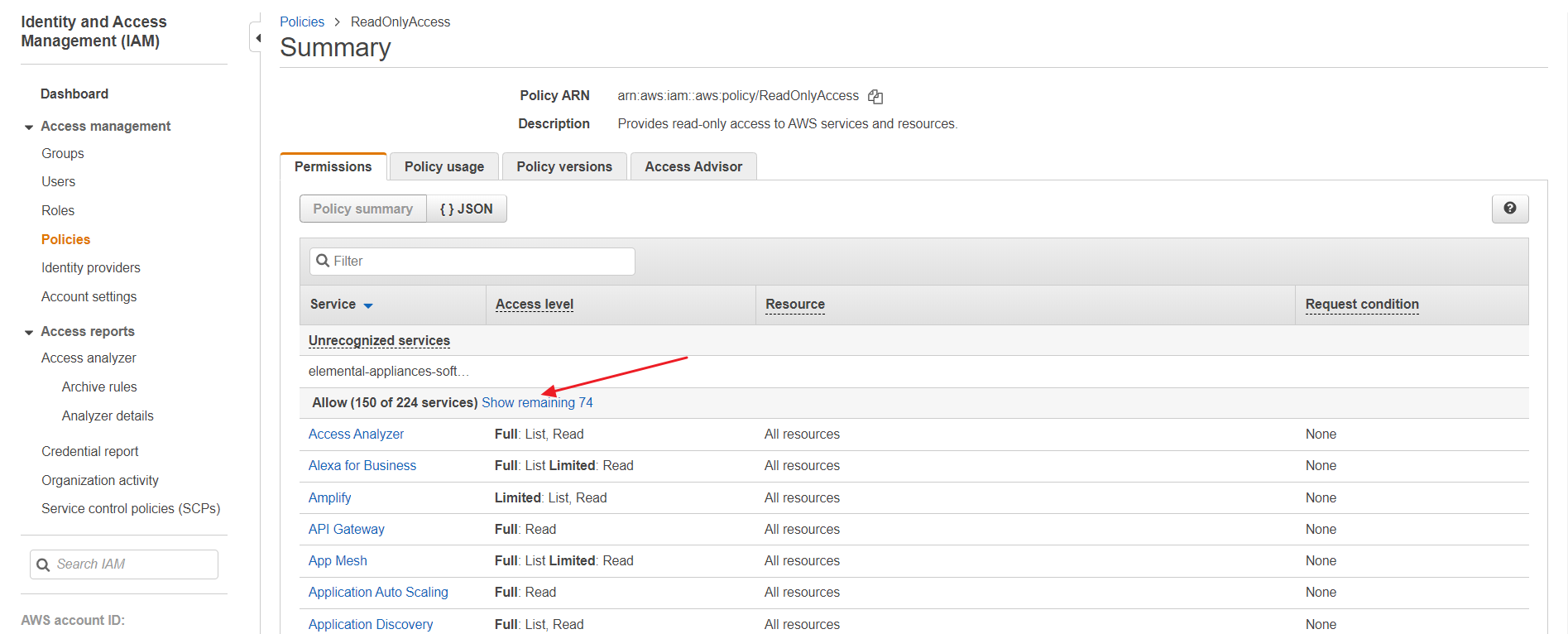
⑶ If so, you need to create a policy and then add permission to the resource because you cannot directly change the ReadOnlyAccess permission for it is an AWS-managed policy. Follow the step ① to ⑥ below:
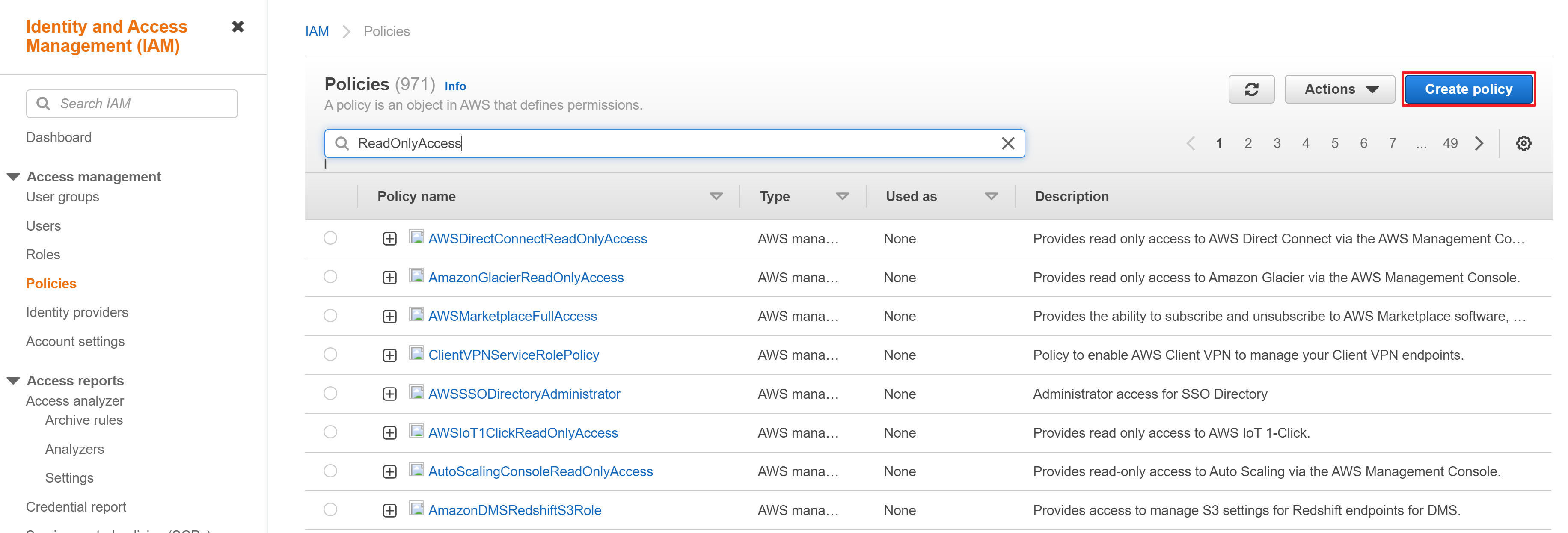
① In the [IAM] menu, go to [Policies] page, and click [Create policy].
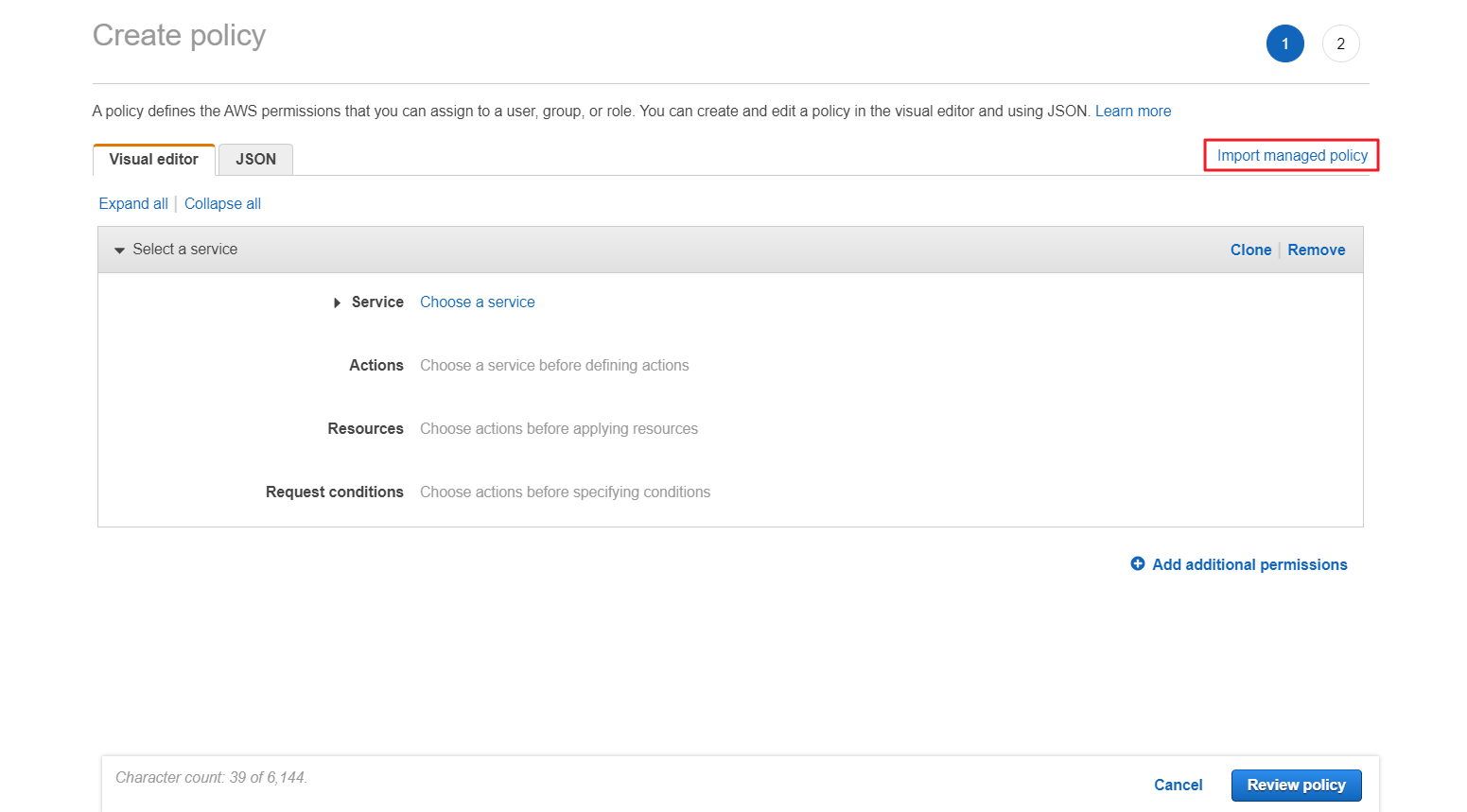
② Click [Import managed policy].
③ Search [ReadOnlyAccess] and click [Import] to import the [ReadOnlyAccess] policy.
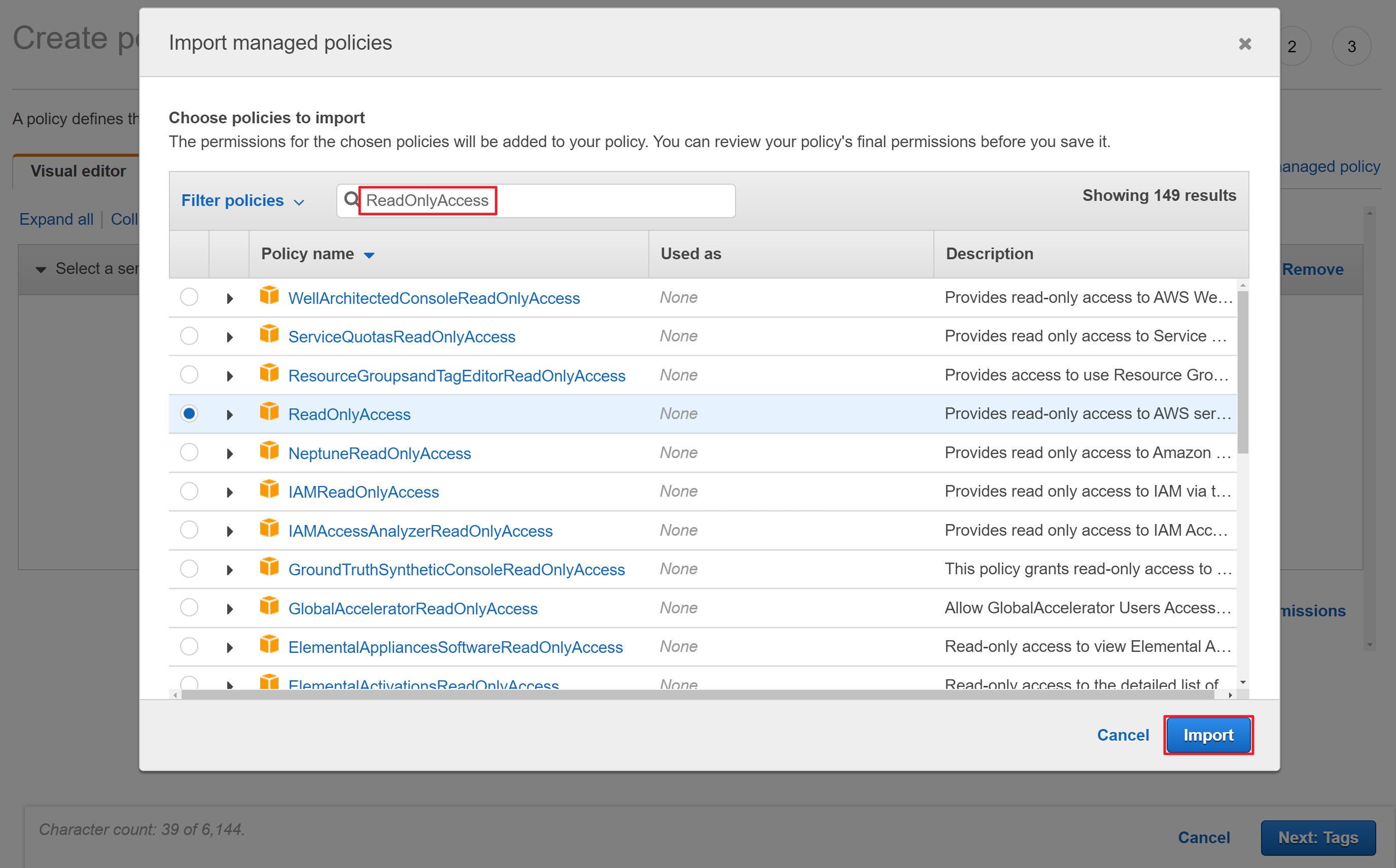
④ Click [Add additional permissions] to select the service you want to add permission.
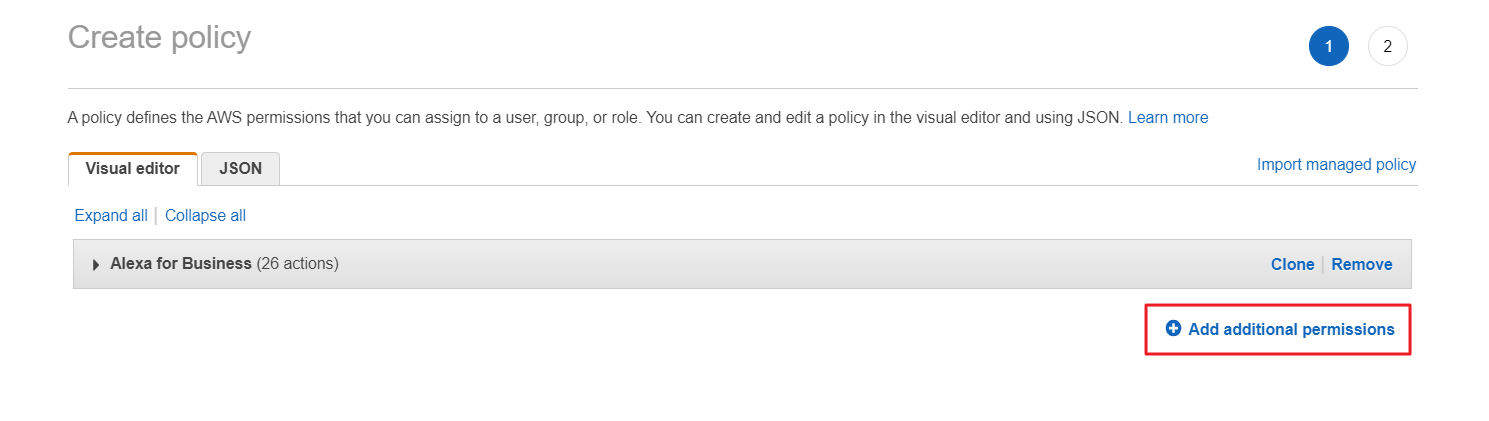
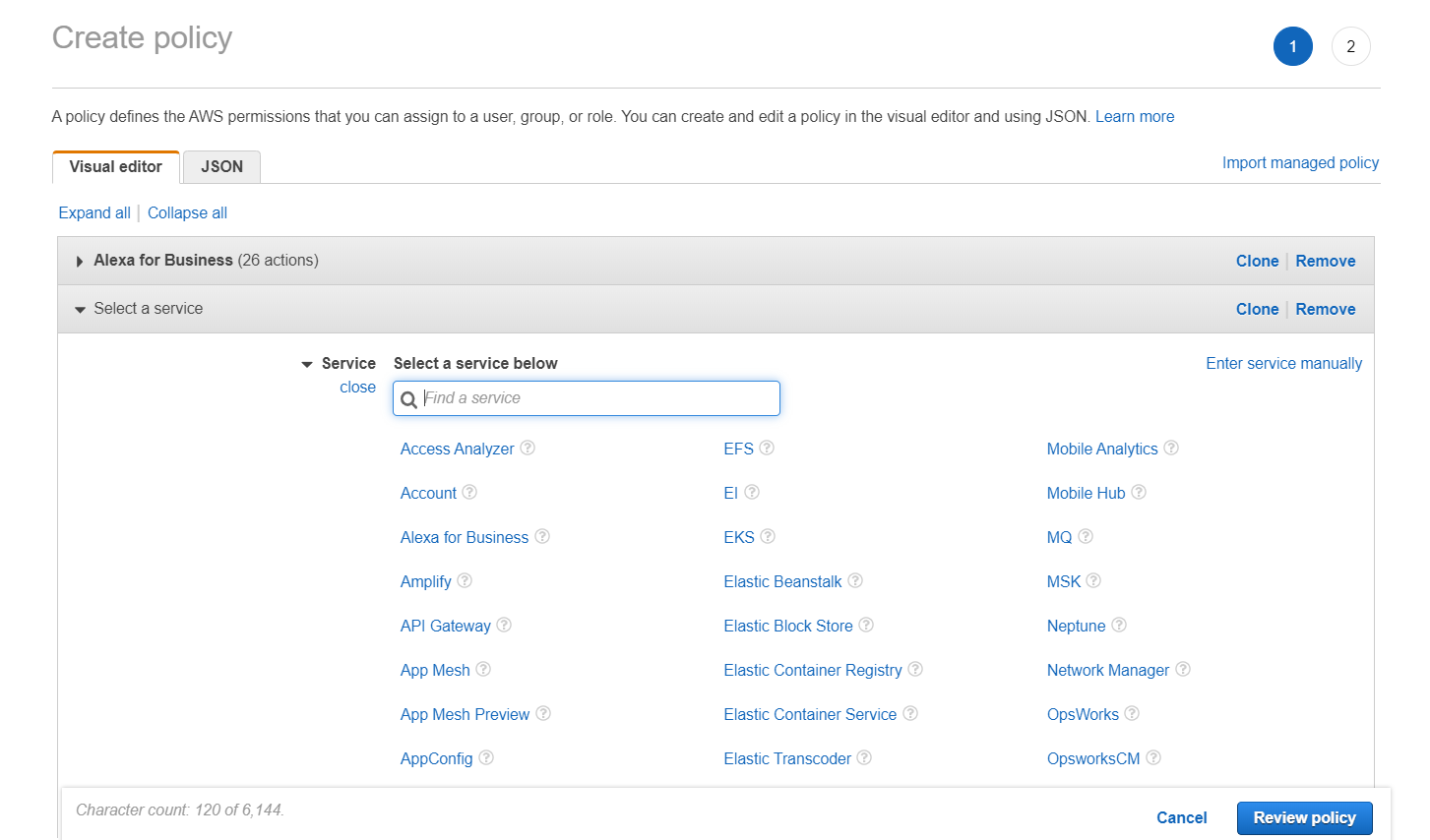
⑤ When you are done with adding permission, click [Review policy] to review the policy, and then click [Create policy].
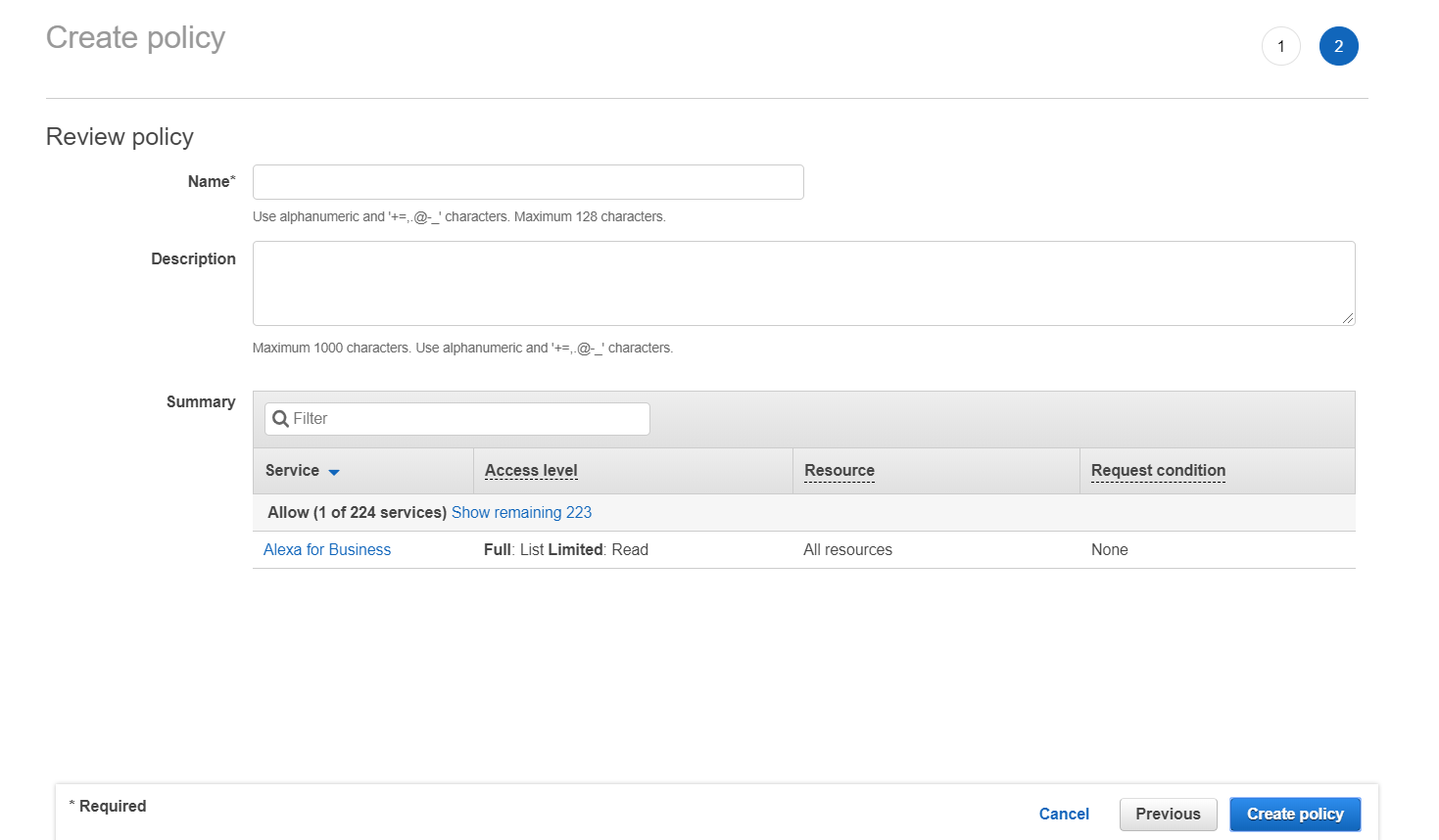
⑥ Now you just updated the IAM policy and permissions in the AWS Management Console. Now you need to update the registered account information in the Service Portal’s [Cloud Account]. For more information, please see Register AWS Accounts > Register with IAM Access Key user guide.
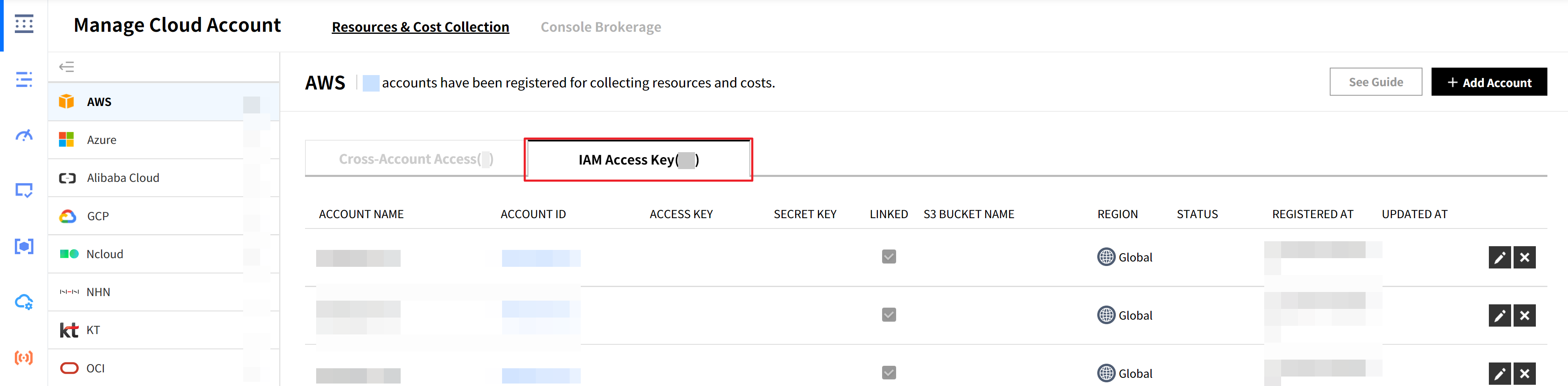
⑷ Check if the latest version is set to default in the Policy versions tab. Click the version name to check if there are any uncollected resources because of the lack of permissions.
⑸ If there exist more resources that you do not have permissions, you need to repeat the above Create Policy(⑶) process to create a policy and add a permission because you cannot directly change the ReadOnlyAccess permission for it is an AWS-managed policy.
Manage IAM Policies to Add the Permissions
You can manage the resource collection and view the list when you click the [Manage Resource Collection] button on the upper-right corner of the Asset Management’s Dashboard page. If some resources are shown as No IAM Permission under the View Permission Column, then you need to update the IAM policy and permissions on the AWS Management Console to configure view permissions.
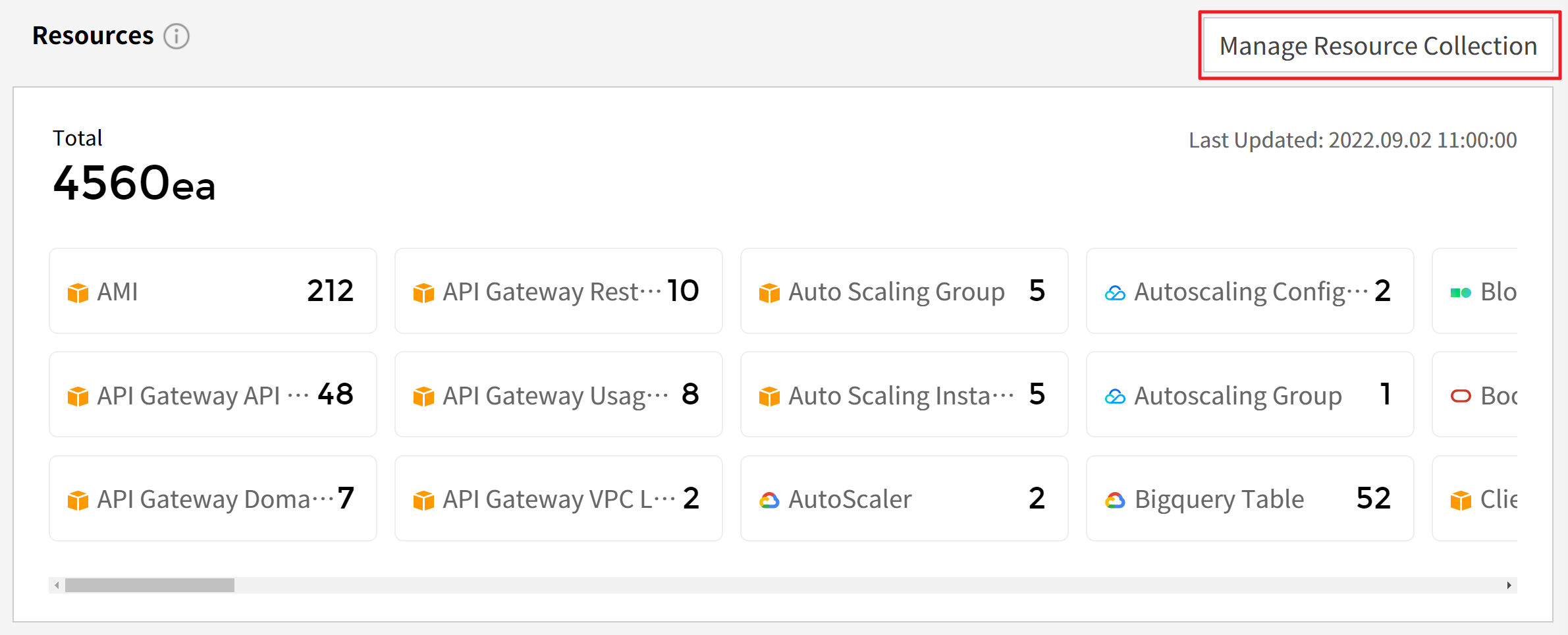
⑴ Sign in to the AWS Management Console and go to the IAM console. In the navigation pane, select Policies. In the list of policies, find the policy name of the policy attached to your cloud account. Most of them are [ReadOnlyAccess]. Search for [ReadOnlyAccess] or use the Filter menu to view the list of policies.

⑵ Click [ReadOnlyAccess] to see the permission. Search [IAM] and click it to see the resources with IAM permissions.
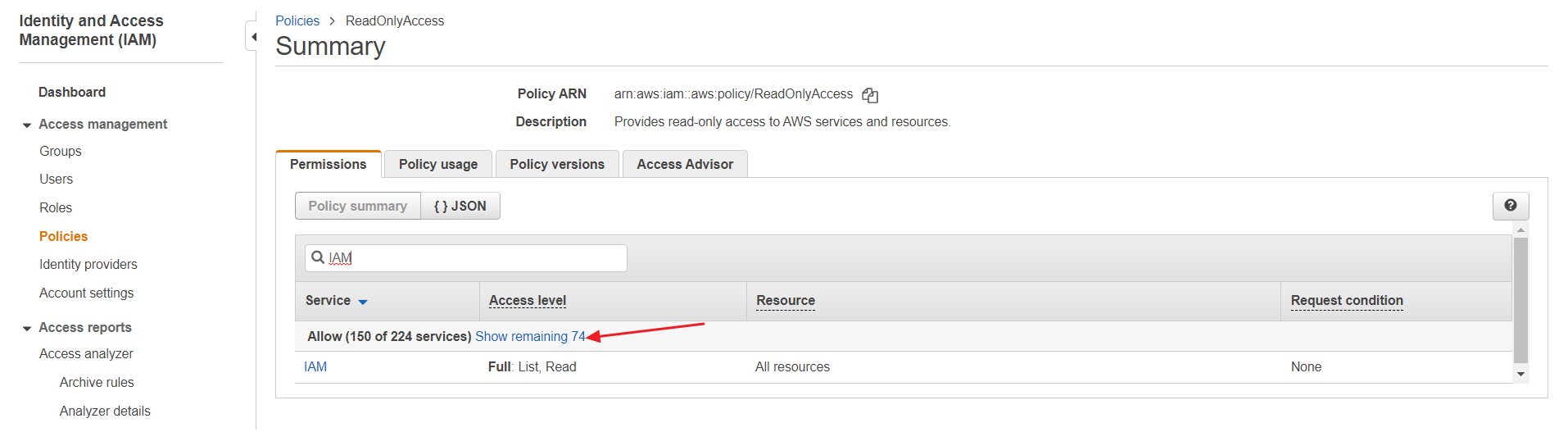
⑶ Click [Show remaining OO] to see if there are any uncollected resources because of the lack of permission. If so, you need to create a policy and then add permission to the resource because you cannot directly change the ReadOnlyAccess permission for it is an AWS-managed policy. Follow the step ① to ⑥ below:
① In the [IAM] menu, go to [Policies] page, and click [Create policy].

② Click [Import managed policy].

③ Search [ReadOnlyAccess] and click [Import] to import the [ReadOnlyAccess] policy.

④ Click [Add additional permissions] to select the service you want to add permission.


⑤ When you are done with adding permissions, click [Review policy] to review the policy, and then click [Create policy].

⑥ Now you just updated the IAM policy and permissions in the AWS Management Console. Now you need to update the registered account information in the Service Portal’s [Cloud Account]. For more information, please see Register AWS Accounts > Register with IAM Access Key user guide.

📌 Important! Charges are being generated by retrieving Amazon S3 resources
If you are retrieving S3 resources, you will be charged for it according to AWS Pricing. With AWS, you pay for requests made using the API/SDK against your S3 buckets and objects. S3 request costs are charged on the quantity of requests. The cost you’re charged depends on the type and quantity of S3 usage. For more information, see Amazon S3 pricing. If you have more questions, please contact our support team.
Servers
Displays the number of cloud services’ servers by status; and you can check their usage and performance status in a graph.
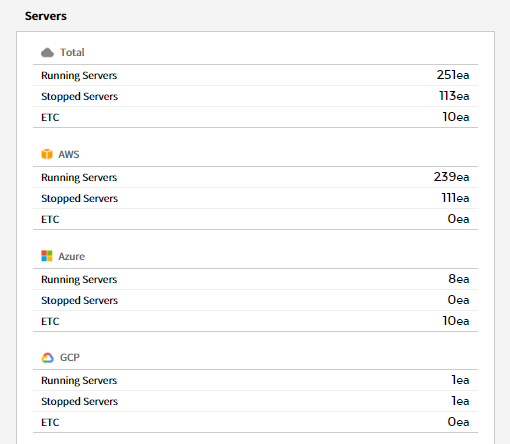
⑴ Server/Usage - Total Instances: Provides the trend chart of server usage for the last 7 days and the last week.
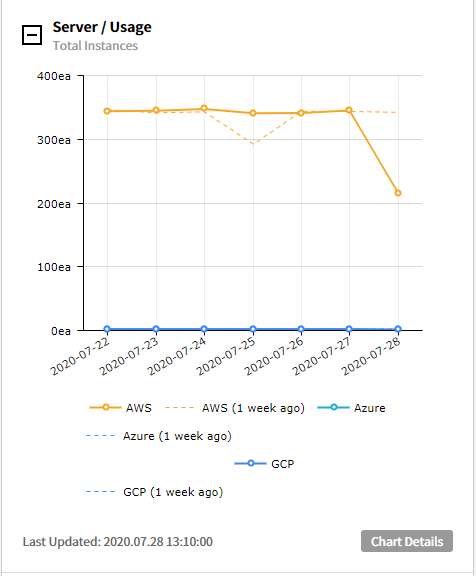
⑵ Server/Performance - Total Avg. of CPU Utilization: Provides the trend chart of average CPU utilization for the last 7 days and the last week.
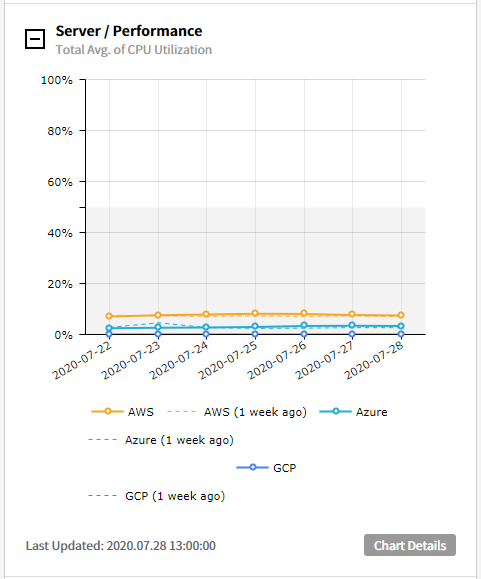
⑶ Server/Performance - CPU Utilization with Threshold: Provides the trend chart of CPU utilization if the threshold is higher or lower than the ones you configured. (Last 7 days / Last week)
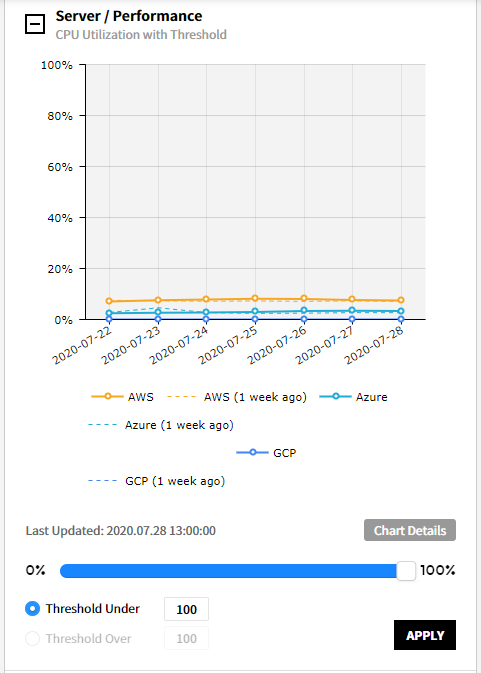
⑷ Server/Performance - Memory Utilization with Threshold: Provides the trend chart of memory utilization if the threshold is higher or lower than the ones you configured. (Last 7 days / Last week)
⑸ Server/Performance - Disk Utilization with Threshold: Provides the trend chart of disk utilization if the threshold is higher or lower than the ones you configured. (Last 7 days / Last week)
Database & Storage
You can check the usage and performance of currently used database, storage and disk in a graph.
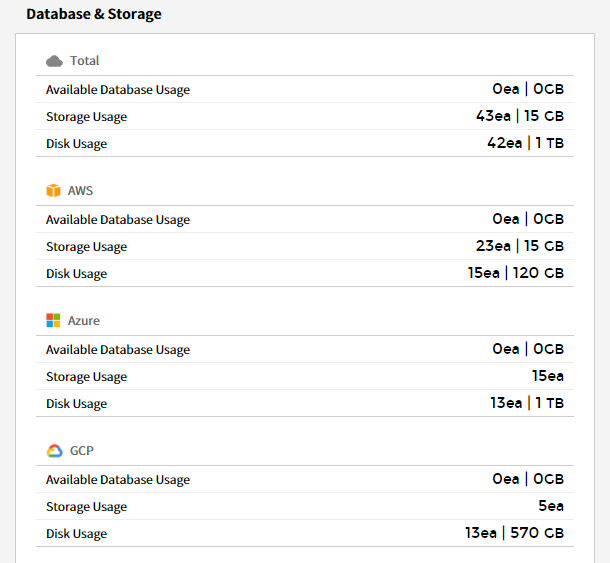
⑴ Database/Usage - Total Instances: Provides the trend chart of DB usage for the last 7 days and the last week.
⑵ Storage/Usage - Total Instances: Provides the trend chart of storage usage for the last 7 days and the last week.
⑶ Disk/Usage - Total Instances: Provides the trend chart of disk usage for the last 7 days and the last week.
⑷ Database/Performance - CPU Utilization with Threshold: Provides the trend chart of CPU utilization if the threshold higher or lower than the ones you configured. (Last 7 days / Last week)
⑸ Database/Performance - Average Read IOPS/Write IOPS: Provides the trend chart of Read IOPS/Write IOPS utilization if the threshold is higher or lower than the ones you configured. (Last 7 days / Last week)
Network
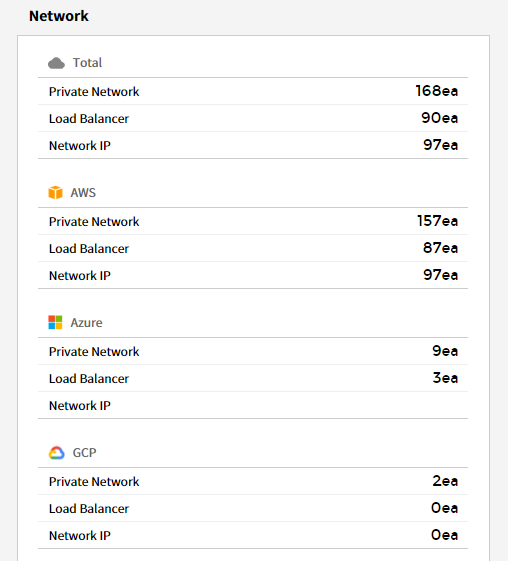
You can check the currently used network usage in a graph.
⑴ Private Network/Usage: Provides the trend chart of Private Network usage for the last 7 days and the last week. At the bottom of the trend chart, it shows a list and the number of resources by cloud service.
You can also check for each resource by clicking each category from the table.
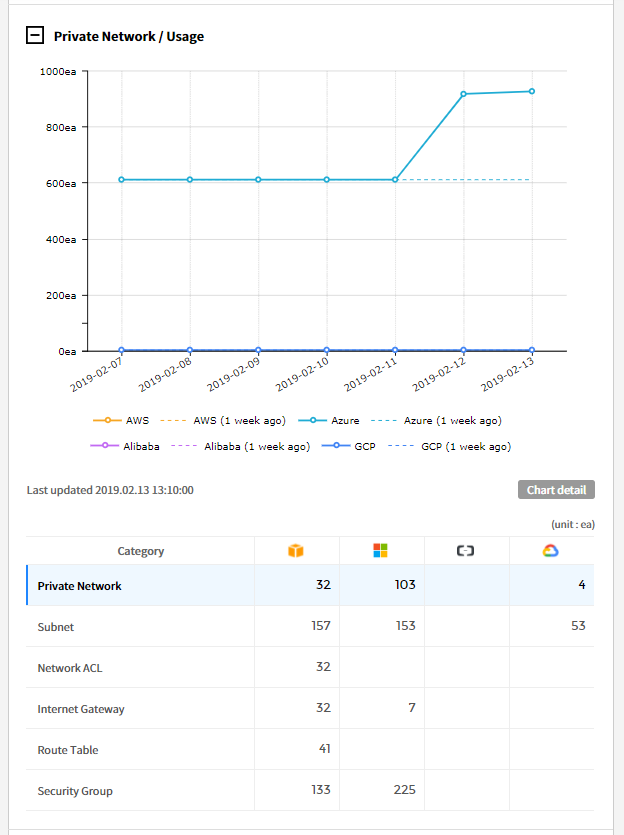
⑵ Network IP/Usage: Provides the trend chart of Network IP usage for the last 7 days and the last week. At the bottom of the trend chart, it shows a list and the number of resources by cloud service.
You can also check for each resource by clicking each category from the table.
Service Group
Asset Management > Service Group
You can freely classify cloud service resources as needed. You can also classify them by creating Views and then creating categories and service groups by created Views. The Service Group menu consists of the following.
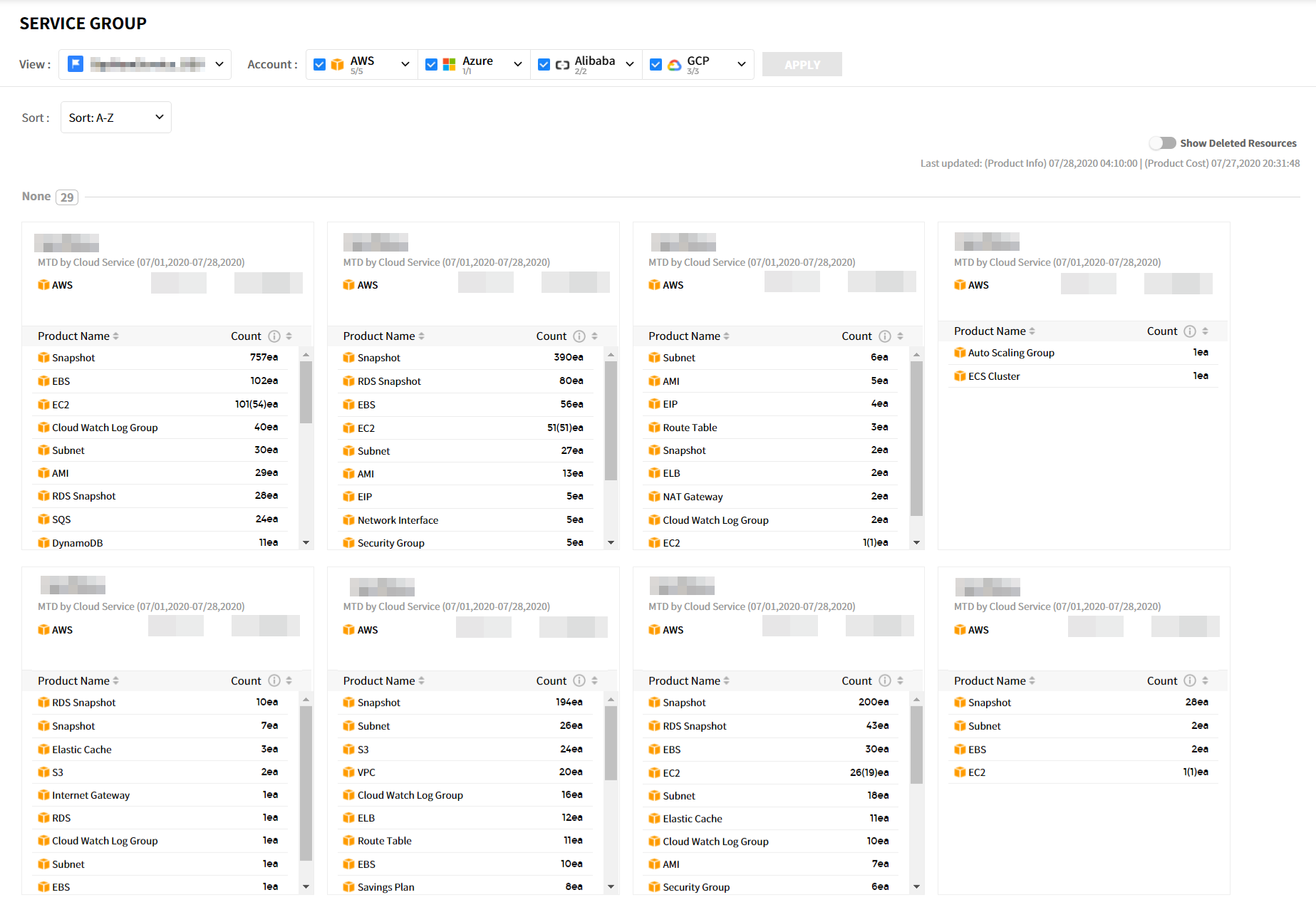
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| View | You can create Views by resources. If you select the created View and click Apply button, you can check the category, resource status per service group, and MTD by Cloud Service. (Default View is set as default) |
| Cloud Service | Displays the cloud services currently in use and the number of resources for each service. If you select the cloud service and click Apply button, the resource status for selected service will be displayed. |
| Show Deleted Resources | Toggling this button to ‘On’ will show the deleted resources in each service group. |
| Service Group Card | Displays the count, type, and costs for the resources used in Service Group.
|
📌 Important! If there are no resources in a service group, you need to create a resource in Service Group menu in Service Portal. For more information, please see Service Portal User Guide > Service Group > Adding Resources.
Usage
Asset Management > Usage
You can check the current status and history of resource usage per cloud service.
Current
You can check resource usage status per cloud service.
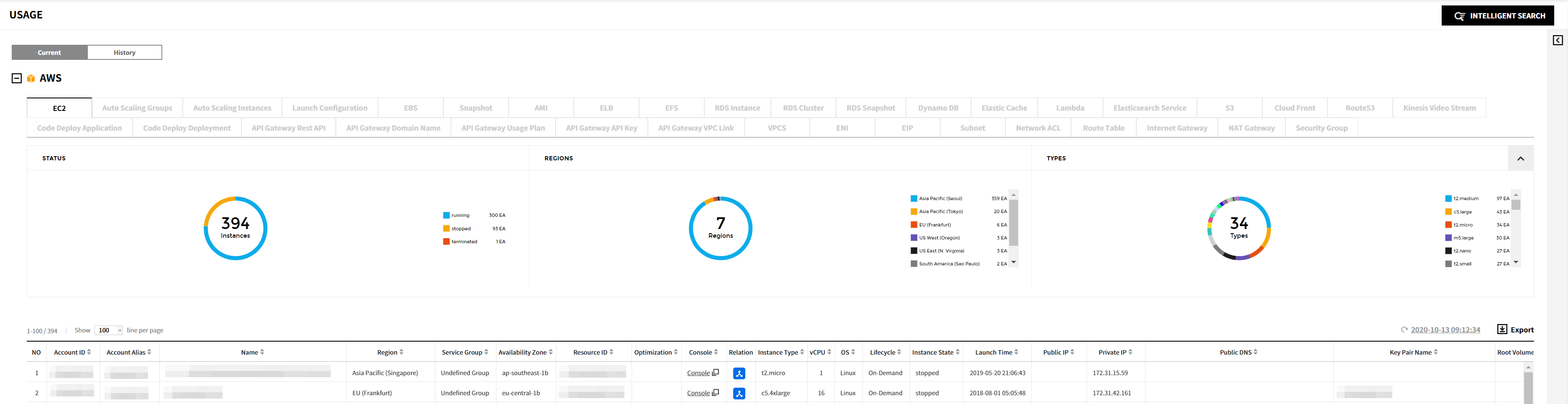
The Current service provides the pie chart of Status, Region and Type respectively for the resources listed below. On the list, you can check the list of resources in use and the details about each resource. For AWS, Azure, GCP, Ncloud, and Alibaba Cloud, you can also see Relation Map for specific resources.
AWS
You can check usage status of AWS resources listed below.
AMI, EBS, EC2, EIP, Internet Gateway, Lambda, Network ACL, RDS, Route Table, S3, Security Group, Snapshot, Subnet, VPCS, ELB, Dynamo DB, Elastic Cache, CloudFront, Kinesis Data Stream, ENI, NAT Gateway
Go to AWS Console
It provides the ability to go to the console so that you can view resource information in the AWS Console. You can go to the AWS Console in one of two ways below:
A. Go to the AWS Console to click the [Console] link of the Console column in the resource list.
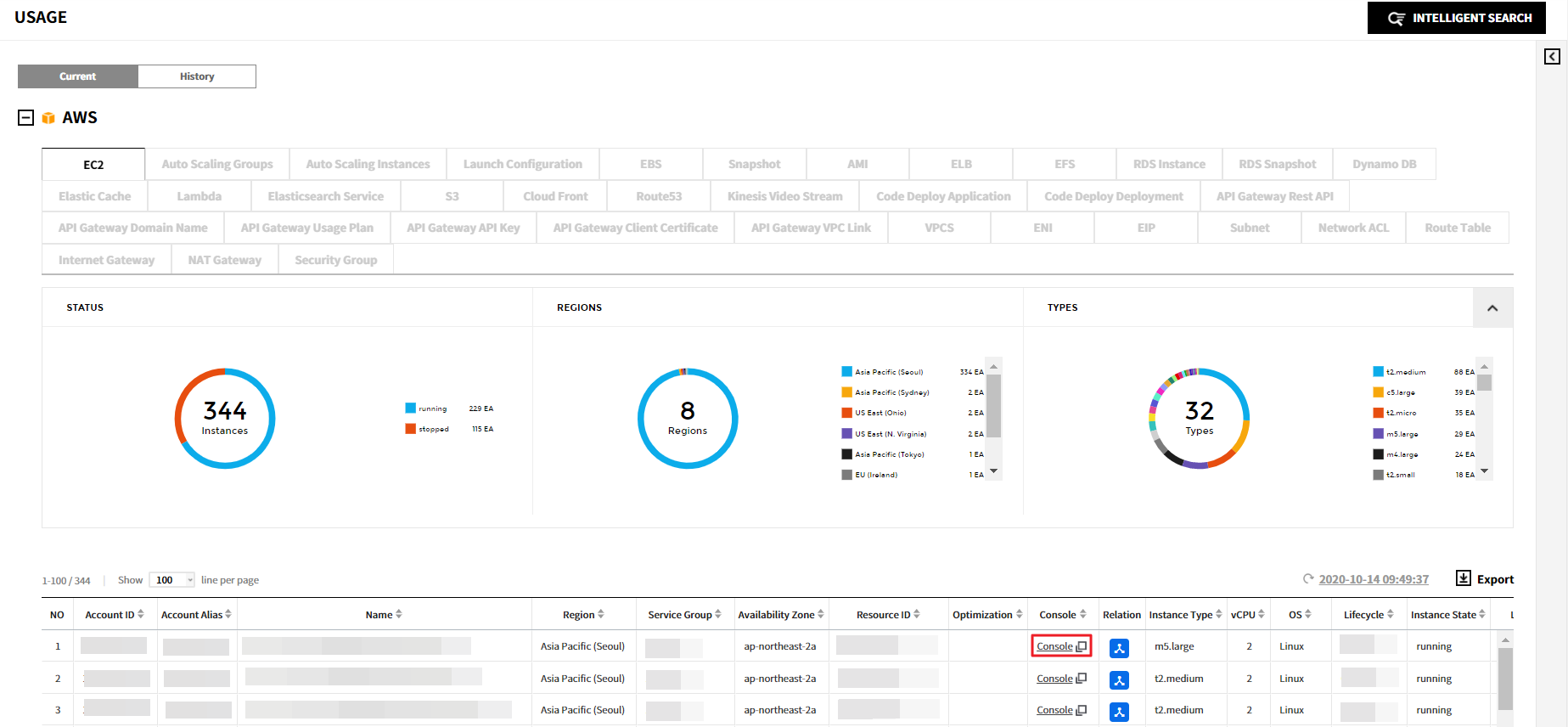
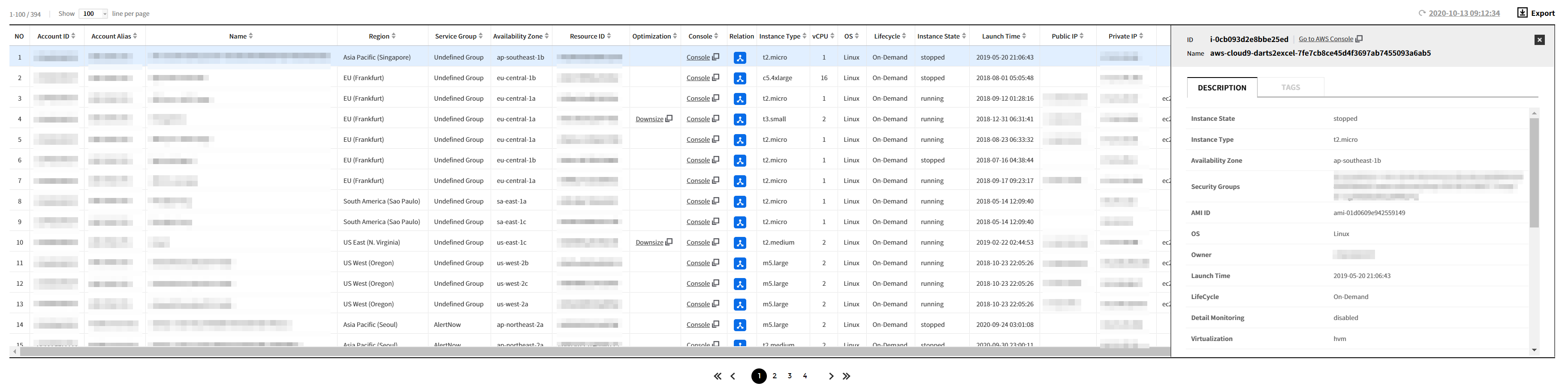
B-1. When you click a resource in the resource list, the details screen will be displayed as below. click Go to AWS Console to go to the Console.
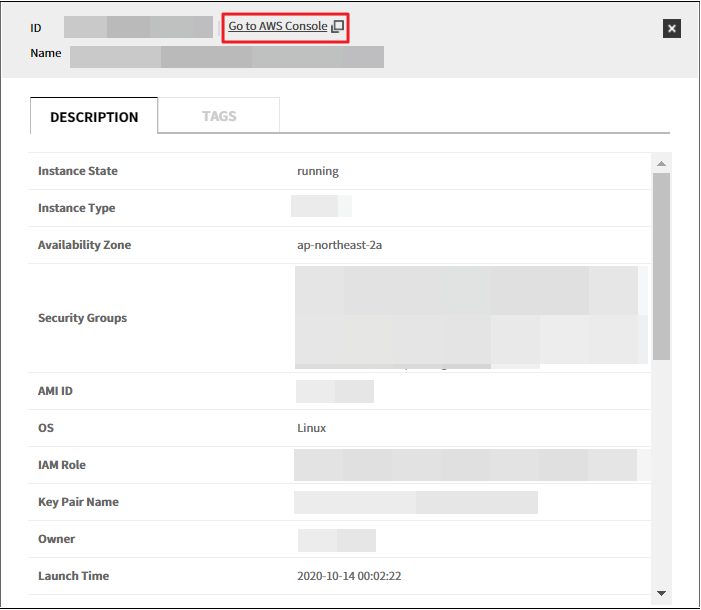
B-2. If you select one of two ways above, the following pop up message will appear and then you’ll be taken to the AWS Console. If you are not signed in to the AWS console, you will go to the sign in page.
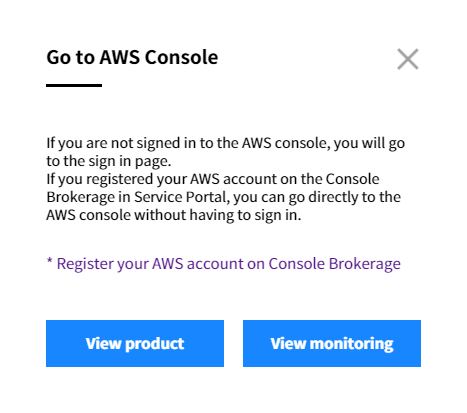
💡 Notification: If you registered your AWS account on the Console Brokerage in Service Portal, you can go directly to the AWS console without having to sign in. For more information on registering AWS account to the Console Brokerage, please see Service Portal User Guide > Console Brokerage.
Azure
You can check usage status of Azure resources listed below.
CDN, Cloud Service, Database, Virtual Network Gateway, Network Security Group, Storage, Virtual Network Subnet, Traffic Manager, Virtual Network, Virtual Machine
GCP
You can check usage status of GCP resources listed below.
VM Instance, Compute Disk, Big Table, Big Query, SQL Instance, Storage Bucket, VPC, Subnet
Go to GCP Console
You can go to GCP Console directly from the current view in order to view detailed information of resources you want to see. There are two options to go to the GCP Console as below.
A. Click Console from the resource list to go to the GCP Console.
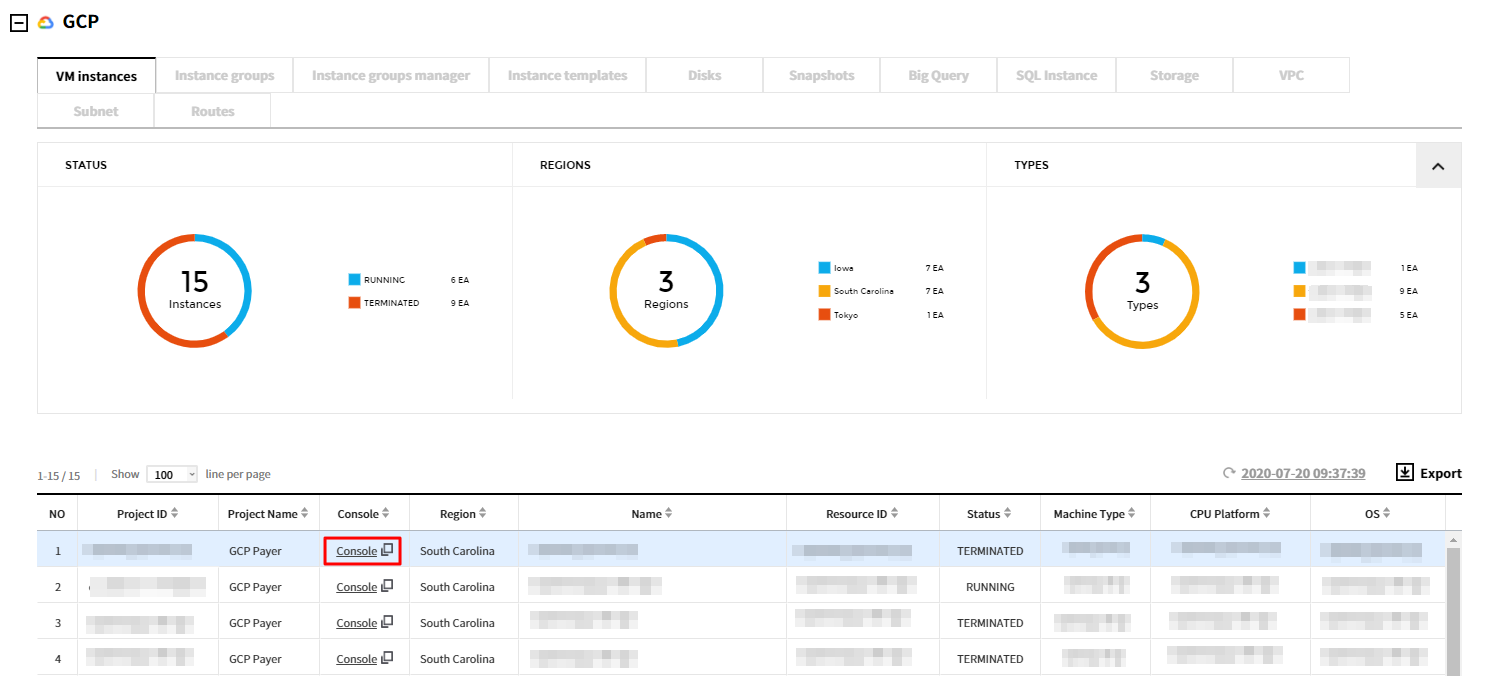
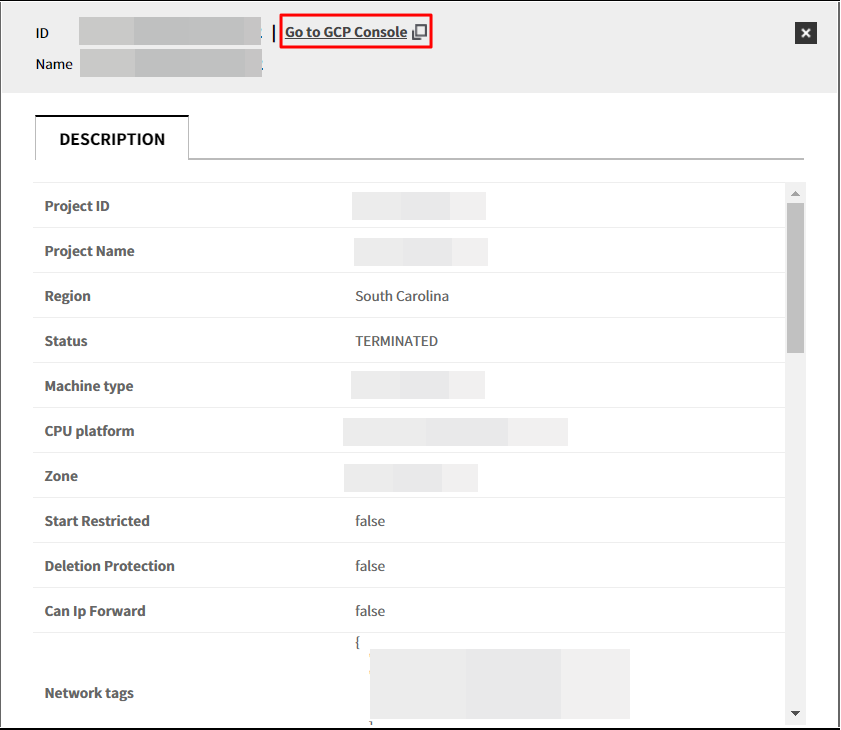
B-1. Click a resource from the list to view the detail page, then select Go to GCP Console button.
B-2. When you click Go to GCP Console, the following pop up message will be displayed. Click View product if you want to view the resource information from the GCP console, and click “View monitoring” to check resource performance.
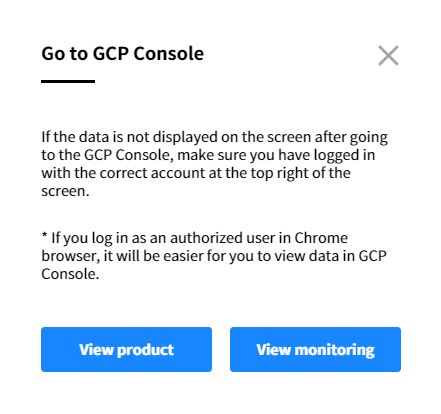
⚠️ Attention: When the data is not displayed after going to the GCP Console, make sure you have logged in with the correct account at the top right of the screen. You can view the data you want when you log in with the privileged account.
💡 Notification: If you log in as an authorized user in Chrome browser, it will be easier for you to view data in GCP Console.
Alibaba Cloud
You can check usage status of Alibaba Cloud resources listed below.
Elastic Compute Service, Cloud Disk, Launch Template, Server Load Balancer, Scaling Group, Scaling Instance, Scaling Configuration, Snapshot, Snapshot Chain, Image, ApsaraDB for RDS, ApsaraDB for MongoDB, ApsaraDB for Redis, ApsaraDB for Memcache, HybridDB for MySQL, HybridDB for PostgreSQL, POLARDB Cluster, POLARDB Instance, Object Storage Service, Alibaba Cloud CDN, Elastic IP Address, Security Group, Virtual Private Cloud, NAT Gateway, VPN Gateway, Network Interface
History
You can check history of resource usage per cloud service.
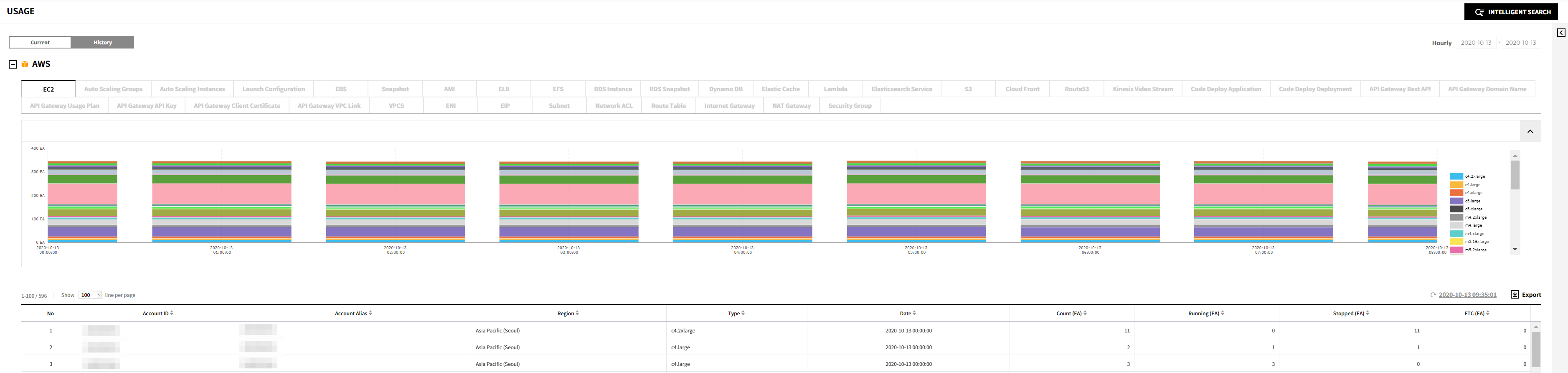
Provides the trend chart of usage history of the resources listed below on an hourly/daily/monthly basis; it also provides details about each resource on the list.
AWS
You can check usage history of AWS resources listed below.
AMI, EBS, EC2, EIP, Internet Gateway, Lambda, Network ACL, RDS, Route Table, S3, Security Group, Snapshot, Subnet, VPCS, ELB, Dynamo DB, Elastic Cache, CloudFront, Kinesis Data Stream, ENI, NAT Gateway
Azure
You can check usage history of Azure resources listed below.
Database, Storage, Virtual Machine
GCP
You can check usage history of GCP resources listed below.
VM Instance, Compute Disk, Big Table, Big Query, SQL Instance, Storage Bucket, VPC, Subnet
Alibaba Cloud
You can check usage history of Alibaba Cloud resources listed below.
Elastic Compute Service, Cloud Disk, Launch Template, Server Load Balancer, Scaling Group, Scaling Instance, Scaling Configuration, Snapshot, Snapshot Chain, Image, ApsaraDB for RDS, ApsaraDB for MongoDB, ApsaraDB for Redis, ApsaraDB for Memcache, HybridDB for MySQL, HybridDB for PostgreSQL, POLARDB Cluster, POLARDB Instance, Object Storage Service, Alibaba Cloud CDN, Elastic IP Address, Security Group, Virtual Private Cloud, NAT Gateway, VPN Gateway, Network Interface
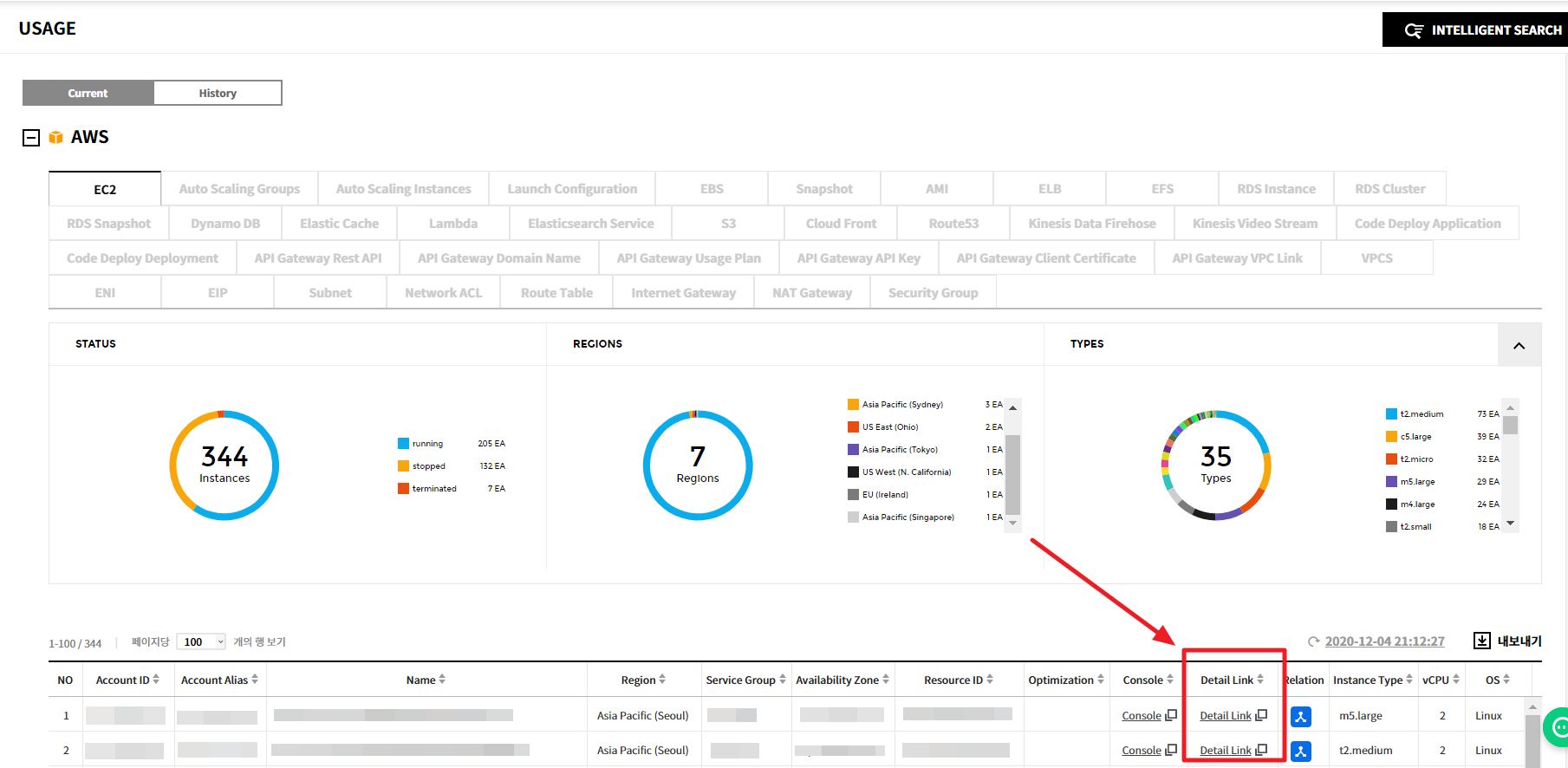
Resource Details
Resource Details helps you to view the detailed information of the resources such as service group, tag, cost, performance data, and activities in a single dashboard.
💡 Notification: You can go to Resource Details directly from the Usage or Right Sizing menu of Asset Management. Or click [Detail Link] of the resource ID you want to view from the Asset Management console.
General
Detailed Information
You can view resource details, service group, and tag list on the detail information tab. This table contains account, life cycle, OS, status, instance type, and region of the selected resource. In the body section, you can find detailed information about AWS method calls as well.
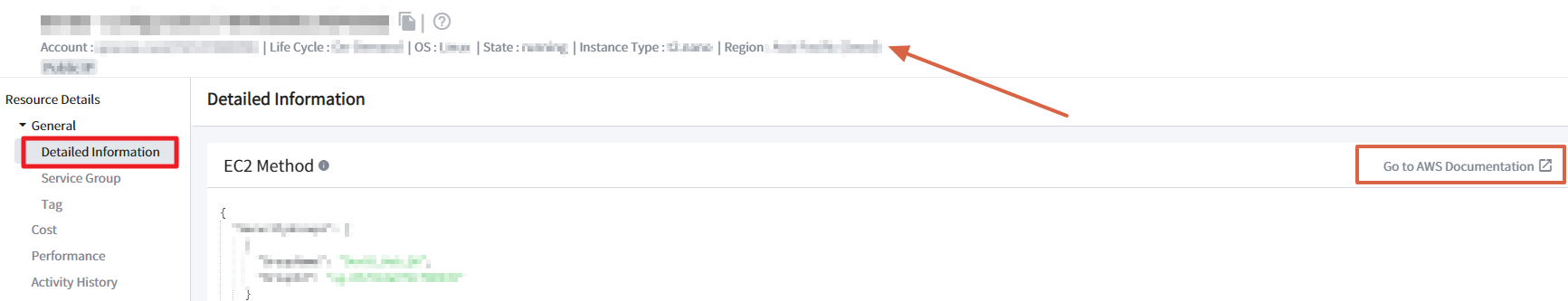
💡 Notification: Click [Go to AWS Documentation] to find out more about the method.
Service Group

If you have already created a service group in Service Portal, you can view the service group of the resource. You can check the View Type, View name, Service Group name and whether the View is selected as a Default View (Y) or not (N). View Type is displayed in either Automated View or Custom View.
You can also view groups that are not grouped in the service group by checking Show Undefined Group.
If you want to see the cost by service groups, click See Cost by Service Group on the upper-right corner of the table. It will lead you straight to Asset Management service > Service Group menu. You can see the number and cost of the resources by service groups under the selected View and Account.
If you want to create or manage service groups, click Go to Manage Service Group. You can create or manage service groups from the Service Portal service > Manage Service Group menu. You can also download the Service Group List in the CSV file by clicking the download button, indicated in a red circle.
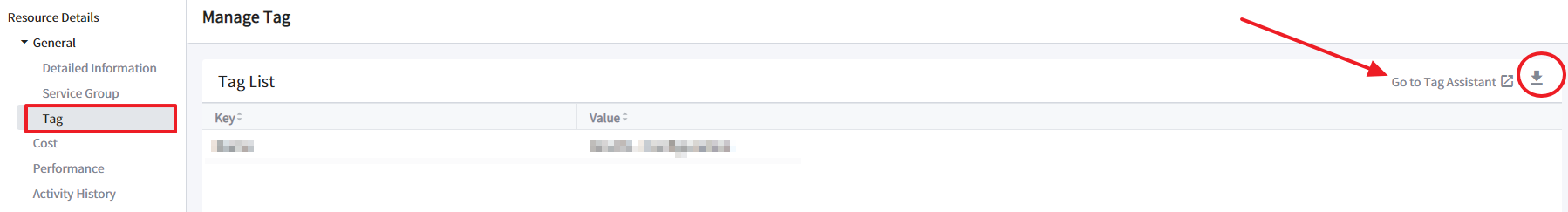
Tag
Here you can view the tag key and tag value of the selected resource. You can go straight to the Tag Assistant menu in the Service Portal by clicking Go to Tag Assistant to set tags for your resources. You can also download the list in the CSV file by clicking the download button next to the link.
Cost
Cost Trend
- Cost Trend shows trends in costs over time. To view the cost trends, specify the data range and select the view option, and select a resource name or resource ID of the resource for grouping conditions. For example, if you select Name for grouping conditions to view daily cost trends in December and the daily chart is selected, you will find the chart below. Items used for grouping conditions are Name, Resource ID, Usage Type, Record Type, Operation Name, Product, Sub Product, and Region.
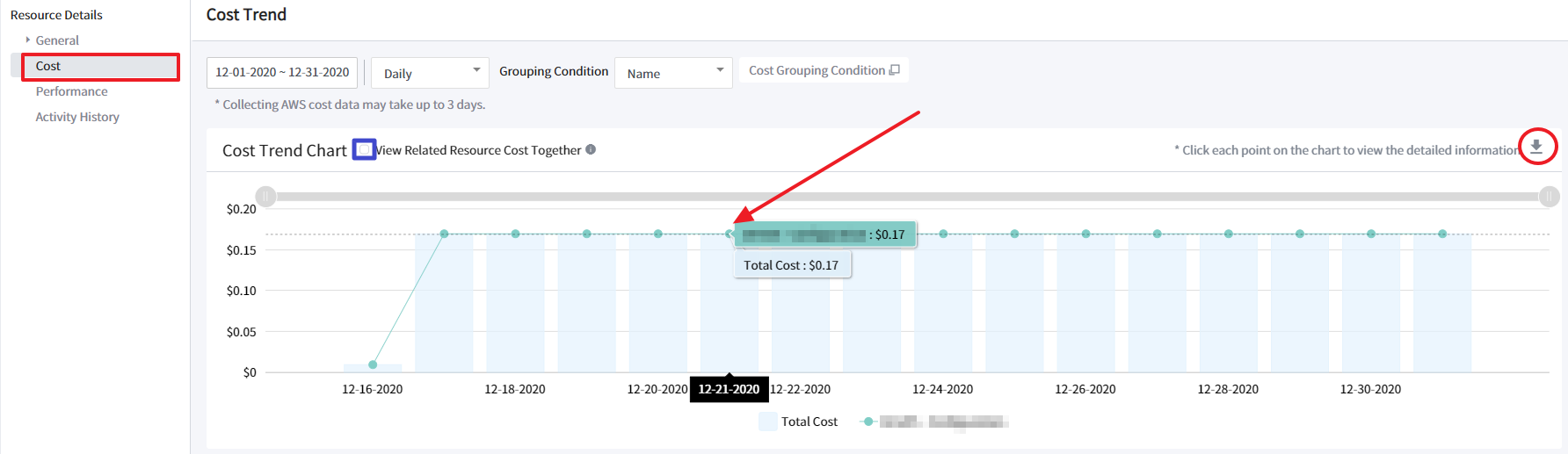
📜 Note: It may take up to three days to collect costs from AWS.
- Select the checkbox of View Related Resource Cost Together to view costs of related resources that are associated with the current resource. For example, you can check the costs of Snapshot or EBS that are operating with EC2. When you hover your mouse to data points on the trend chart, a tooltip appears displaying detailed information about the field. You can also download the CSV file to view the whole data.
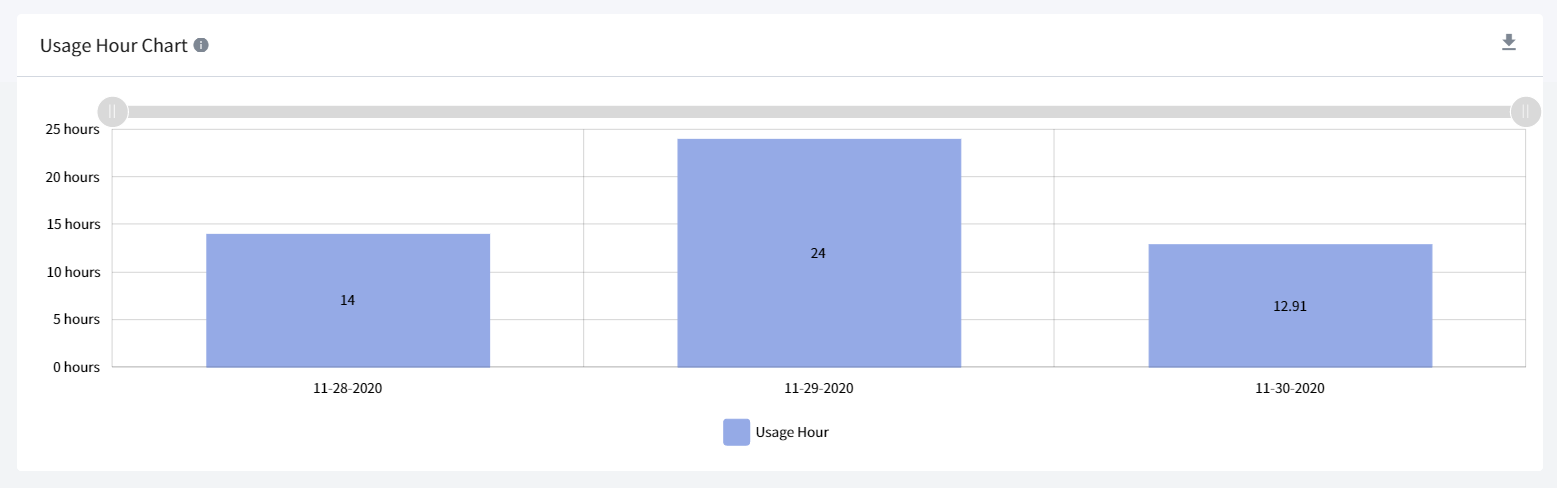
Usage Hour Chart
Usage hour chart shows the total number of hours the instance was running during the day.
Performance
You can view data points as a percentile over a specified period for filtering resource performance by metrics. Percentiles are statistical measures that can show you how data points compare to a total distribution over time. If outliers can skew how the distribution displays in your chart, making it difficult to notice patterns or average values, visualize data by excluding outliers from the data range and displaying the 5th-95th percentiles. You may drag the gray bar on the chart to zoom in and out to adjust the period once again.
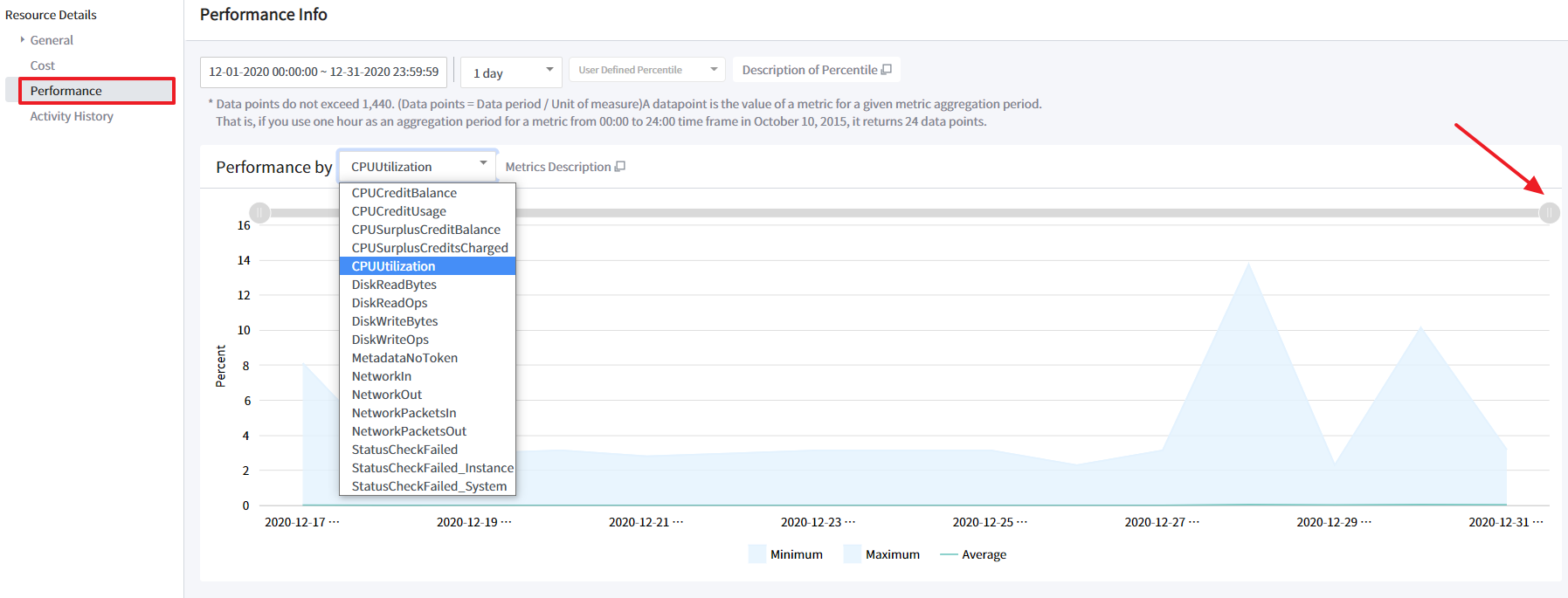
The maximum number of data points returned from a single call is 1,440, so if you request more than 1,440, it will return an error message. To reduce the number of data points, you need to narrow the specified time range or increase the specified period.
📜 Note: Metrics like CPUUtilization and NetworkIn used for performance are imported from AWS.
Activity History
Look up and view the past activities of the resource. On this page, you can filter, search and view Management Events or CloudTrail Insights events that are captured by CloudTrail. It may take up to 15 minutes to view after the event occurrence. Select period and event names that you wish to view. You can only look up events that occurred in the resources within the last 90 days using the CloudTrail. Events older than 90 days will not be archived in CloudTrail.

You can only filter and search within the current view. If additional data exists for the looked up data on the current view, a plus (+) sign will appear next to the number, shown right side of AWS LookUpEvent. Scroll down to view additional data. You can also download the CSV file of the activity history.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Event Time | The local time that the event occurred. |
| Event Name | The name of the event occurred in the resources. This is typically the API name that is associated with the event, such as CreateTrail. |
| User Name | The name of the user who triggered the event or the User ID referenced in the event. For example, this can be an IAM user, an IAM role name, or a service role. |
| Event Source | The AWS API endpoint where the event originated, such as ec2.amazonaws.com |
| Resources Referenced | Resources referenced describes the name or ID of resources that are referenced by the event. For example, the resource name might be auto-scaling-test-group for an Auto Scaling group, or i-123456789012 for an Amazon EC2 instance. Resources referenced can be resources that were read or changed by an event. |
| Event Record | The Event record, sometimes called the event payload, is the full JSON text of an event. The record contains fields that help you determine the requested action as well as when and where the request was made. |
| AWS Access Key | The AWS access key ID that was used to sign the request. If the request was made with temporary security credentials, this is the access key ID of the temporary credentials. |
| Read Only | The read type of the event. Events are categorized as read events or write events. |
Performance
Asset Management > Performance
You can view the performance of all your resources.
Current
You can view the performance of resources that you are currently using. If you have registered your AWS account in Cloud Account on the Service Portal, you can view CPU Usage by default. In order to view both Memory Usage and Disk Usage, you need to install AWS CloudWatch agent. Refer to the installation guide of each cloud vendor.
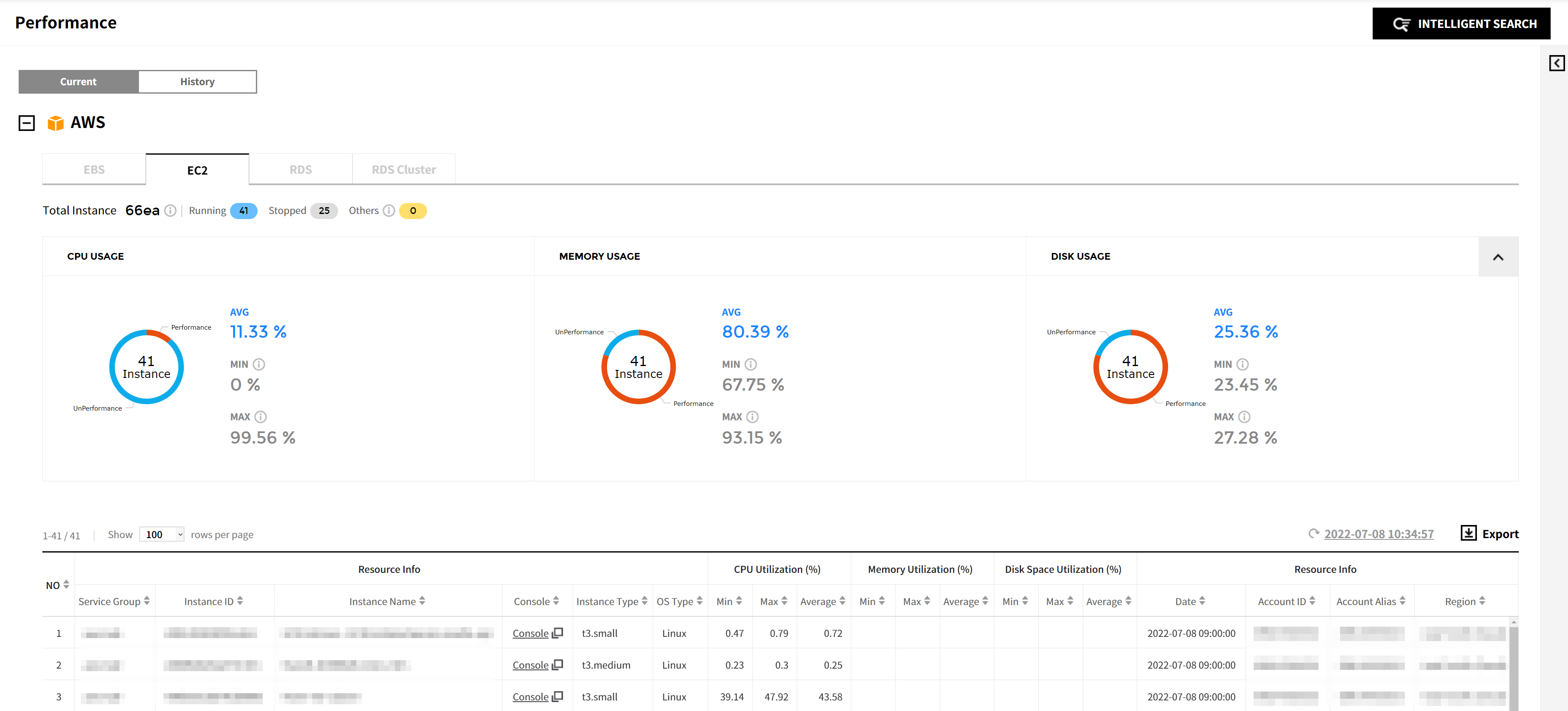
AWS
You can check performance status of AWS resources listed below.
| Resource | Item | Note |
|---|---|---|
| EC2 | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Memory Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Disk Space Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| EBS | Resource Info | |
| VolumeQueue Length (EA) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| VolumeRead IOPS (EA) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| VolumeWrite Bytes (MB) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| VolumeWrite IOPS (EA) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| RDS | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Freeable Memory (MB) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Free Storage Space (MB) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Read IOPS (EA) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Write IOPS (EA) | Min, Max, Avg |
Prerequisites for Installing the AWS CloudWatch Agent
⑴ Step 1. Create IAM Roles to Use with the CloudWatch Agent on Amazon EC2 Instances
To create the IAM role necessary for each server to run the CloudWatch agent:
① Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the IAM console.
② In the navigation pane, choose Roles and then click Create role.
③ Under Select type of trusted entity, choose AWS service.
④ Immediately under Common use cases, choose EC2, and then click Next: Permissions.
⑤ In the list of policies, select the check box next to CloudWatchAgentServerPolicy. If necessary, use the search box to find the policy.
⑥ Choose Next: Tags.
⑦ (Optional) Add one or more tag-key value pairs to organize, track, or control access for this role, and then choose Next: Review.
⑧ For Role name, enter a name for your new role, such as CloudWatchAgentServerRole or another name that you prefer.
⑨ (Optional) For Role description, enter a description.
⑩ Confirm that CloudWatchAgentServerPolicy appear next to Policies.
⑪ Choose Create role.
⑵ Step2. Attaching an IAM Role
Attach the IAM role that you created in the Step 1 to the EC2 instances that you intend to install the CloudWatch Agents on.
① Open the EC2 Management Console.
② In the navigation pane, choose Instances and check instances to attach the IAM Role to.
③ Click Actions > Security > Modify IAM Role.
④ Choose the CloudWatchAgentServerRole in the select box and Save it.
Installing AWS CloudWatch Agent - Linux
⑴ Step 1: Install CloudWatch Agent on Server
| OS | CLI Commands to install the CloudWatch Agent |
|---|---|
| Amazon Linux 2 | 1. The CloudWatch agent is available as a package in Amazon Linux. $ sudo yum install amazon-cloudwatch-agent |
| Amazon Linux, Amazon Linux 2, CentOS, RedHat, Suse | 1. Download the agent package (AMD64 or ARM64). $ wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazoncloudwatch- agent/amazon_linux/amd64/latest/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.rpm $ wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazoncloudwatch-agent/amazon_linux/arm64/latest/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.rpm 2. Install the package. If you downloaded an RPM package on a Linux server, change to the directory containing the package. $ sudo rpm -U ./amazon-cloudwatch-agent.rpm |
| Debian | 1. Download the agent package. (AMD64 only). $ wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazoncloudwatch-agent/debian/amd64/latest/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.deb 2. Install the package. If you downloaded an RPM package on a Linux server, change to the directory containing the package. $ sudo dpkg -i -E ./amazon-cloudwatch-agent.deb |
| Ubuntu | 1. Download the agent package (AMD64 or ARM64). $ wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazoncloudwatch-agent/ubuntu/amd64/latest/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.deb $ wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazoncloudwatch-agent/ubuntu/arm64/latest/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.deb 2. Install the package. If you downloaded an RPM package on a Linux server, change to the directory containing the package. $ sudo dpkg -i -E ./amazon-cloudwatch-agent.deb |
⑵ Step 2: Create the CloudWatch Agent Configuration File
Copy and Paste the JSON configuration into a json file named ‘cw-agent-config.json’ after you create it in the desired server directory. Please modify the ‘agent.region’ value to meet the needs of your cloud resources region.
📜 Note: Please note that the file path will be used at the Step 4.
{
"agent": {
"metrics_collection_interval": 60,
"region": "ap-northeast-2",
"logfile": "/opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/logs/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.log",
"debug": false
},
"metrics": {
"namespace": "CWAgent",
"metrics_collected": {
"collectd": {
"metrics_aggregation_interval": 60
},
"disk": {
"measurement": [
"used_percent"
],
"metrics_collection_interval": 60,
"resources": [
"/"
]
},
"mem": {
"measurement": [
"mem_used_percent"
],
"metrics_collection_interval": 60
}
},
"append_dimensions": {
"InstanceId": "${aws:InstanceId}"
}
}
}
⑶ Step 3: Verify Internet Access
Your Amazon EC2 instances must have outbound internet access to send data to CloudWatch or CloudWatch Logs. For more information about how to configure internet access, see Internet Gateways in the Amazon VPC User Guide.
⑷ Step 4: Start the CloudWatch Agent Using the Command Line
① As a root user, create necessary directories and files in advance for the agent to use.
$sudo -i
$mkdir /usr/share/collectd/
$touch /usr/share/collectd/types.db
$exit
② Run the following command to start the CloudWatch agent.
$sudo amazon-cloudwatch-agent-ctl -a fetch-config -m ec2 -s -c file:./cw-agent-config.json
③ Confirm the service is running
$systemctl status amazon-cloudwatch-agent
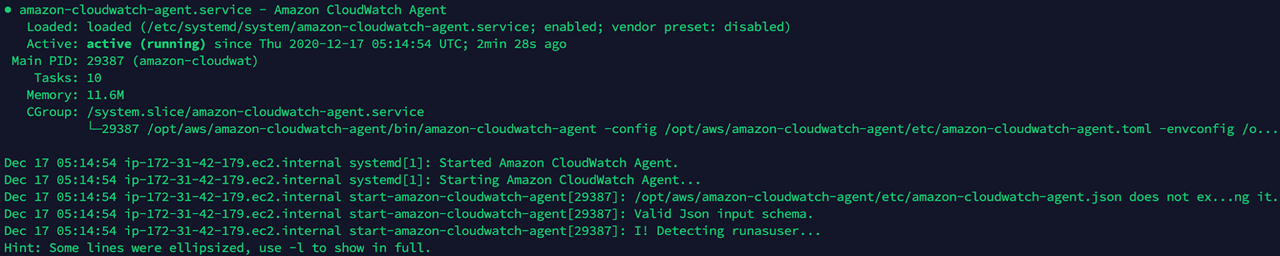
⑸ Step 5: Check Metrics Collected under CWAgent Namespace in CloudWatch Console
💡 Notification: Check metrics in the CloudWatch Console.
Installing AWS CloudWatch Agent - Windows
⑴ Step 1: Install CloudWatch Agent on Server
① Open a powershell window as administrator and execute the following command to download installation file.
Invoke-WebRequest https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazoncloudwatch-agent/windows/amd64/latest/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.msi -OutFile C:-cloudwatch-agent.msi
② If you downloaded an MSI package on a server running Windows Server, change to the directory containing the package and enter the following:
msiexec /i amazon-cloudwatch-agent.msi
⑵ Step2: Create a CloudWatch Agent Configuration File with the Following Code Snippet
Modify the 'agent.region' value to meet the needs of your cloud resources region, and place the file in your desired server directory for later use at Step 3.
(File name: configuration-file-path)
{
"agent": {
"metrics_collection_interval": 60,
"region": "ap-northeast-2",
"logfile": "/opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/logs/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.log",
"debug": false
},
"metrics": {
"namespace": "CWAgent",
"metrics_collected": {
"LogicalDisk": {
"measurement": [
{
"name":"% Free Space",
"rename":"DiskFreeSpaceUtilization",
"unit":"Percent"
}
],
"metrics_collection_interval": 60,
"resources": [
"C:"
]
},
"Memory": {
"measurement": [
{
"name":"% Committed Bytes In Use",
"unit":"Percent"
}
],
"metrics_collection_interval": 60
}
},
"append_dimensions": {
"InstanceId": "${aws:InstanceId}"
}
}
}
⑶ Step 3: Start the CloudWatch Agent with the Following Command in PowerShell
& “C:Files-cloudwatch-agent-ctl.ps1” -a fetch-config -m ec2 -s -c file:configuration-file-path
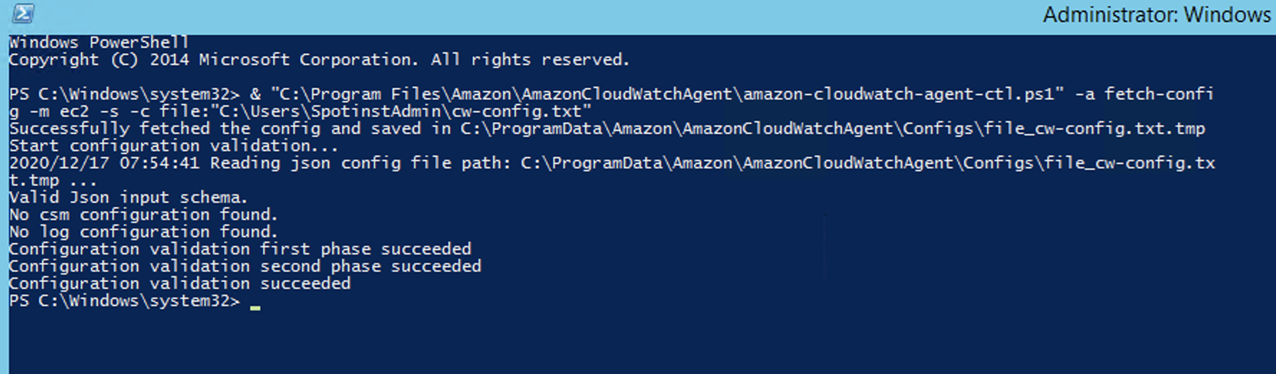
⑷ Step 4: Check Metrics Being Collected in CloudWatch Console
💡 Notification: Check it on the CloudWatch Console.
Azure
You can check the performance of Azure resources listed below. If you have registered your Azure account in Cloud Account on the Service Portal, you can view CPU Usage by default. In order to view both Memory Usage and Disk Usage, you need to install Azure Monitor agent.
| Resource | Item | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Virtual Machine | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Memory Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Disk Space Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| SQL Database | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Physical Data Read Percent (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Connection Success (EA) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Connection Fail (EA) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| DTU Consumption (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| DeadLock (EA) | Min, Max, Avg |
Prerequisites for Installing the Azure Monitor Agent
⑴ Step 1: Enable Guest Level Monitoring
① Login to your Azure Portal.
② Click on a VM.
③ Select Diagnostics settings from the Azure UI blade.
④ Under the Overview tab:
⑤ Pick a Storage account: Select your storage account so that the metrics stats can be stored.
⑥ Click on Enable guest level monitoring and wait for the process to complete.
⑦ Under the Overview tab:
⑧ Pick a Storage account: Select your storage account so that the metrics stats can be stored.
⑨ Click on Enable guest level monitoring and wait for the process to complete.
⑩ Check the Confirmation Message.
⑪ Click on the Performance Counters tab of the VM and ensure Memory is checked.
⑵ Step 2: Check Metrics
① Navigate to Metrics under Monitoring.
② Choose Guest (Classic) for Metric Namespace.
③ Choose (_Total)% Free Space for Metric.
④ Choose Aggregation Type depending on your needs.
⑤ Navigate to Metrics under Monitoring.
⑥ Choose Guest (Classic) for Metric Namespace.
⑦ Choose % Committed Bytes In Use for Metric.
⑧ Choose Aggregation Type depending on your needs.
GCP
You can check performance status of GCP resources listed below.
| Resource | Item | Note |
|---|---|---|
| VM Instance | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Memory Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Disk Space Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Compute Disk | Resource Info | |
| Read IOPS | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Write IOPS | Min, Max, Avg | |
| SQL Instance | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Memory Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Disk Space Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg |
Prerequisites for Installing the GCP Ops Agent
To collect Disk and Memory metrics on VM instances, GCP provides the Ops Agent. Before install the Agent, it is required to configure the settings below for Linux and Windows VM instances.
① Go to GCP console > APIs & Services > Enabled APIs & services, and select [Cloud Monitoring API] and set the status to [Enabled].
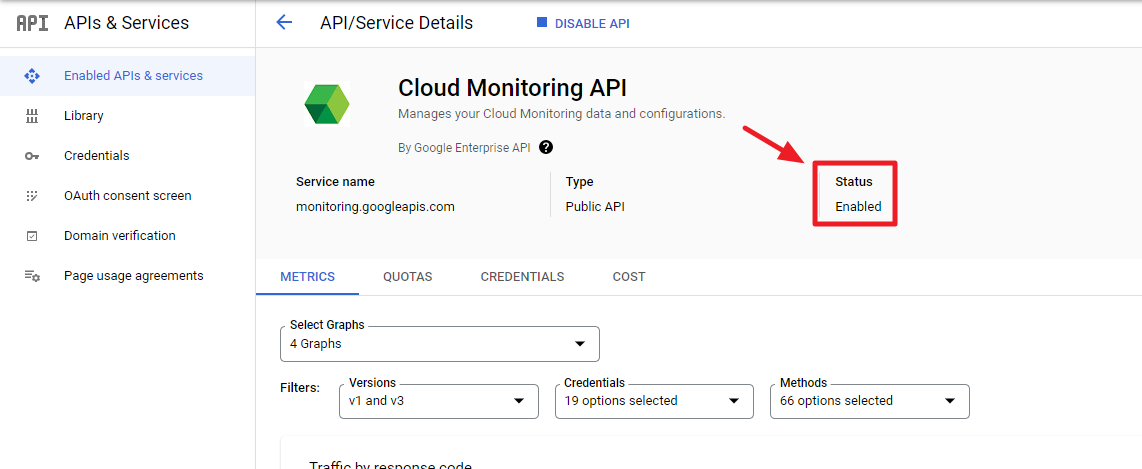
② Go to IAM & Admin > Roles, and choose [CREATE ROLE]. Then, grant [monitoring.timeSeries.create] to your service account.
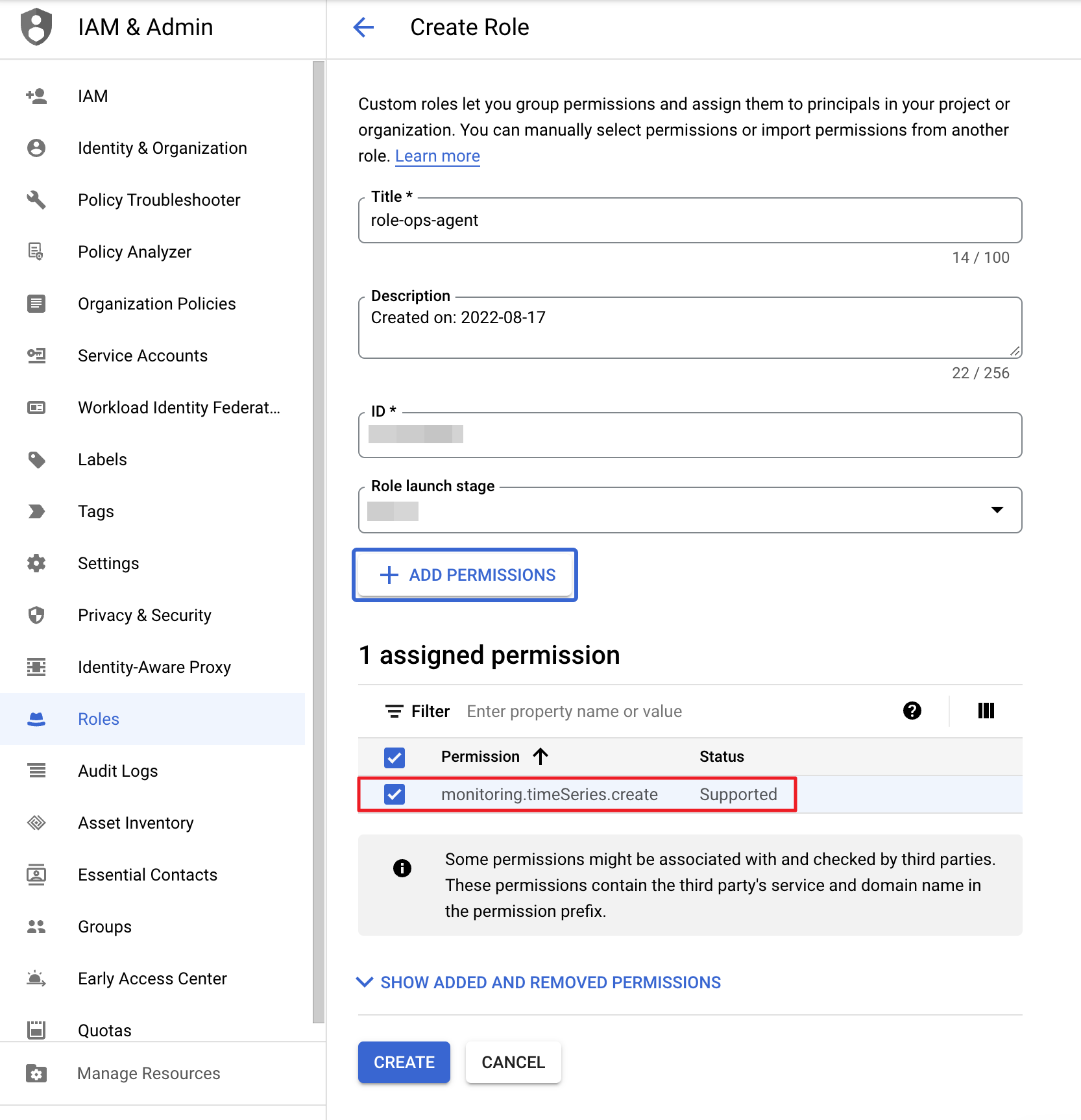
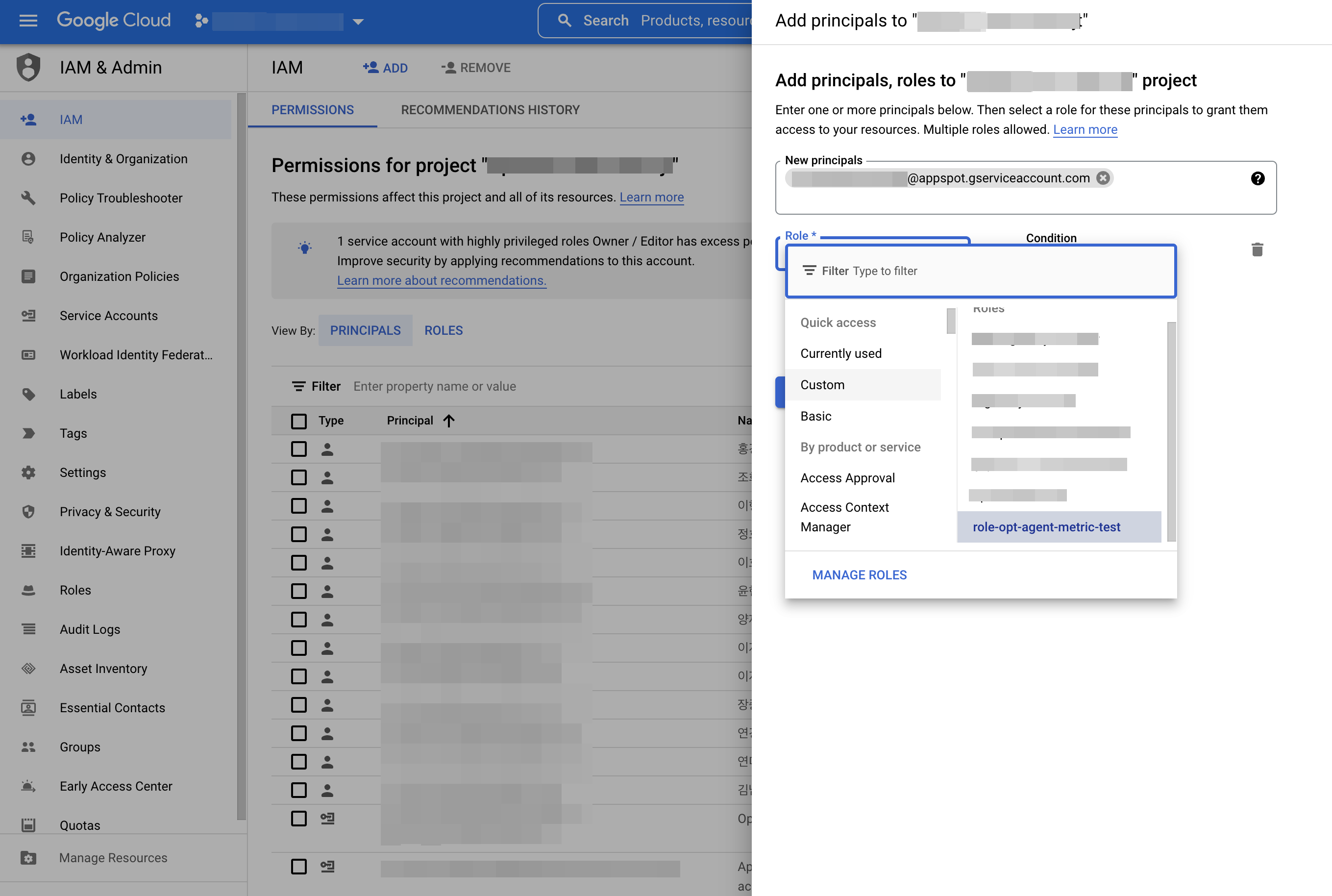
③ Add the role you created to your service account by choosing the [ADD] button in IAM & ADMIN.
Installing the Ops Agent - Linux
① When you create a new instance, choose a Linux operating system like Ubuntu 18.04LTS for boot disk, and grant monitoring.timeSeries.create to your service account. If you already have instances created, skip to the next step.
② To install the agent, connect to your instance using SSH and run the following command.
curl -sSO https://dl.google.com/cloudagents/add-google-cloud-ops-agent-repo.sh
sudo bash add-google-cloud-ops-agent-repo.sh --also-install
③ Verify whether the agent is working as expected.
• To verify that the agent is properly working, run the following command.
sudo systemctl status google-cloud-ops-agent"*" *
📜 Note: When you run
sudo service google-cloud-ops-agent status *and can see Active displayed, the agent is properly installed.
• To verify the agent version on your system, run the following commands.
dpkg-query --show --showformat \
'${Package} ${Version} ${Architecture} ${Status}\n' \
google-cloud-ops-agent
• To restart the agent due to changes in configuration files, run the following command.
sudo service google-cloud-ops-agent restart
• To verify the collected logs, run the following command.
/var/log-> syslog
📜 Note: If metrics are not collected while Permission Denied is displayed, please check whether permission is properly granted.
Installing the Ops Agent - Windows
① When you create a new instance, choose a Windows operating system like Windows Server 2016 Datacenter for boot disk, and grant monitoring.timeSeries.create to your service account. If you already have instances created, skip to the next step.
② To install the agent, connect to your instance using RDP. Open a PowerShell terminal with administrator privileges and then run the following PowerShell commands.
(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("https://dl.google.com/cloudagents/add-google-cloud-ops-agent-repo.ps1", "${env:UserProfile}\add-google-cloud-ops-agent-repo.ps1")
Invoke-Expression "${env:UserProfile}\add-google-cloud-ops-agent-repo.ps1 -AlsoInstall"
③ Verify whether the agent is working as expected.
• To verify that the agent is properly working, run the following command.
googet installed google-cloud-ops-agent
📜 Note: If the agent is properly installed, the agent collects Memory and Disk Utilization data.
💡 Notification: Please refer to Ops Agent Installation Guide for installing the agent and Troubleshoot the Ops Agent for troubleshooting.
Go to GCP Console
You can go to GCP Console directly from the current view in order to view detailed information of resources you want to see. There are two options to go to the GCP Console as below.
Click Console from the resource list to go to the GCP Console.
![]()
Click a resource from the list to view the detail page, then select Go to GCP Console button.
![]()
When you click Go to GCP Console, the following pop up message will be displayed. Click View product if you want to view the resource information from the GCP console, and click “View monitoring” to check resource performance.
![]()
When the data is not displayed after going to the GCP Console, make sure you have logged in with the correct account at the top right of the screen. You can view the data you want when you log in with the privileged account.
📜 Note: If you log in as an authorized user in Chrome browser, it will be easier for you to view data in GCP Console.
Alibaba Cloud
You can check performance status of Alibaba Cloud resources listed below.
| Resource | Item | Note |
|---|---|---|
| ECS | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Memory Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Disk Space Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| RDS | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Memory Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Disk Space Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| IOPS (%) | Min, Max, Avg |
History
You can view the performance history of resources.
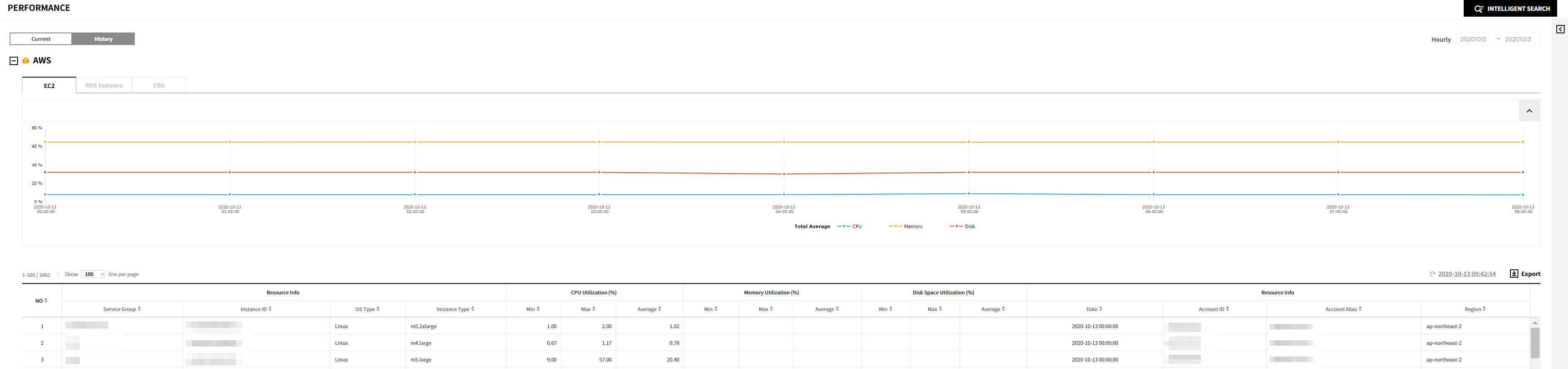
AWS
You can check the performance of AWS resources listed below.
| Resource | Item | Note |
|---|---|---|
| EC2 | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Memory Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Disk Space Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| EBS | Resource Info | |
| VolumeQueue Length (EA) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| VolumeRead IOPS (EA) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| VolumeWrite Bytes (MB) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| VolumeWrite IOPS (EA) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| RDS | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Freeable Memory (MB) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Free Storage Space (MB) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Read IOPS (EA) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Write IOPS (EA) | Min, Max, Avg |
Azure
You can check the performance history of Azure resources listed below.
| Resource | Item | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Virtual Machine | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Memory Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Disk Space Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| SQL Database | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Physical Data Read Percent (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Connection Success (EA) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Connection Fail (EA) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| DTU Consumption (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| DeadLock (EA) | Min, Max, Avg |
GCP
You can check performance history of GCP resources listed below.
| Resource | Item | Note |
|---|---|---|
| VM Instance | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Memory Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Disk Space Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Compute Disk | Resource Info | |
| Read IOPS | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Write IOPS | Min, Max, Avg | |
| SQL Instance | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Memory Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Disk Space Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg |
Alibaba Cloud
You can check performance history of Alibaba Cloud resources listed below.
| Resource | Item | Note |
|---|---|---|
| ECS | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Memory Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Disk Space Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| RDS | Resource Info | |
| CPU Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Memory Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| Disk Space Utilization (%) | Min, Max, Avg | |
| IOPS (%) | Min, Max, Avg |
Intelligent Search
Provides Intelligent Search feature based on the relationship between resources that are in use. It shows a list of all resources used for a certain period of time; and you can use them as search conditions. You can use Intelligent Search feature in Usage and Performance menu.
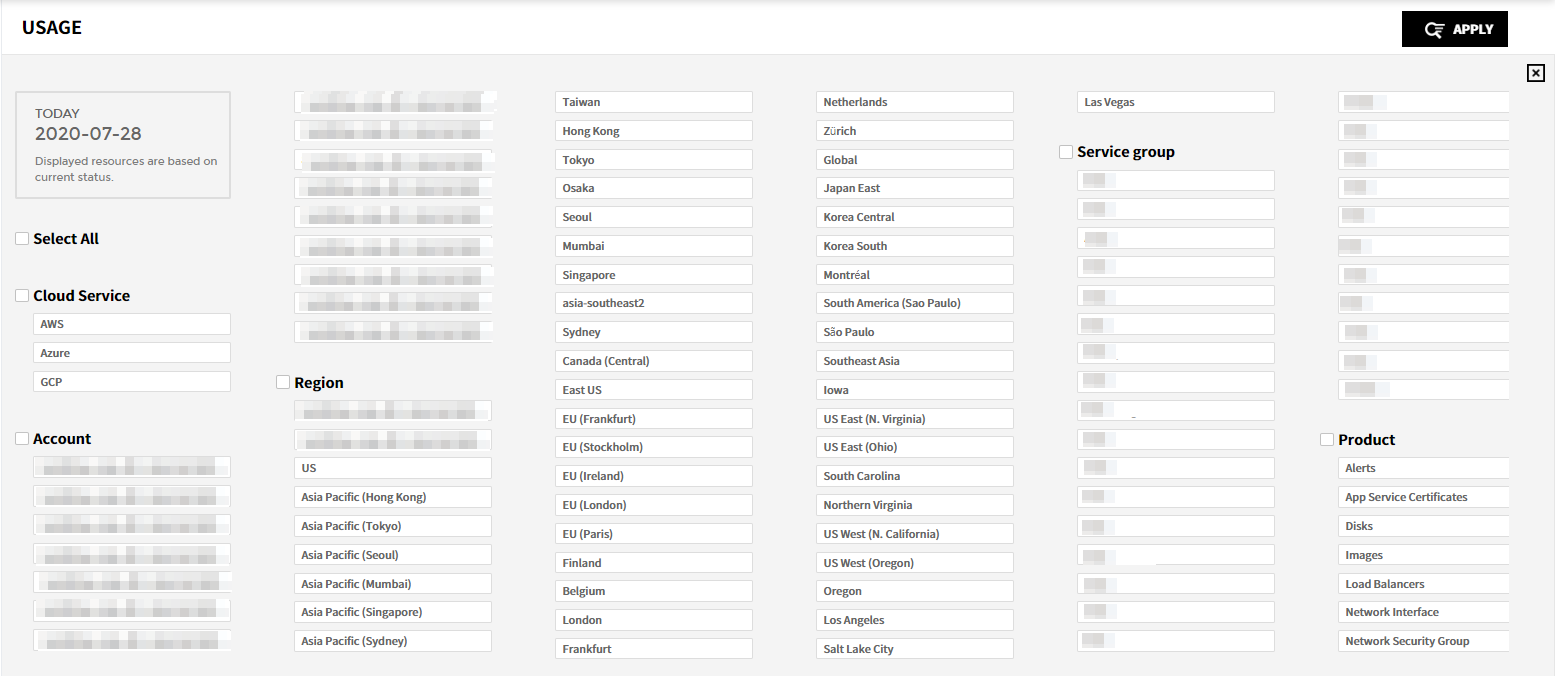
Period: In Current, you can check the resource usage history for the current day. In History, you can select the period to see the resource usage history. The selectable search conditions may change based on the selected period; and the resources used within that period will be automatically included in search conditions. You can set in hourly, daily, weekly, monthly basis.
Search Condition: The Cloud Service, Account, Region, Service Group, Product, and Tag are the items fo search conditions. When you select the conditions, you can only select the related search conditions. For example, if you select AWS for the cloud service, you cannot select other cloud services’ resources. Set the period and search conditions and click [Apply] button. Then, the results for the selected period and search conditions will be displayed.
![]()
Resource Optimization
By using Resource Optimization, you can view the status of entire resources and whether resources are used with maximum efficiency compared to its performance. This feature optimizes the resource environment by removing unnecessary resources. Resource Optimization contains Summary, Unused Resource, Right Sizing, and Settings.
| Summary | Display the summary of Unused Resource and Right Sizing resources. |
| Unused Resource | For resources that are already created but not used or considered as not used, they are recommended as Unused Resource for saving costs. |
| Right Sizing | Through a resource performance analysis, it recommends Downsizing, Upsizing, Modernize, or Idle to the current resources according to the user-defined setting. |
| Settings | Users can add, edit and delete the setting information for Resource Optimization. When accessing the settings for the first time, the default condition is created automatically, and the system recommends Unused Resource and Right Sizing resources daily based on the default settings. |
Summary
The summary shows Estimated Savings, Unused Resource, and Right Sizing resources at a glance. You can check the estimated savings for each cloud service, and also check the unused resources and resources that require right sizing. Users can set the recommendation condition for Unused Resource and Right Sizing on the Settings menu.
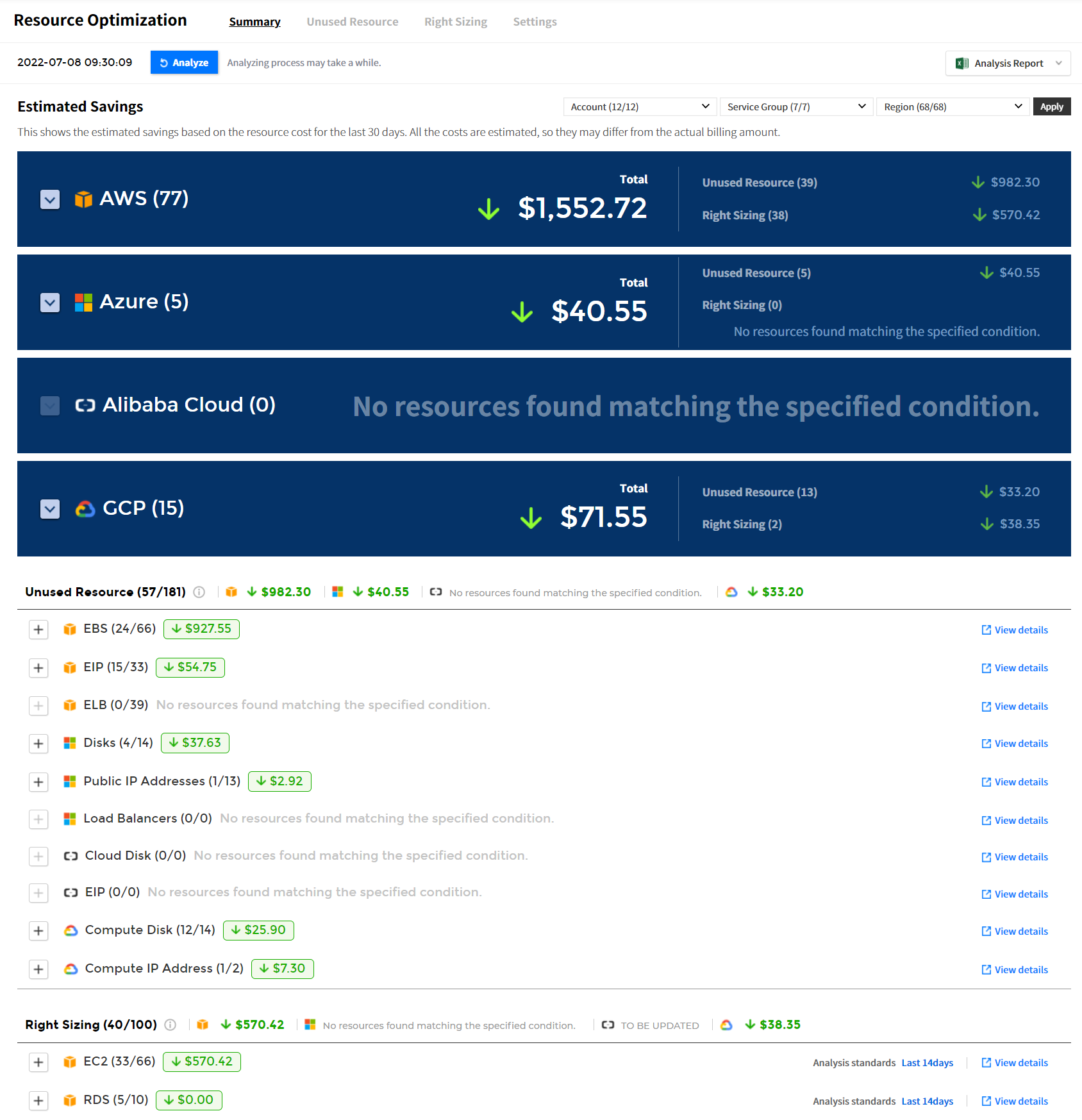
Estimated Savings
You can view the estimated savings of resources that are not being used and resources that need right sizing for the purpose of the use.
- ⓐ The date/time displayed on the left of the [Analyze] button indicates the last time a resource optimization task was performed.
- ⓑ Click the [Analyze] button to update the resource optimization to the latest version.
- ⓒ Select the drop-down list of Account, Service Group, and Region in the upper right corner, and click [Apply] to view the necessary data only.
- ⓓ Select a cloud service to view the estimated savings by Total, Account, and Region.
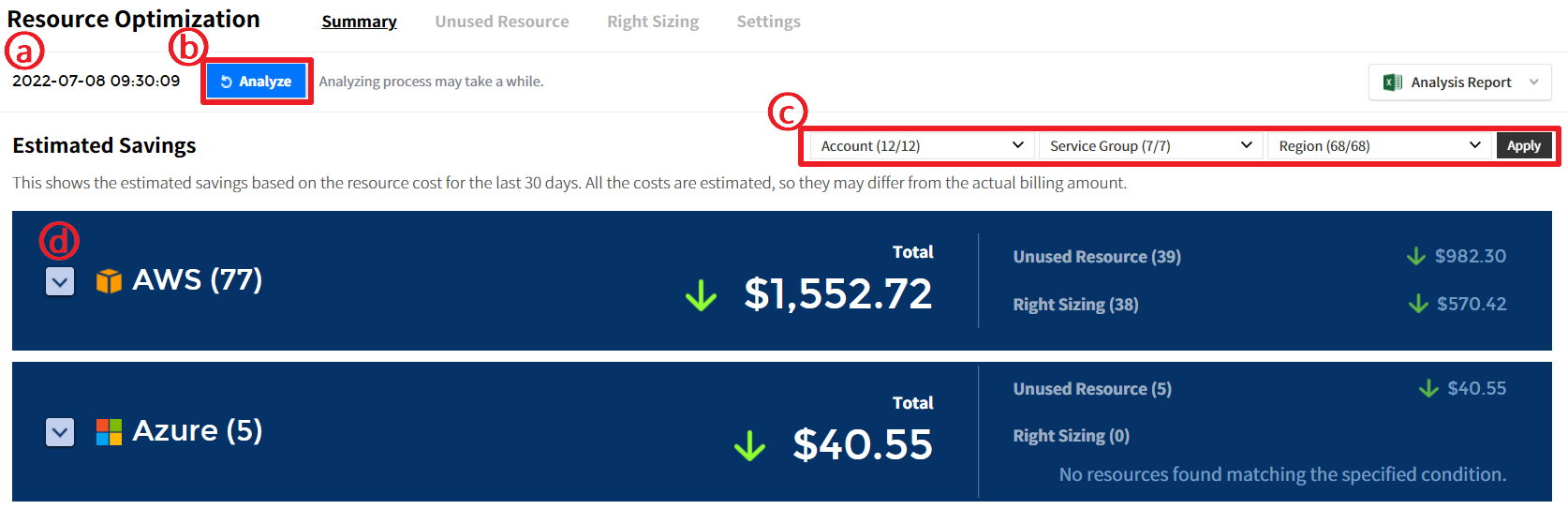
Total
You can check the number of resources available for Unused Resource and Right Sizing and its estimated savings.
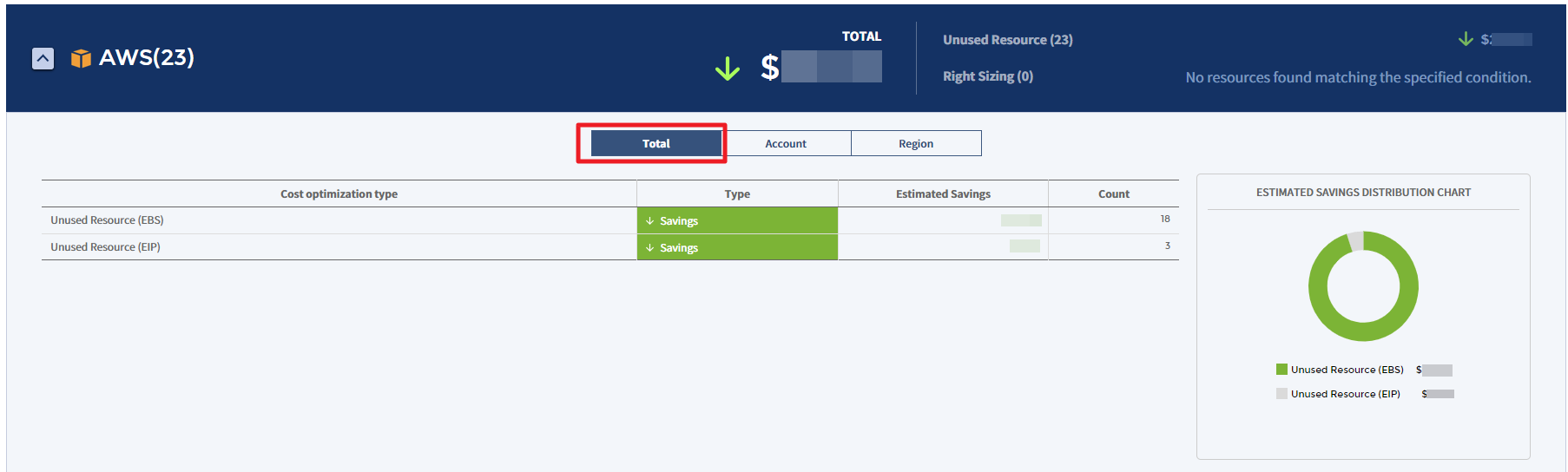
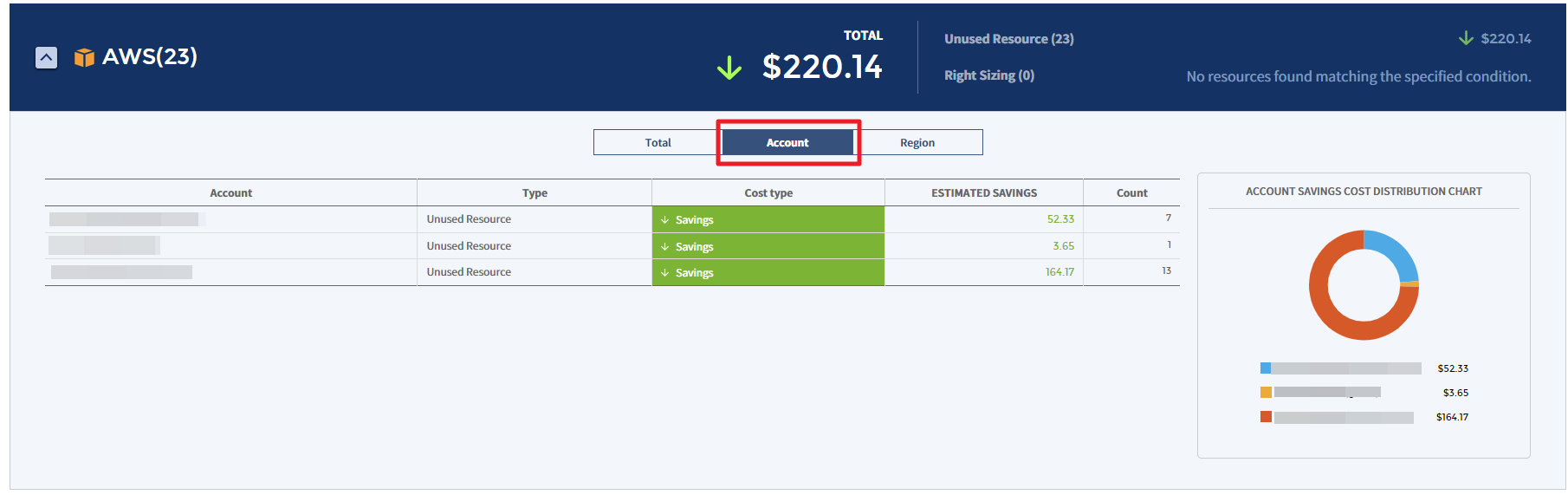
Account
You can view the estimated savings or estimated increase by account in the table chart and graph.
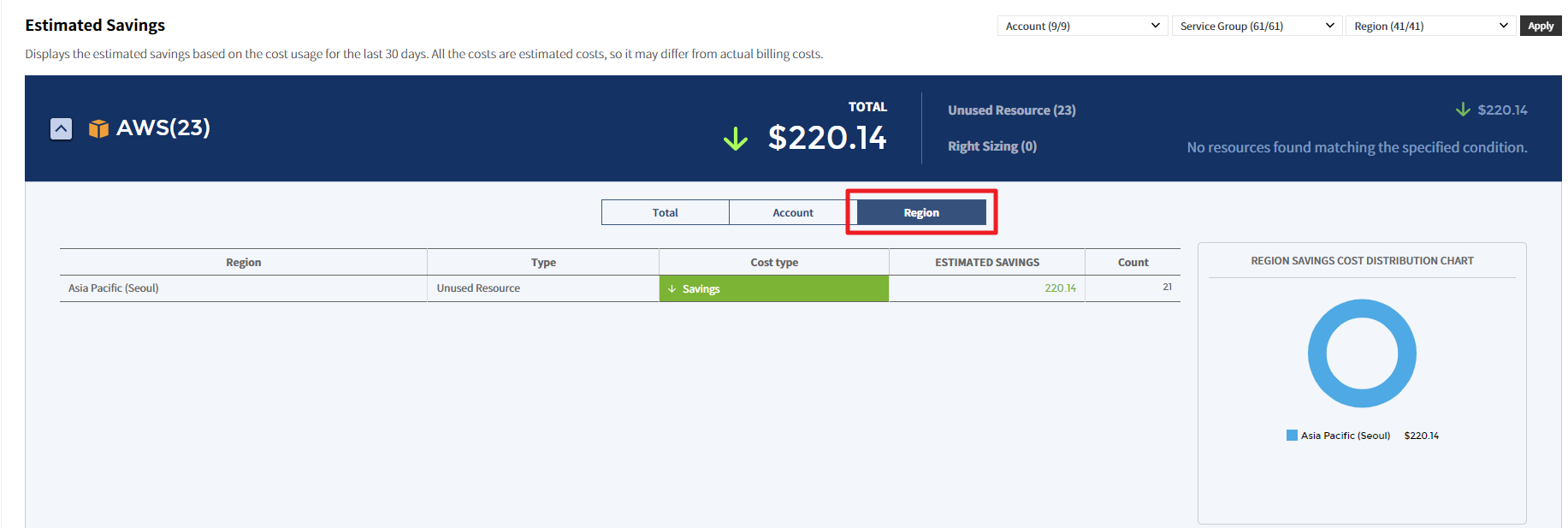
Region
You can view the estimated savings or estimated increase by region in the table chart and graph.
Unused Resource
The Unused Resource analyzes your data and identifies resources that are wasting money due to they were not used. You can identify resources that are not being used by cloud service, and view the estimated savings if resources are used based on the recommendations.
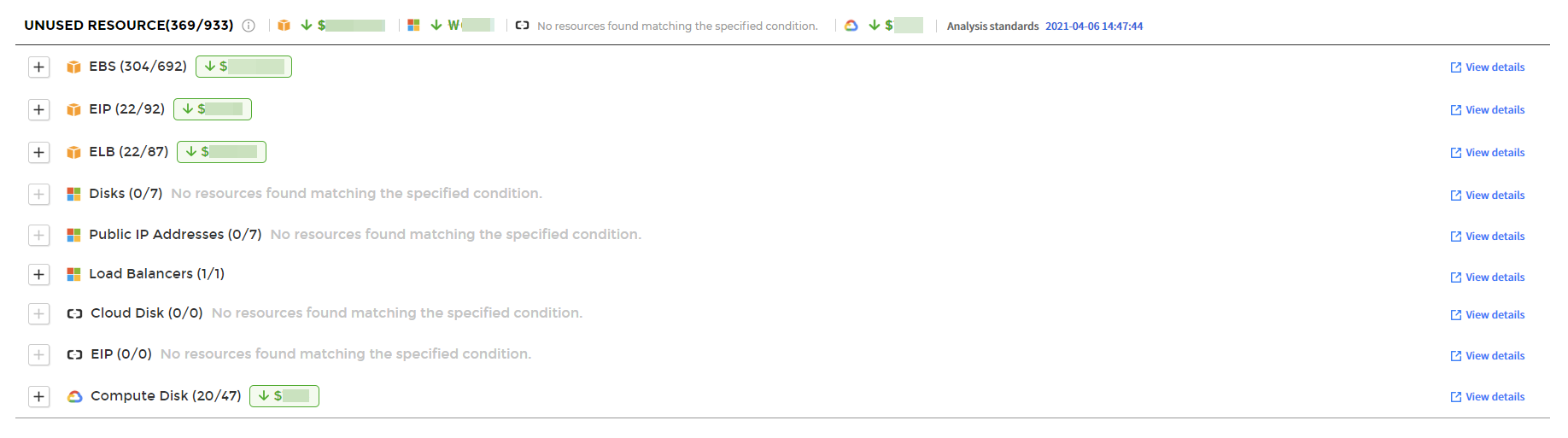
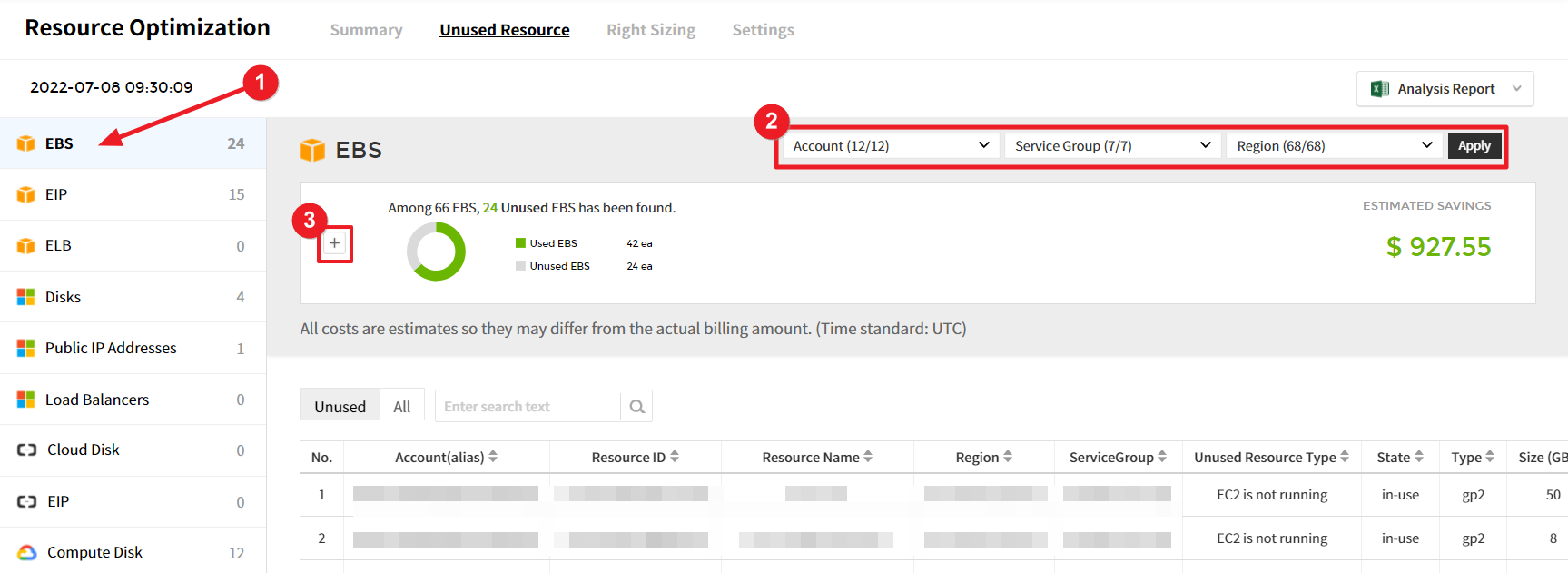
① Select a service from the list on the left side of the Unused Resource page to view the detailed information about the selected service.
② Use the Account, Region, and Service Group drop-down menus to set the data you need to view.
③ Click the [+] button to view unused resources by account, region, or service group in the pie chart and table chart.
You can also download the recommended resources in Excel format and analyze the unused resources offline.
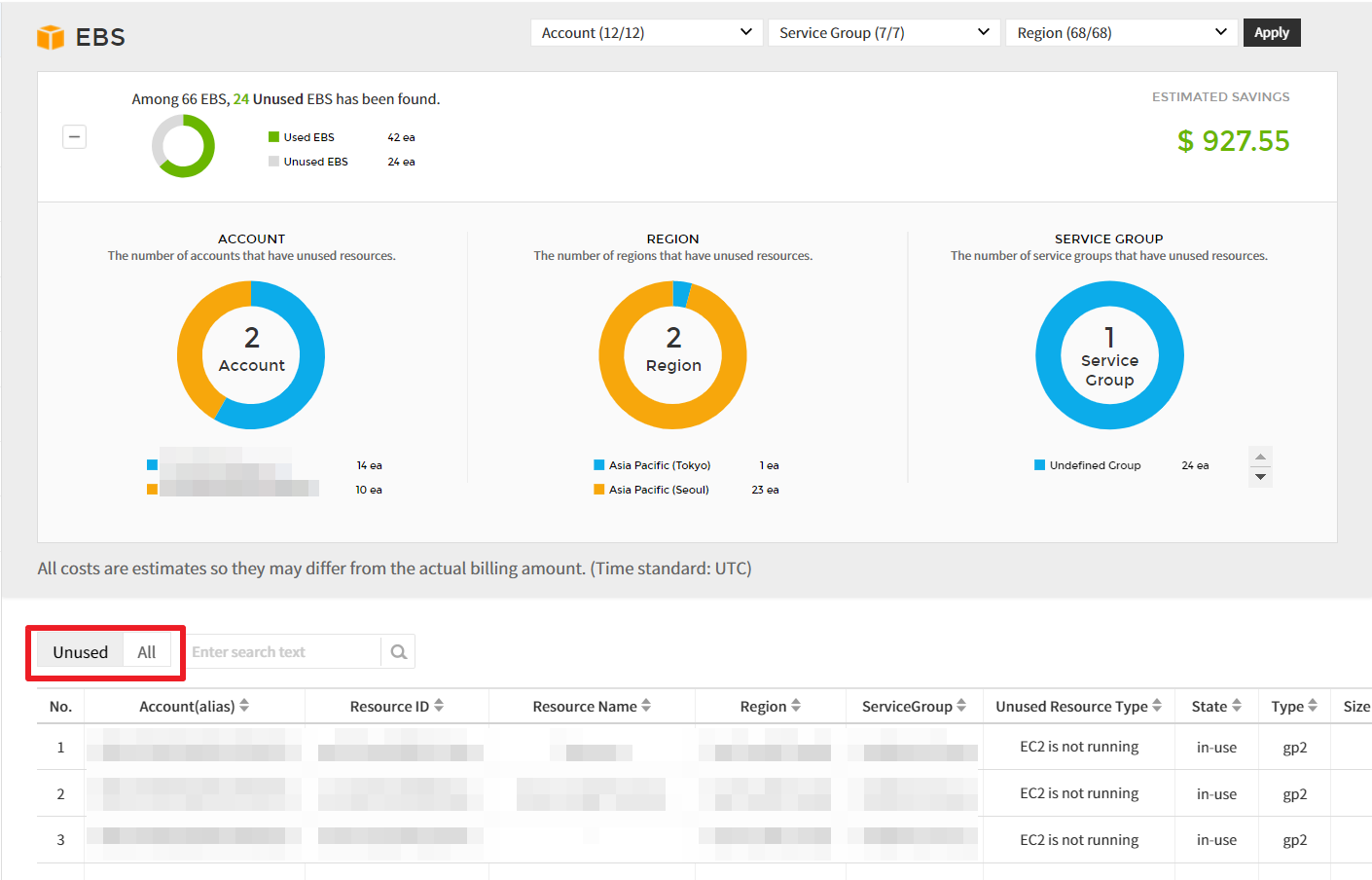
In addition, you can select Unused (recommended resources) or All (entire resources) located on the left side of the table chart to view unused resources only. Resources can be filtered with Account, Service group, and Region drop-down buttons.
Right Sizing
Right Sizing is one of the features to optimize resources and costs, helping you to manage your resources rationally by matching the instance type and size to your workload performance or capacity requirements. It allows you to identify resources that are being wasted due to too large or too small resources for your workload.
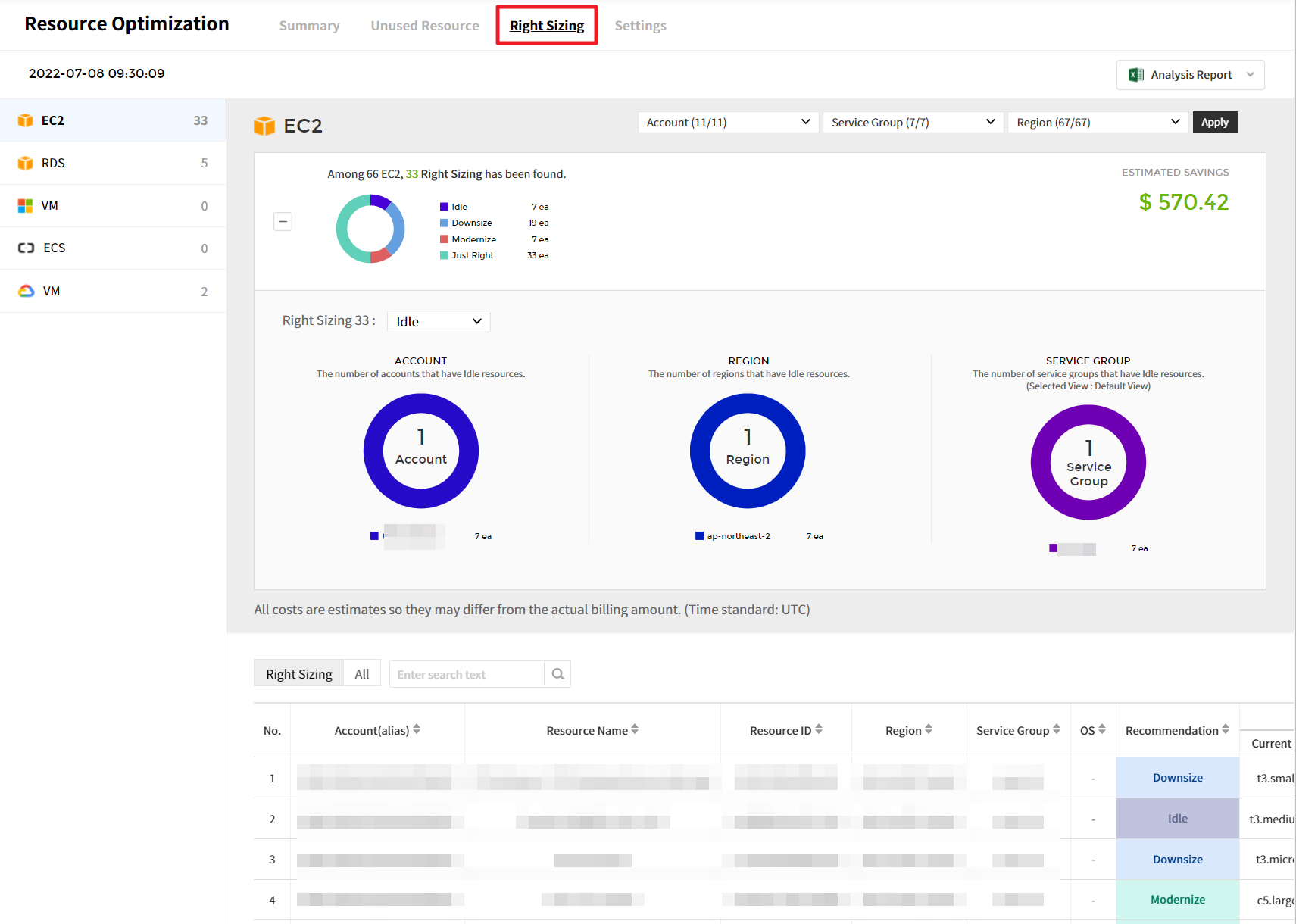
Detailed screen
① In Filter dropdowns, you can select accounts, service groups, and regions, and click [Apply] to view the recommended resources based on the condition you set.
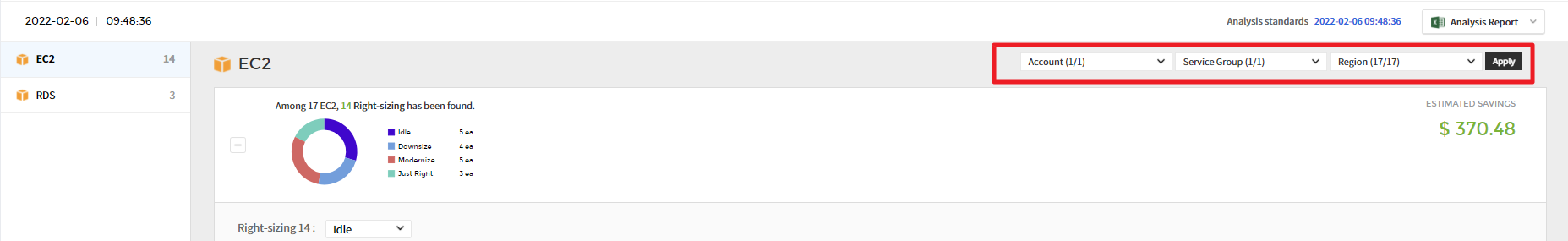
② Based on the analysis conditions defined in the settings menu, it recommends resources that require right sizing. Right Sizing feature analyzes resources and recommends them as Downsize, Upsize, Idle, or Modernize, and optimizes the resource and cost based on the recommendations.
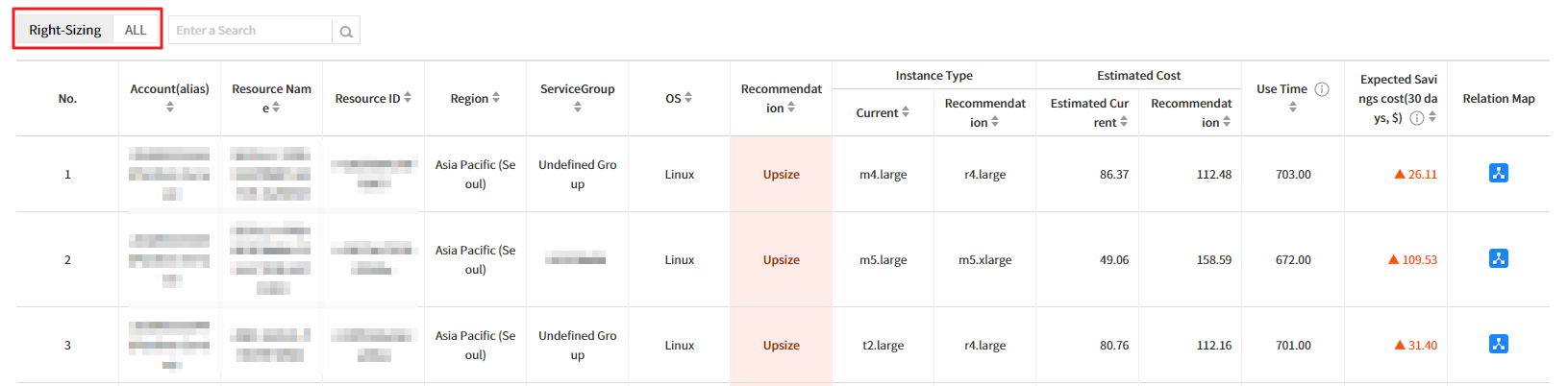
💡 Notification: For EC2 only, you can view the Relation Map for the selected resource by clicking the icon located at the far right of the table list.
Settings
You can set up recommendation conditions for resource optimization. When you access the resource optimization for the first time, a default condition is created automatically, and Unused Resource and Right Sizing resources are provided based on the condition. Users can directly create new recommendation conditions based on their needs.
Create a Condition
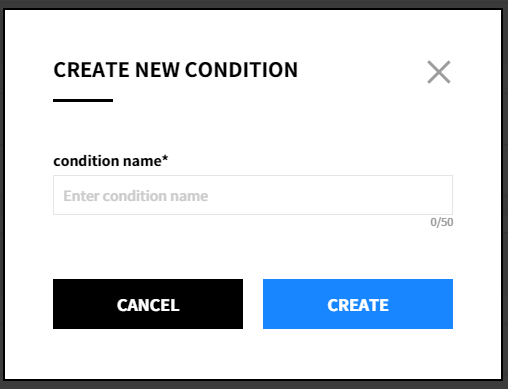
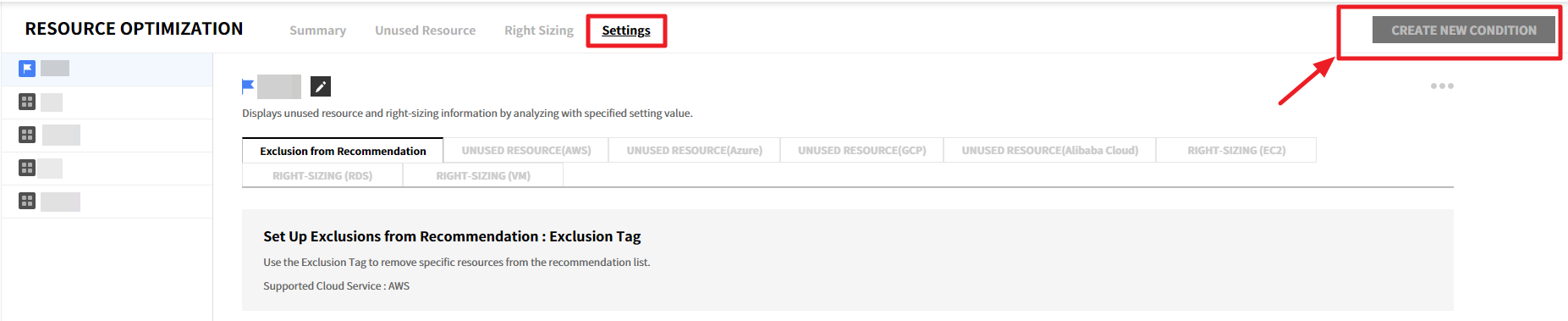
To create a recommendation condition, follow the steps below:
① Click the [Create New Condition] button.
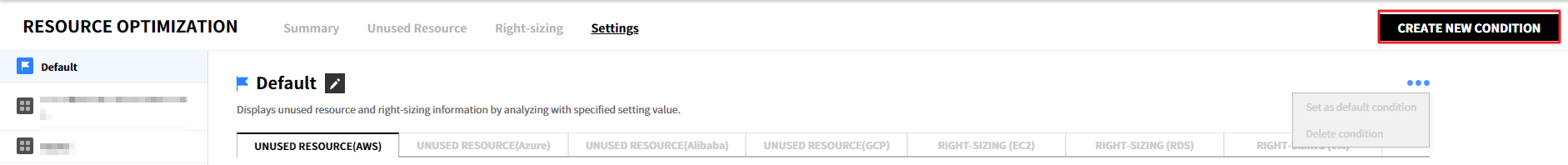
② After entering the condition name, click the [Create] button to create the condition. Only up to 5 conditions can be created.
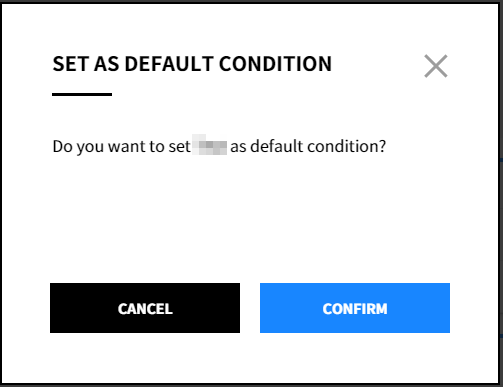
③ Click the icon next to the condition name or click the ![]() icon to change it to [Set as Default Condition].
icon to change it to [Set as Default Condition].
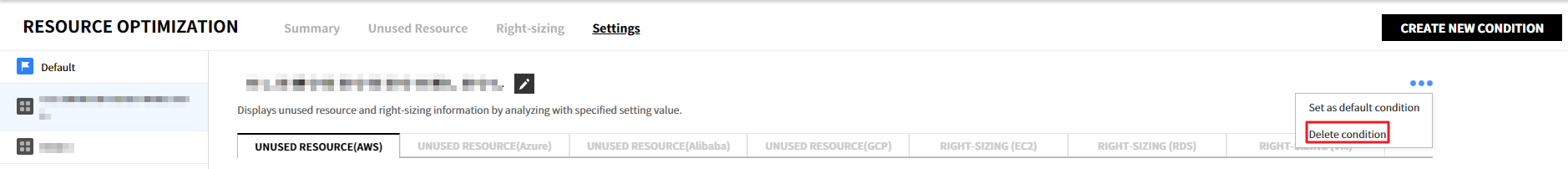
④ Select the ![]() icon of the created condition, and click [Delete Condition] to delete the condition.
icon of the created condition, and click [Delete Condition] to delete the condition.
Condition Type
Exclude from Recommendations
Use the Exclusion Tag to remove specific resources from the recommendation list in order not to receive recommendations for certain resources. To use this feature, It is required to set Tag Key and Tag Value.
💡 Notification: This feature currently supports AWS only, and other cloud services will be supported in the future.
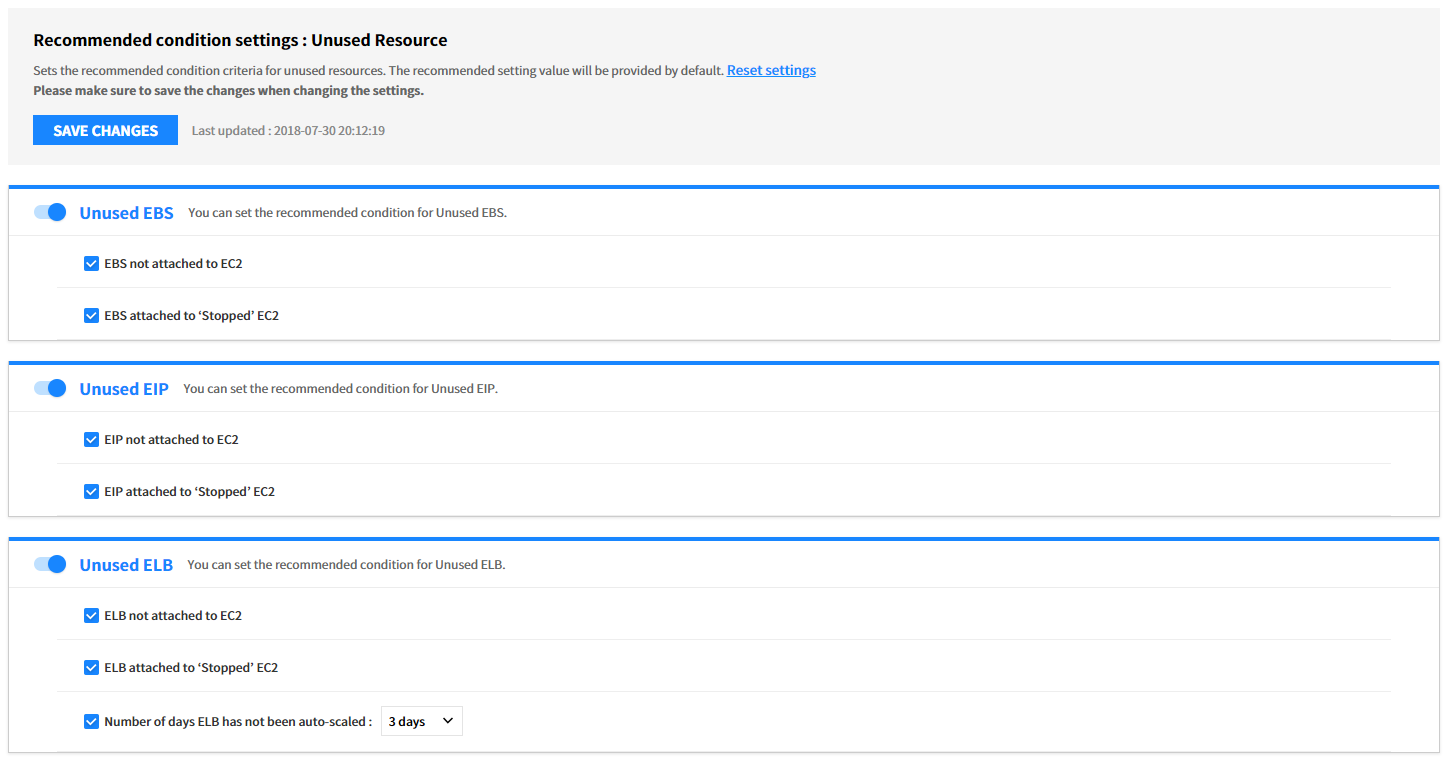
Unused Resource
You can set conditions for Unused Resource analysis by a cloud service. Use the toggle buttons and checkboxes to activate required items for recommendations. After changing the settings, click the [Save Changes] button to save the changes.
Right Sizing (EC2, RDS, and VM)
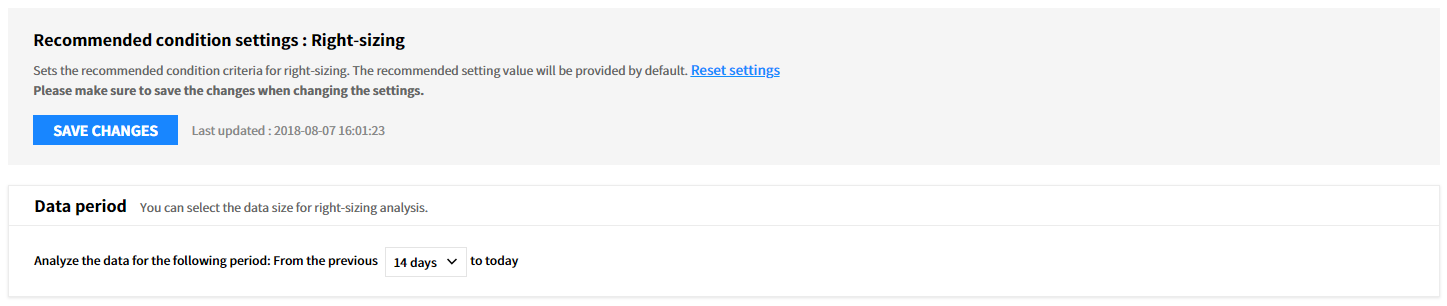
You can set conditions for Right Sizing analysis by a cloud service.
⑴ Step 1: Set Data Analysis Period
You can select the data size for right sizing analysis.
⑵ Step 2: Set Recommendation Conditions
You can set the recommendation criteria for each item.
- Idle: Recommend to terminate the resource if the usage is less than the defined usage after analyzing the usage of CPU, Network, and Memory.
- Upsize: Recommend to change to a higher performance resource if the usage exceeds the defined threshold after analyzing the usage of CPU, Network, and Memory.
- Downsize: Recommend to change to a lower price of resource if it falls below the usage defined during setting after analyzing the usage of CPU, Network, and Memory.
- Modernize: Recommend to change the current resources to the latest generation of the same resource type for a lower price and better performance.
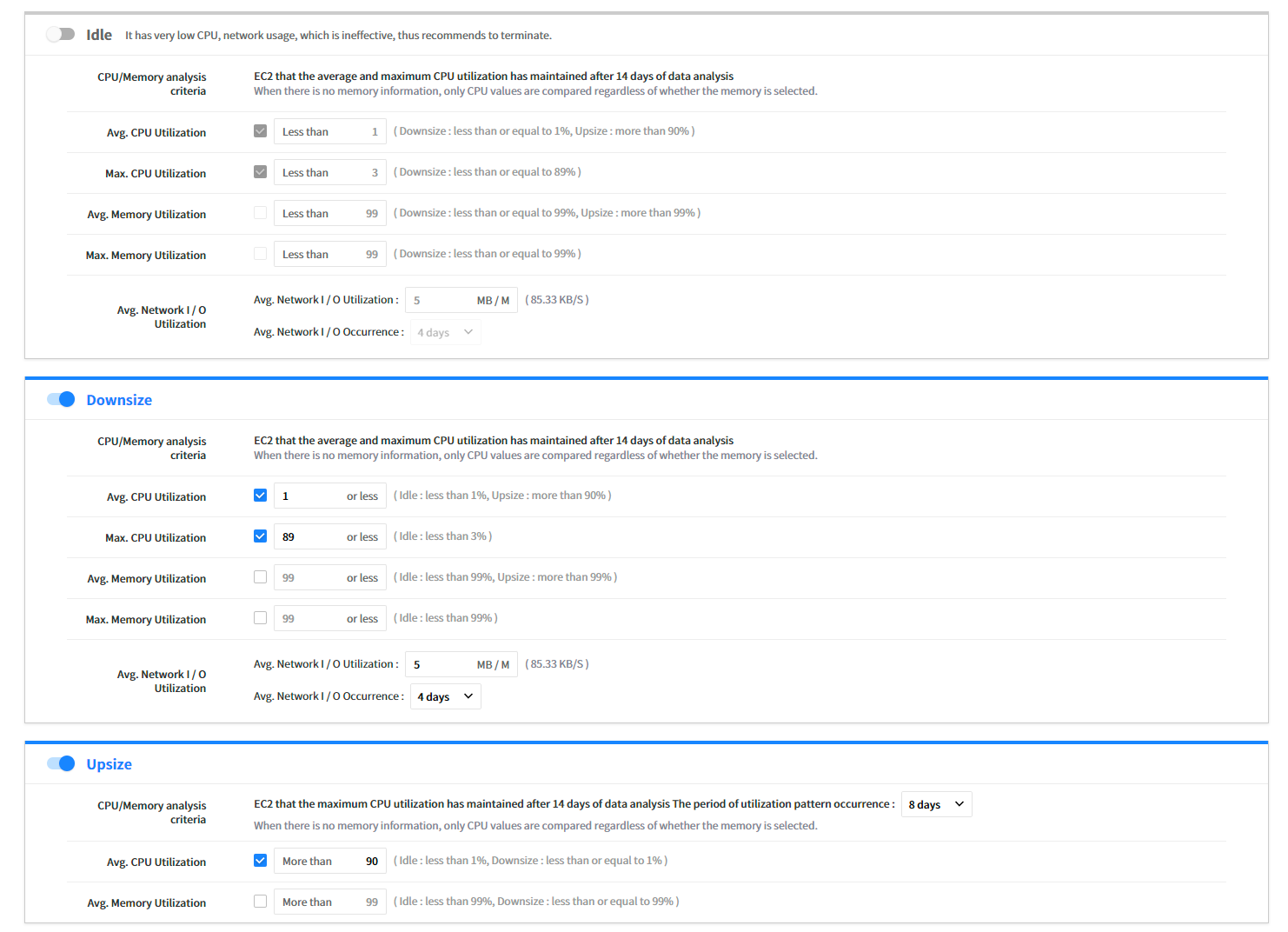
| Analysis Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Avg. CPU Utilization | For Avg. CPU Utilization of Idle, it cannot have higher Avg. CPU Utilization value if it is recommended to Downsize. For Avg. CPU Utilization of Downsize, it cannot have lower Avg. CPU Utilization value if it is recommended to Idle EC2. For Avg. CPU Utilization of Downsize, it cannot have higher Avg. CPU Utilization value if it is recommended to Upsize. |
| Max. CPU Utilization | For Avg. CPU Utilization of Idle, it cannot have higher Avg. CPU Utilization value if it is recommended to Downsize. For Avg. CPU Utilization of Downsize, it cannot have lower Avg. CPU Utilization value if it is recommended to Idle EC2. |
| Avg. Memory Utilization | For Avg. Memory Utilization of Idle, it cannot have higher Avg. Memory Utilization value if it is recommended to Downsize. For Avg. Memory Utilization of Downsize, it cannot have lower Avg. Memory Utilization value if it is recommended to Idle EC2. |
| Max. Memory Utilization | For Avg. Memory Utilization of Idle, it cannot have higher Avg. Memory Utilization value if it is recommended to Downsize. For Avg. Memory Utilization of Downsize, it cannot have lower Avg. Memory Utilization value if it is recommended to Idle EC2. |
| Avg. Network I/O Utilization | By selecting the checkbox, the network metric data will be collected from CloudWatch. Based on the collected data, EC2 that volume is kept below the one set during the Data Period will be included in the recommendation condition of Idle EC2 and Downsize. |
Memory Metric Source
For more accurate Right Sizing analysis, it collects the memory metric by installing a script for your OS. You can download the script by selecting Windows, CentOS, Amazon Linux, or Ubuntu buttons. Click the [Save Changes] button at the top of the screen to complete the recommendation condition setting for Right Sizing resource.
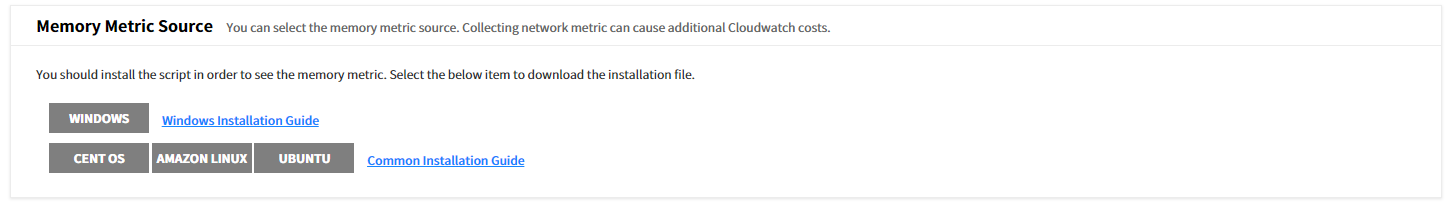
⚠️ Attention: Additional CloudWatch costs may arise if you collect network metrics.
Report
Asset Management > Report
The Report allows users to view detailed information about resource information with resource performance, resource usage, and service group. There are two types of reports: Custom Report and Basic Report. With custom reports, users can quickly configure and create their own reports to view filtered data specific to their needs. Basic reports are provided by default with a predefined set of criteria. In addition, reports can be downloaded in Excel or PDF format.
Custom Report
Users can configure and create their own reports with data provided by Asset Management. It enables you to customize reports with different formats based on the template provided by default.
Console Configuration
The Custom report consists of the following.
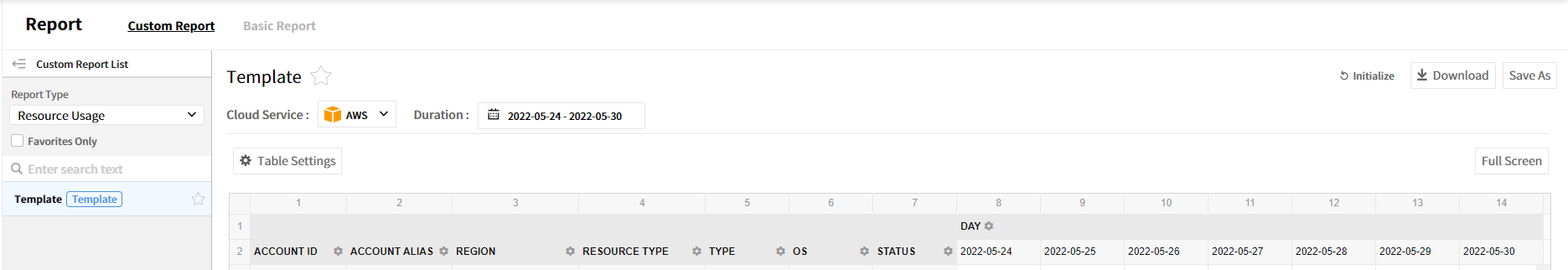
- Favorites Only: Select the checkbox to view reports specified as favorites only.
- Duration: Set the date range to be displayed on the report. The options to choose the date range are the previous 7 days, 14 days, 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year. Select Custom to select the period manually.
- Download: Download custom reports in Excel format.
- Save As: Create a new report with a new name based on the conditions of the currently selected report.
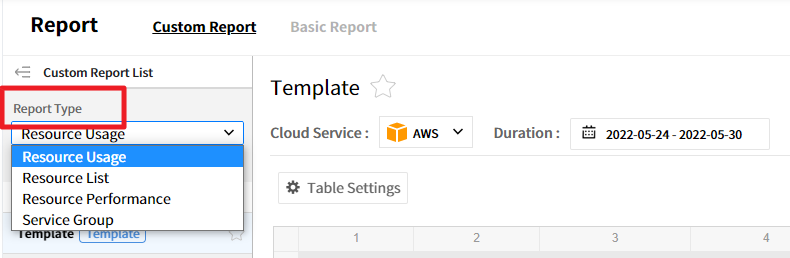
Report Type
Users can create a new report by selecting the report type, and data conditions differ depending on the report type. There are 4 types of reports: Resource Usage, Resource List, Resource Performance, and Service Group. Available data conditions for report types are different.
Create a Custom Report
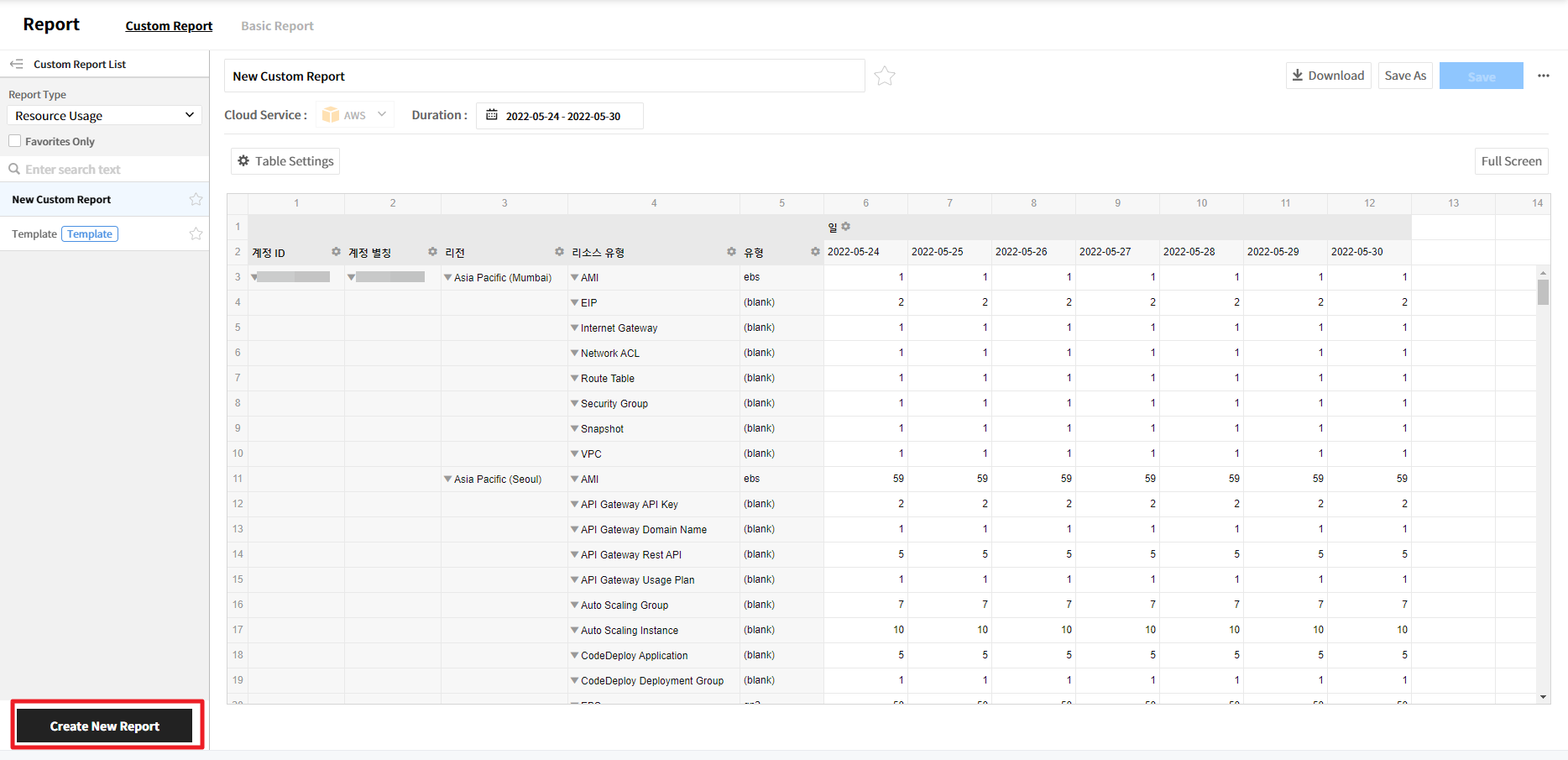
Click the [Create New Report] button.
![]()
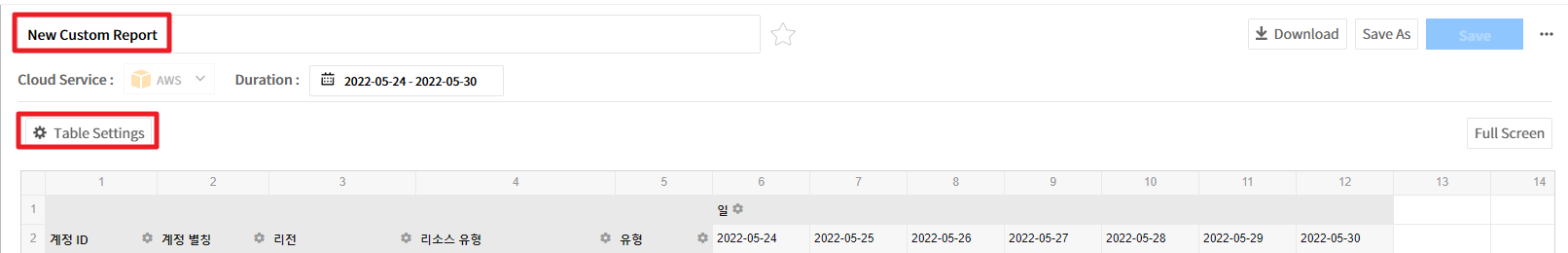
New Custom Report will be created.
![]()
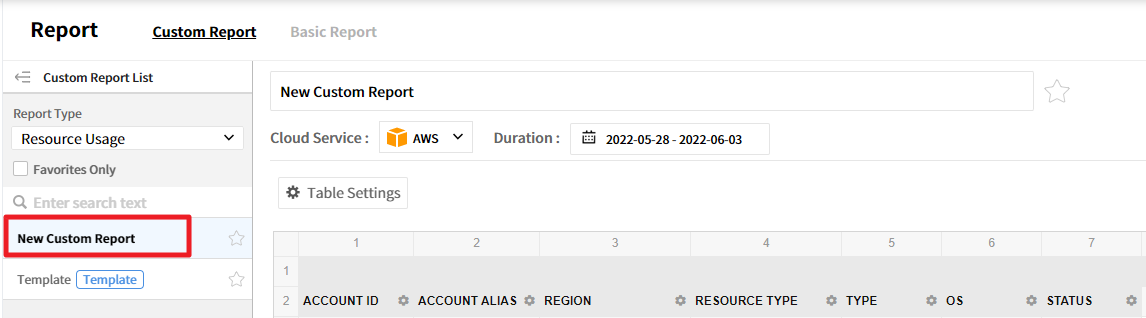
Select New Custom Report and change the name, and click [Table Settings] to set items required for the report.
![]()
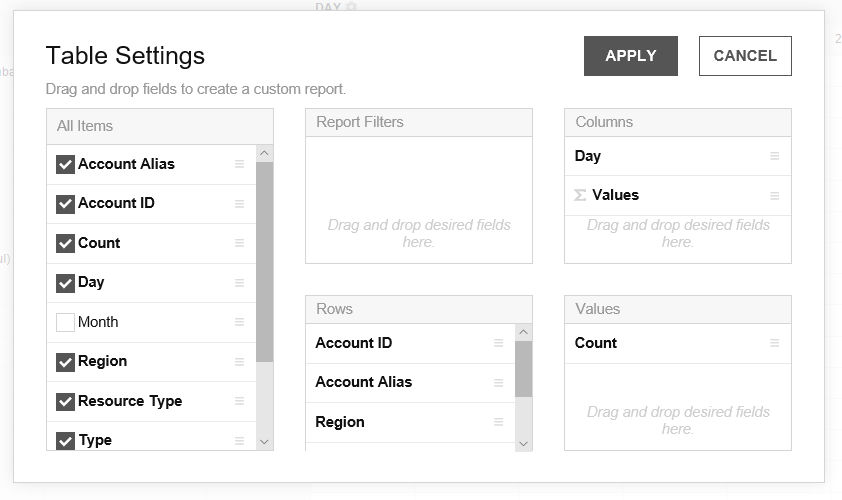
Drag items from the popup window of the table settings to Report Filters, Rows, Columns, and Values and click [Apply].
![]()
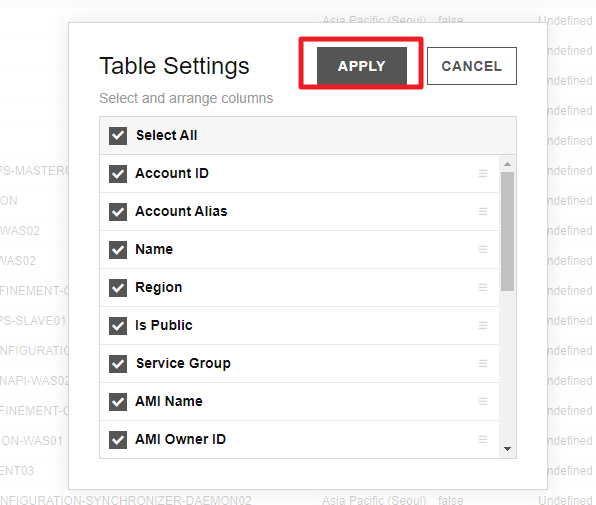
Select the resource list as the report type and click [Table Settings], and then a popup window will appear. Complete the settings and click [Save].
![]()
💡 Notification: If No data available is displayed, you may set the date range to short. Try extending the range and you will see the data correctly.
Modify Custom Reports
You can modify the report name, data conditions, fields to display on the table, and the field values. The items to modify are different for each report type. For report name, you can modify it directly on the name field or click [Save As] and rename it. Modifying custom reports goes through the same process as creating it, and click Save to modify the report.
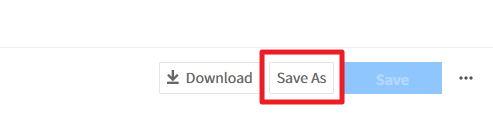
📌 Important: For data conditions, you can set the cloud service-related conditions (Cloud Service Provider, Metric, and Resource) only when you create a report for the first time, and after creating the report, you can modify duration and View only.
Delete Custom Report
Click the [Delete Report] button at the top right of the report screen to delete the report.
Basic Report
The Basic Report provides 5 types of report templates.
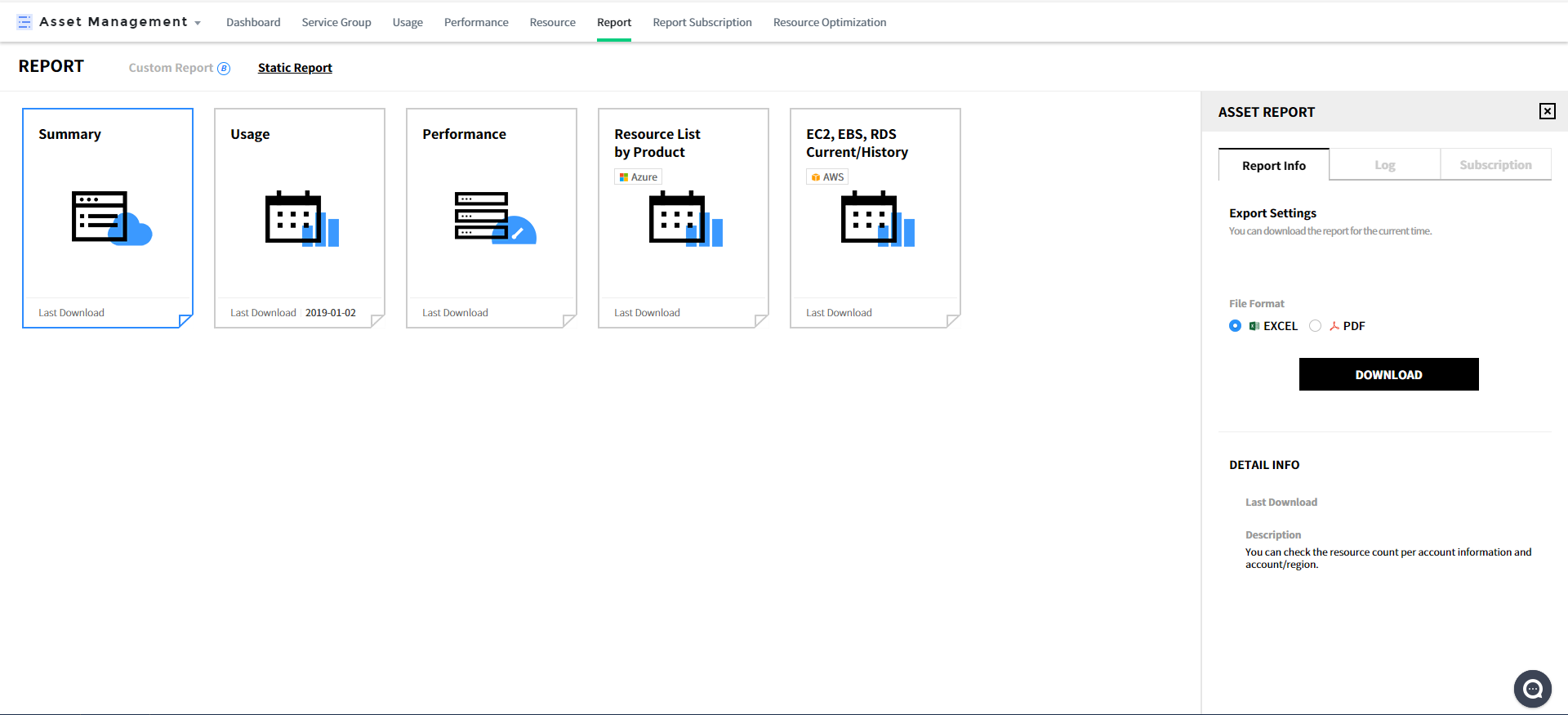
Report Type
- Resource Summary: Can check the account information, and resources by account and region.
- Resource Usage: Can check the list of resources by account and region and their status.
- Resource Performance: Can check the performance information by resource for the selected period.
- Resource List by Product: No longer supported. Can be available in the Custom Report.
- EC2, EBS, RDS Current/History: Can check the current and history information of EC2, EBS and RDS.
Report Component
Report Information: Users can download reports for the current time. For the performance report, date range can be set. Select the file format as Excel or PDF and click [Download] to download. Click each template to view template settings of the report on the right, and the settings are composed of the following three tabs.
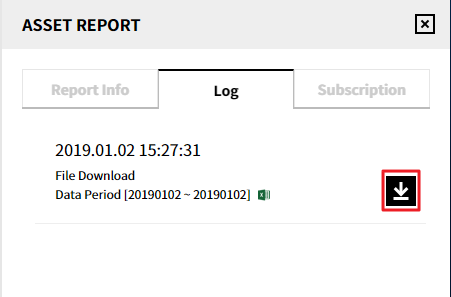
Log: View the history logs of reports downloaded, and click the icon to download the report again.
![]()
Subscription: Users can subscribe to reports via email registered in the service. You can subscribe on a daily, weekly and monthly basis; and you can specify a time to receive reports. There are two different kinds of subscriptions; subscriptions you created manually and subscriptions the authorized user specified you as a subscriber. You can create, delete and modify the subscriptions you created, but you can only view the subscriptions that the authorized user has specified you as a subscriber.
Create a new subscription
① Click [Create New Subscription] in the Subscription tab.
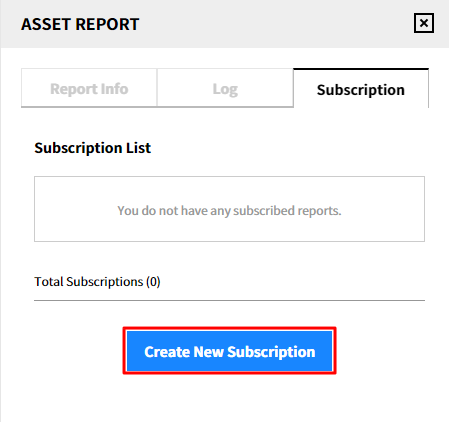
② Enter the required items in the subscription settings and click [Save]. The subscription name consists of the report template name, cycle and language as default.
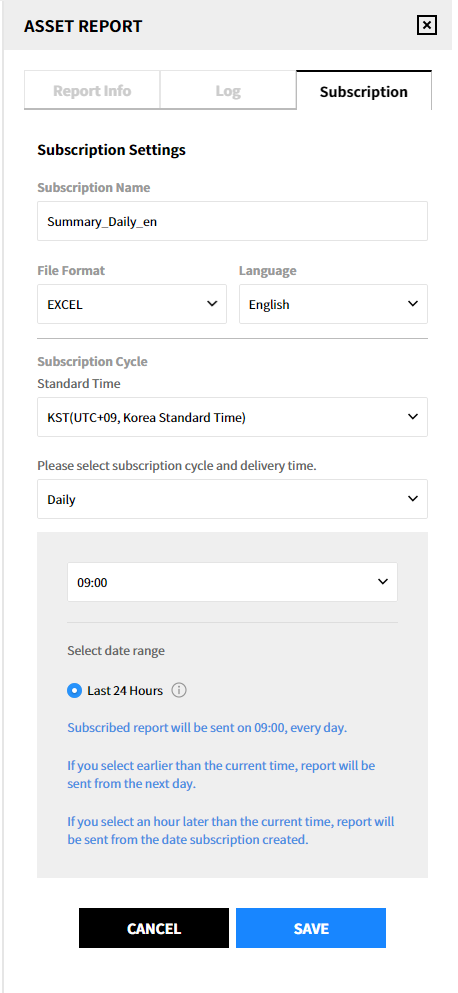
③ The created subscription will be displayed as below.
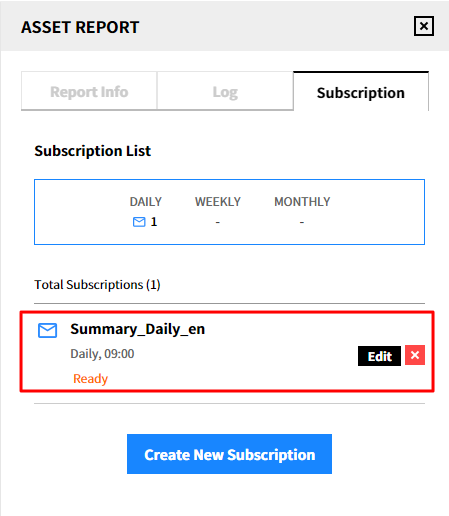
Modify the subscription
① Click [Edit] of the subscription that you want to edit.
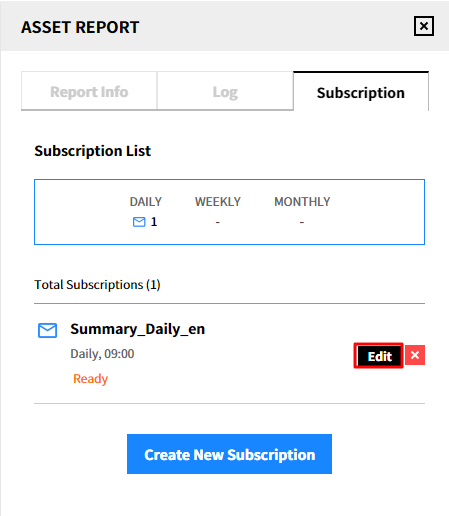
② After modification, click the [Save] button.

Delete the subscription
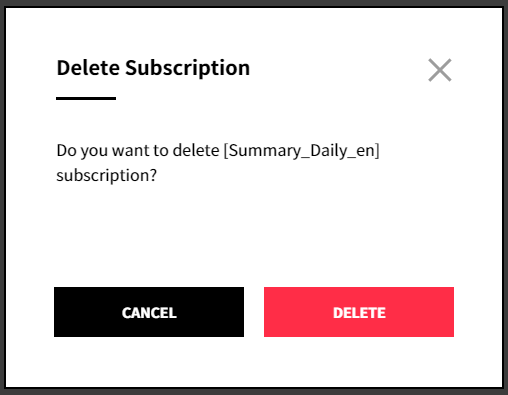
① Click the [Delete] icon.
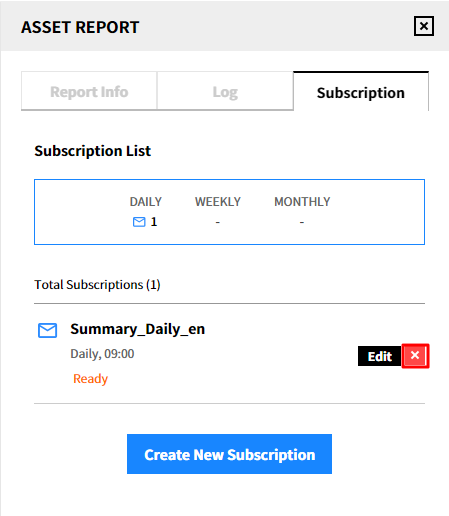
② Click [Delete] in the popup window to delete the subscription from the list.
Report Subscription
Asset Management > Report Subscription
The Report Subscription provides automatic mailing feature to users with authentication to modify subscriptions. In this menu, you can create, modify, or delete subscriptions, view subscription history, and re-download reports that have already been sent. You can also manage recipients by creating and deleting email addresses, and specify recipients when creating and modifying subscriptions.
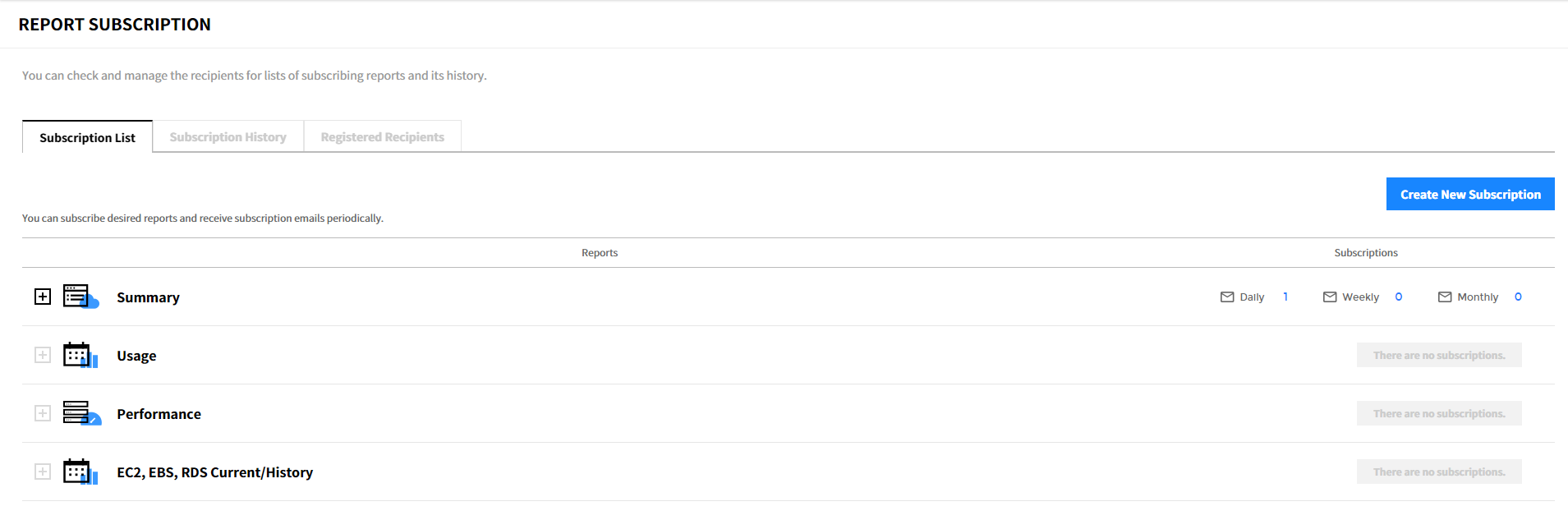
Subscription List
You can create subscriptions by report type (Summary, Usage, Performance, and EC2, EBS, RDS Current, History), and modify and delete the created subscription.
Create Subscription
① Click [Create New Subscription] in the subscription list.
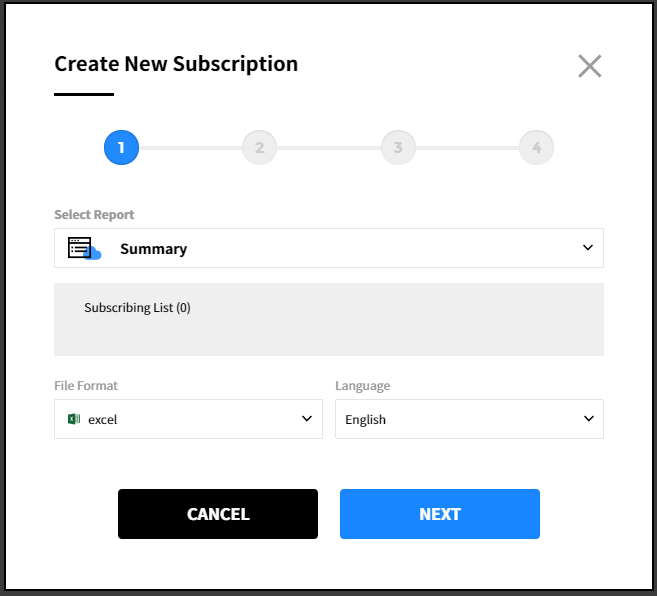
② Select a report to subscribe. Click [Next] after selecting the report type, file format, and the language.
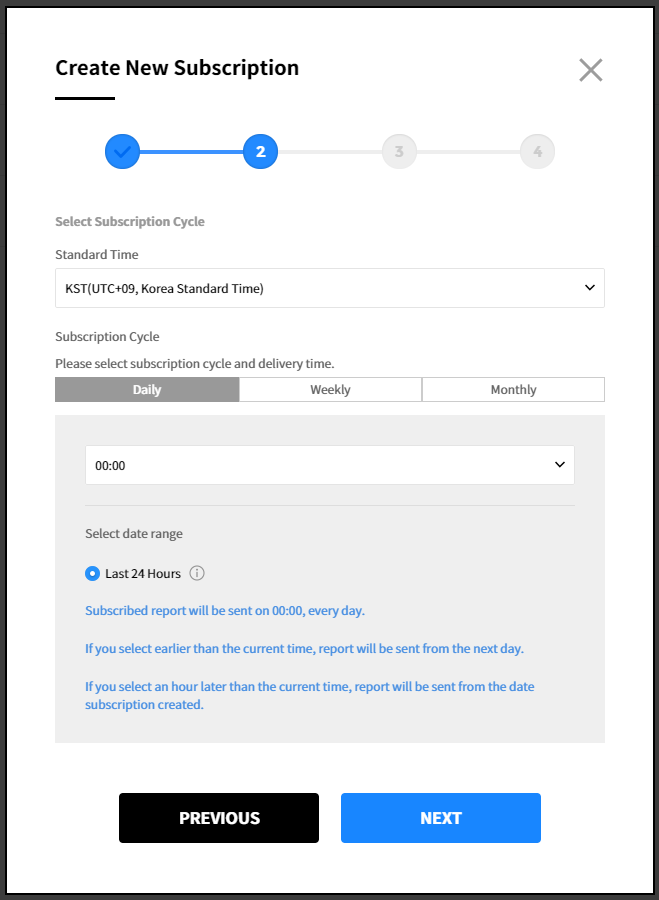
③ Select subscription cycle. Choose the time zone and select the cycle for your subscription. The cycle can be set on a daily, weekly, and monthly basis. If you choose to receive subscriptions on the 31st day, you will receive subscriptions at the last date for the months that have no 31st day.
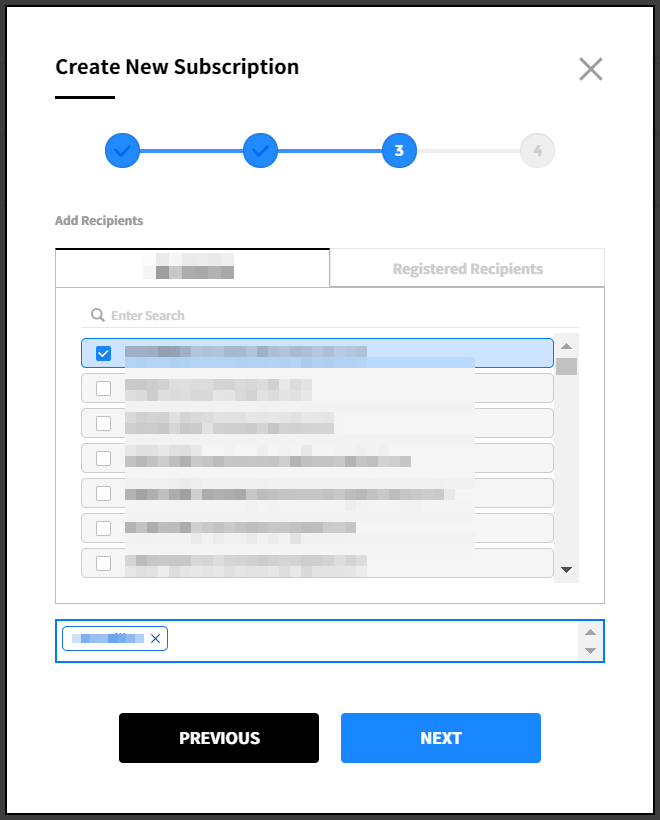
④ Add recipients. Up to 10 recipients can be added. There are two types of recipients; users who belong to the company with authorization to access the Service Portal and registered recipients you manually registered in the Report Subscription. Select recipients and click the Next button.
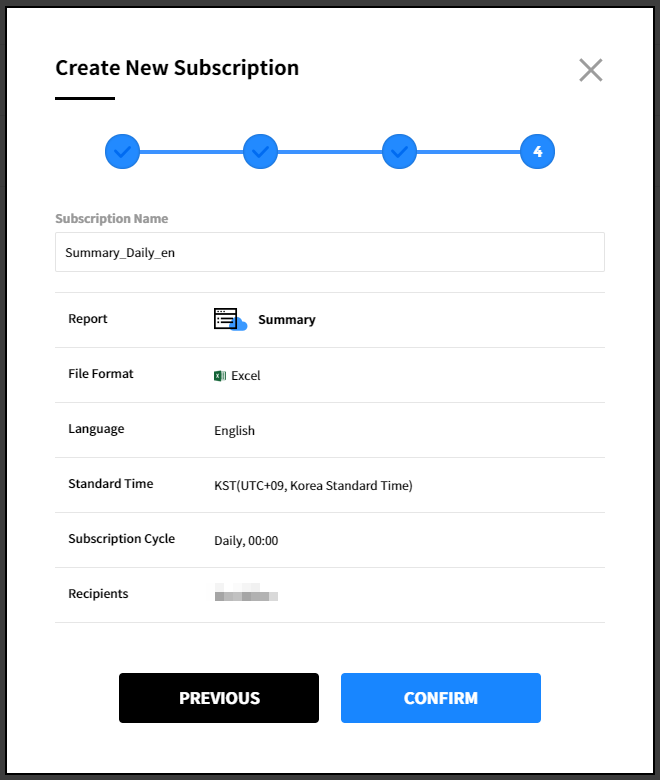
⑤ Enter a subscription name. The subscription format should be report type_cycle_language as default, and the name can be changed. Review the items configured in the previous steps, and click [Confirm] to create a subscription.
Modify Subscription
① Click the modify icon from the subscription list.
![]()
② The subscription information you previously set is displayed. Click [Modify] after choosing a subscription that you want to edit and apply the changes.
Unsubscribe reports
① Click the red [X] icon from the subscription list to unsubscribe the reports.
![]()
② Click [Delete] to delete a subscription. If this subscription has been previously sent, you can also see the history log from Subscription History tab.
Subscription History
You can view the history of subscriptions that were sent, and can download files that were recently sent.
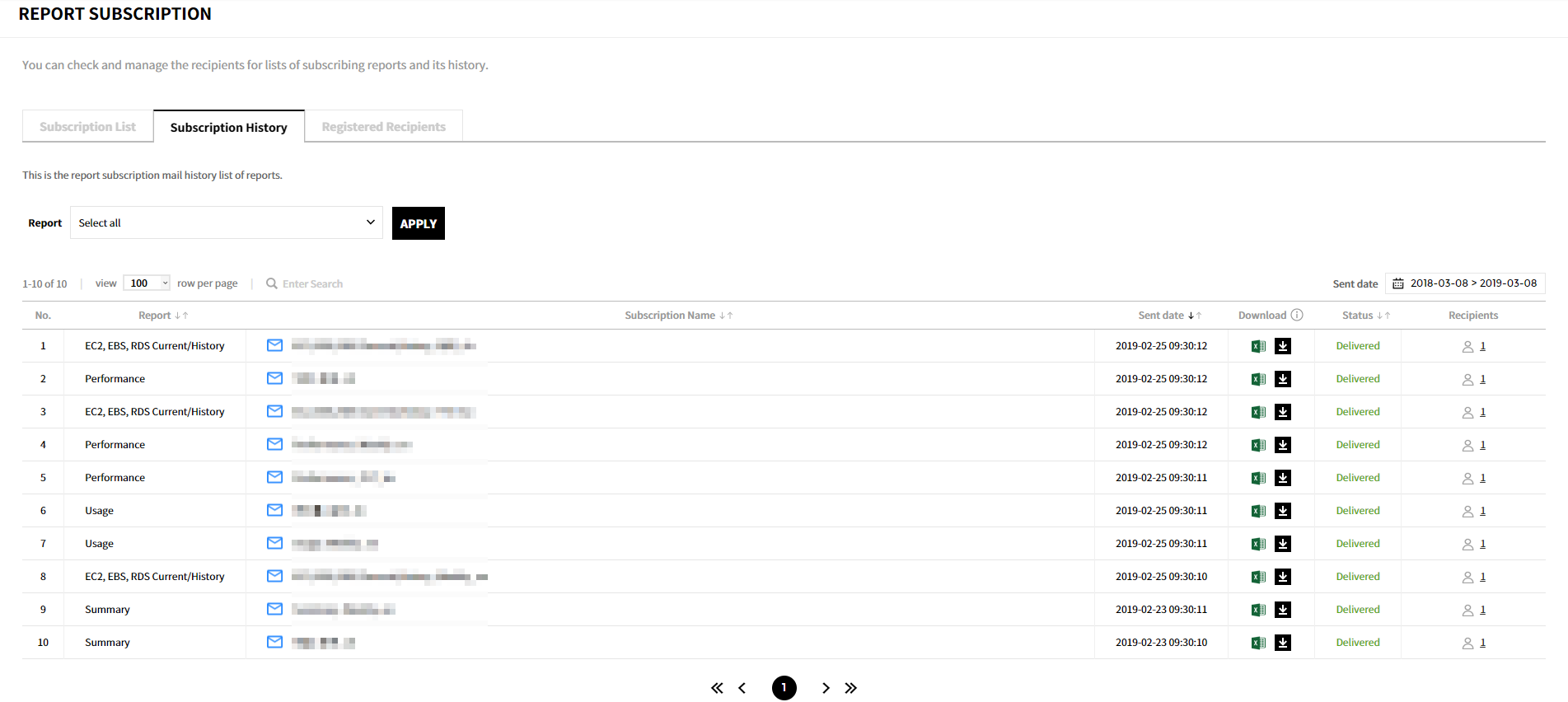
- Report: Display the report type selected when creating a subscription.
- Subscription Name: Name of subscription, default name or a name that the user entered, will be displayed.
- Date Sent: Date and time subscriptions were sent.
- Download: Download files sent for the last 30 days by clicking the download icon. Failed to send subscriptions or subscriptions sent a month ago cannot be downloaded again.
- Status: The status of subscriptions.
- Recipients: Display the number of recipients for the subscription. Click the recipient icon to see the recipient list.
Registered Recipients
In the Registered Recipients, you can manually add recipients to subscribe reports, and edit and delete registered recipients.
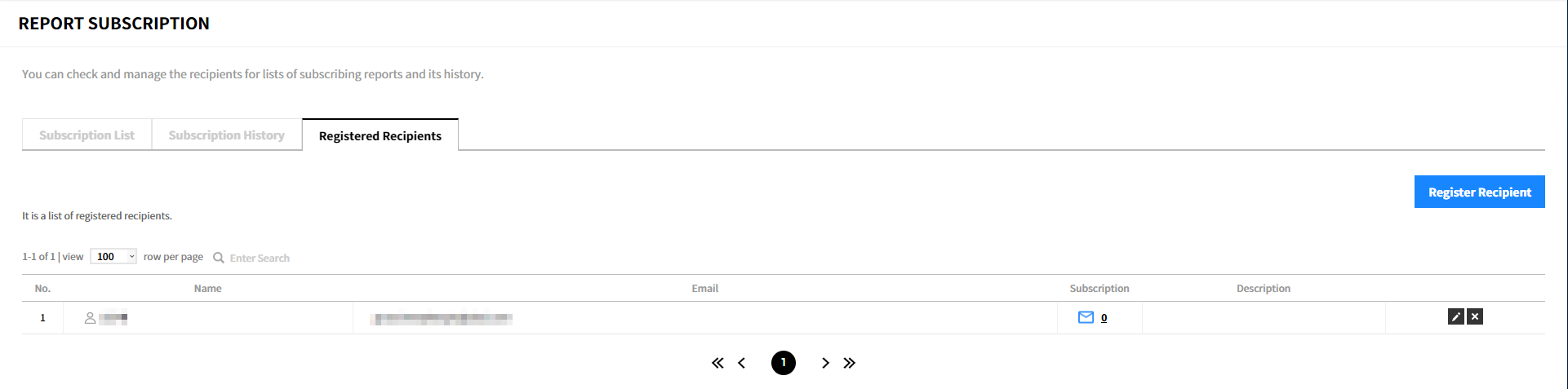
- Name: Name of recipient is displayed.
- Email: The recipient’s email address is displayed.
- Subscription: The number of reports you are subscribing. Click the number to view a list of reports you are subscribing to.
- Description: The description about the subscription is displayed.
Add Recipients
① Click [Register Recipient].
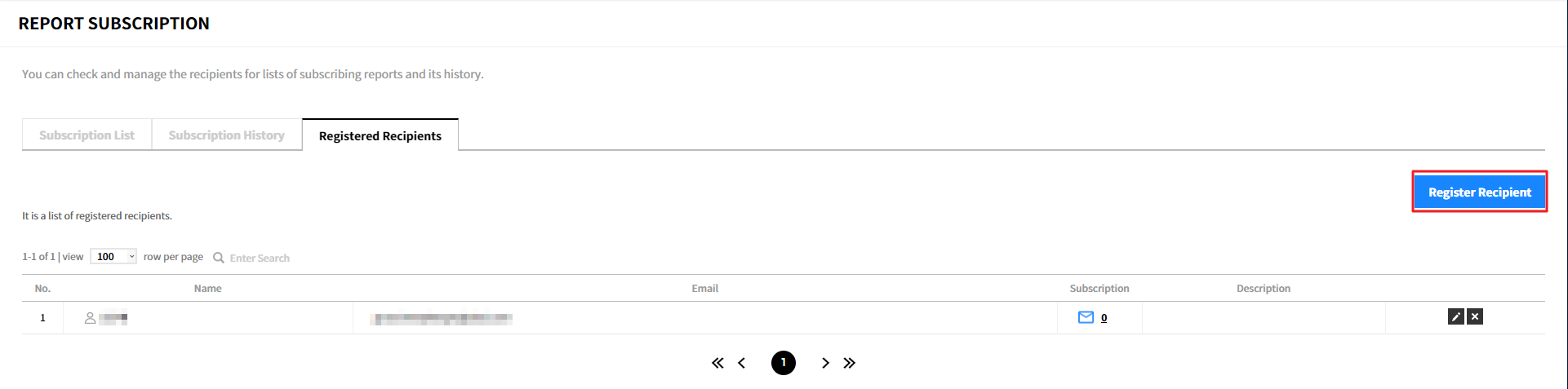
② Enter the required information in the popup window and click the [Confirm] button. To register multiple recipients, click the [Save and Register Recipients] button.

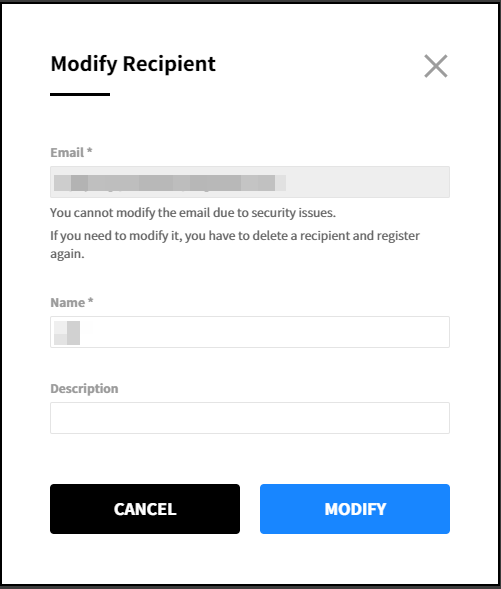
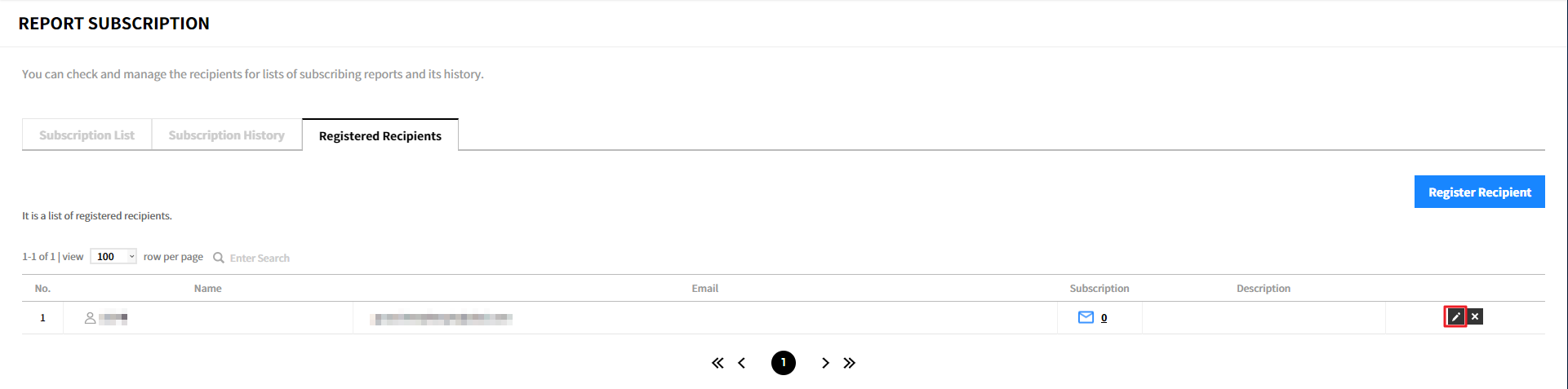
Modify Recipient
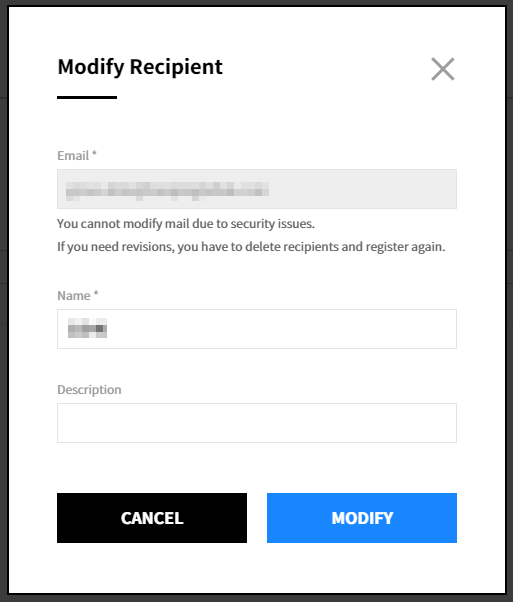
① Click the modify icon.
② Apply the changes and click the [Modify] button. You cannot modify the email address in the popup window. To modify the email address, you must delete and register the recipient again.
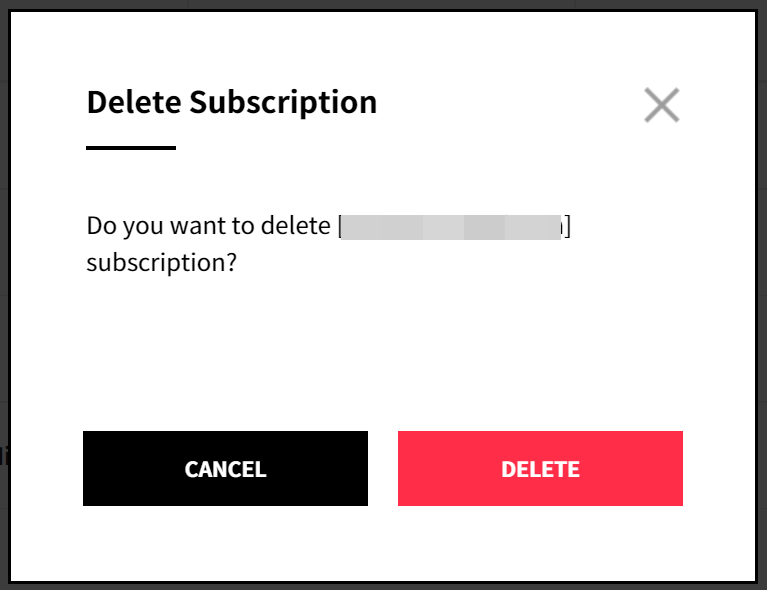
Delete Recipient
① Click the delete icon.
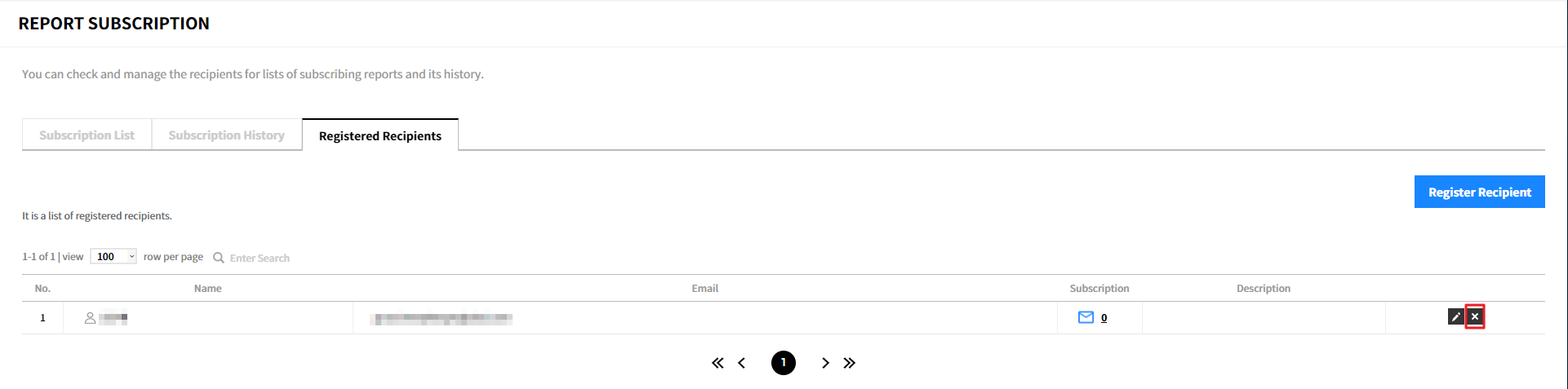
② Click [Confirm] to delete the recipient. When you delete the recipient, the recipient also will be deleted from the recipient list.
Resource Alert
Asset Managetment > Resource Alert
Resource Alert is a service that detects resource anomalies based on rules set by user and sends alerts. It helps you to manage resources more closely by preventing you from missing resource anomalies.
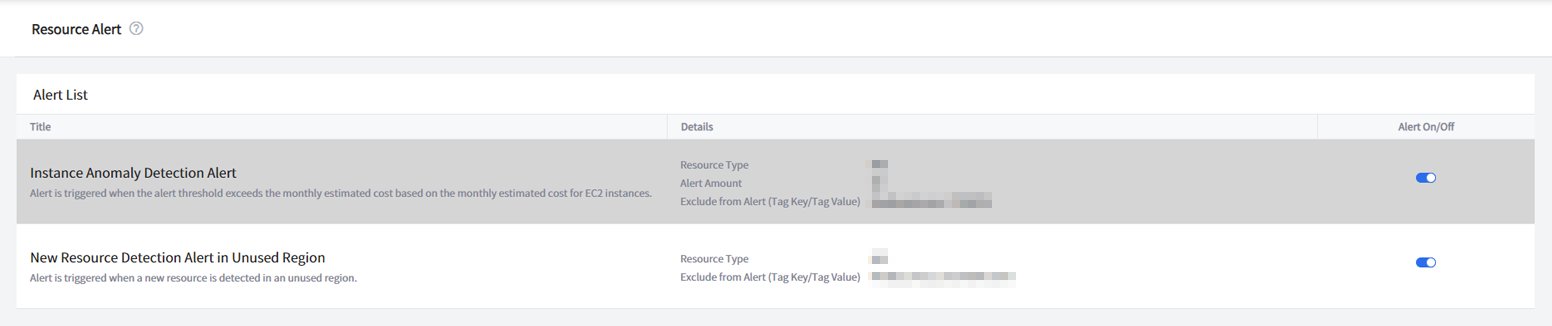
Resource Alert Types
There are two types of alerts; Instance Anomaly Detection Alert and New Resource Detection Alert in Unused Region.
Instance Anomaly Detection Alert
It is triggered when the monthly estimated cost of EC2 On-Demand instance price exceeds the alert amount. The estimated cost is calculated based on EC2 Linux instances.
| Title | Display the title and description of resource alert. |
| Details | Display the alert amount and the tag key and tag value to exclude from being triggered an alert. |
| Alert On/Off | Toggling this button to On will receive resource alerts. |
New Resource Detection Alert in Unused Region
It is triggered when a new resource is detected in an unused region.
| Title | Display the title and description of resource alert. |
| Details | Display the tag key and tag value to exclude from being triggered an alert. |
| Alert On/Off | Toggling this button to On will receive resource alerts. |
Edit Resource Alert
Click the resource alert to edit from the alert list. Edit Alert screen will be displayed as below.
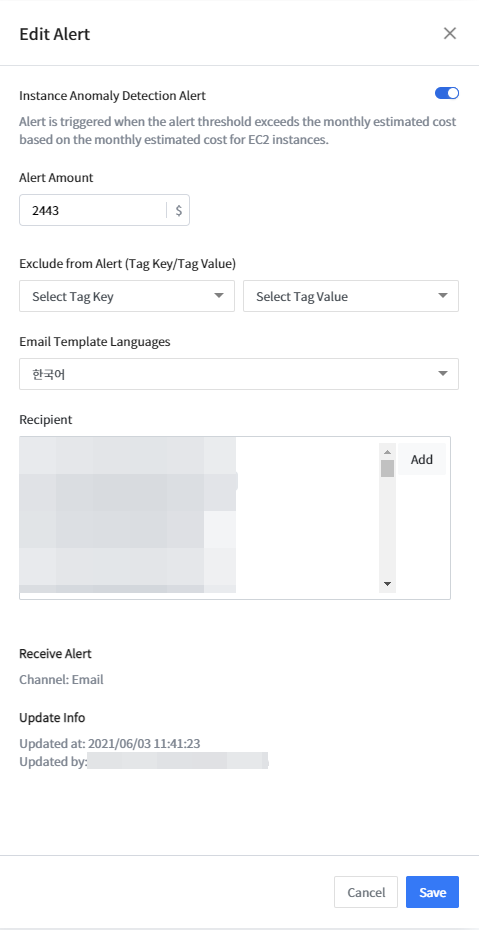
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Title | Title of the resource alert. You can’t edit the default title. |
| Description | Description of the resource alert. |
| Alert Amount | Trigger alerts when exceeding the predefined dollar amount. |
| Exclude from Alert | You can exclude certain tag key and value from being triggered an alert. |
| Update Info | Display the date and time when the alert setting was updated and the user who last updated the alert setting. |
| Receive Alert | Display the channel and recipient of the resource alert. |
| Email Template Language | Select a language you want to use when receiving email alerts. |
| Recipient | Add a recipient to receive email alerts. |
Click the [Save] button to save changes.
Note: You can unsubscribe by clicking Unsubscribe button at the bottom of an email.
Resource Scheduler
Asset Managetment > Resource Scheduler
With Resource Scheduler, you can schedule instances to start or stop automatically whenever you want. Only run the resources when you are actually using them and save cloud costs dramatically by turning off the unused resources. Resource Scheduler starts and stops resources based on AWS resource tags or GCP resource labels.
🔔 Notification: Depending on your country or region, this feature may not be available.
Required Permission to Use Resource Scheduler
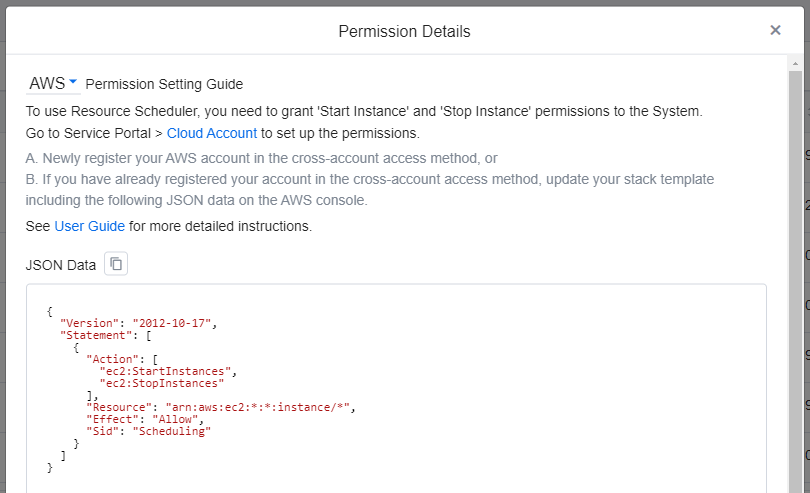
You need to grant Start Instances and Stop Instances permissions to the System to use the Resource Scheduler.
AWS Permissions
To grant permissions that would allow the System to start and stop AWS resources, you need to do the following in Service Portal > Cloud Account.
A. Add your AWS account in Cross-Account Access method, or
B. Update your stack template if you have already registered your account in the cross-account access method, including the following JSON data on the AWS console.
💡 Notification: How to Register with Cross-Account Access Method
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"ec2:StartInstances",
"ec2:StopInstances"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:ec2:*:*:instance/*",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Sid": "Scheduling"
}
]
}
You can check out the details by clicking the Permission Details button on the Schedule page.
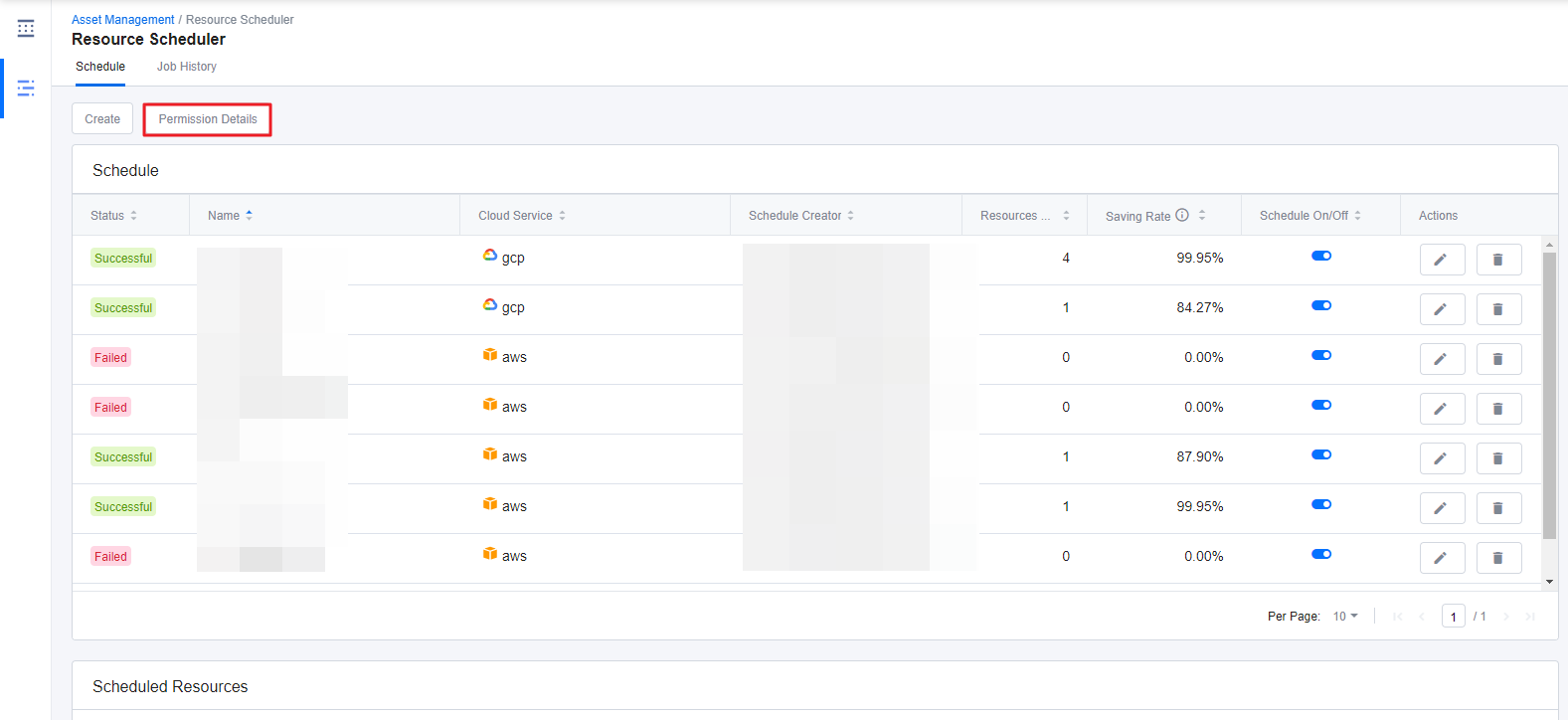
📜 Note: When registering AWS accounts, the System strongly recommends the cross-account access method, and therefore, Resource Scheduler only supports the accounts that registered with cross-account access method.
GCP Permissions
You need to grant ‘compute.instances.start’ and ‘compute.instances.stop’ permissions to the System to use Resource Scheduler. Follow the instructions below to grant necessary permissions by creating a role on the GCP console to the System.
📜 Note: Only the Owners who has the permissions to create a role can grant such permissions to the System.
① Go to GCP Console Home and move to IAM & Admin > Roles page.
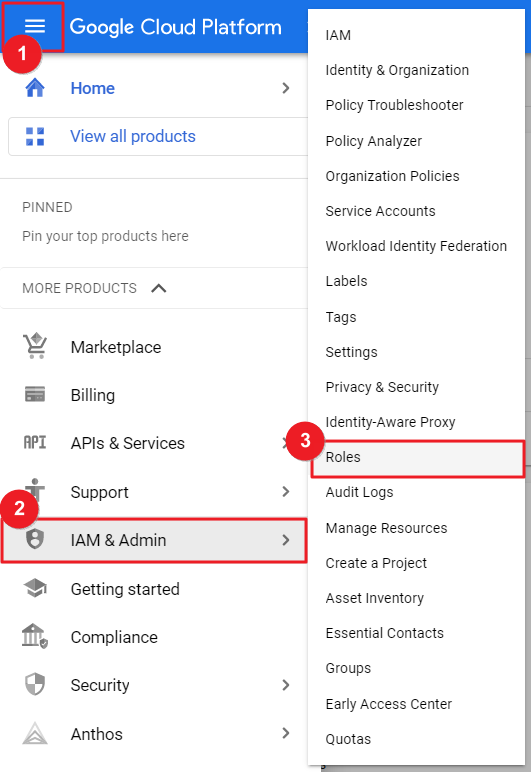
② Click [CREATE ROLE].
③ Enter Title and ID and select General Availability for the Role launch stage.
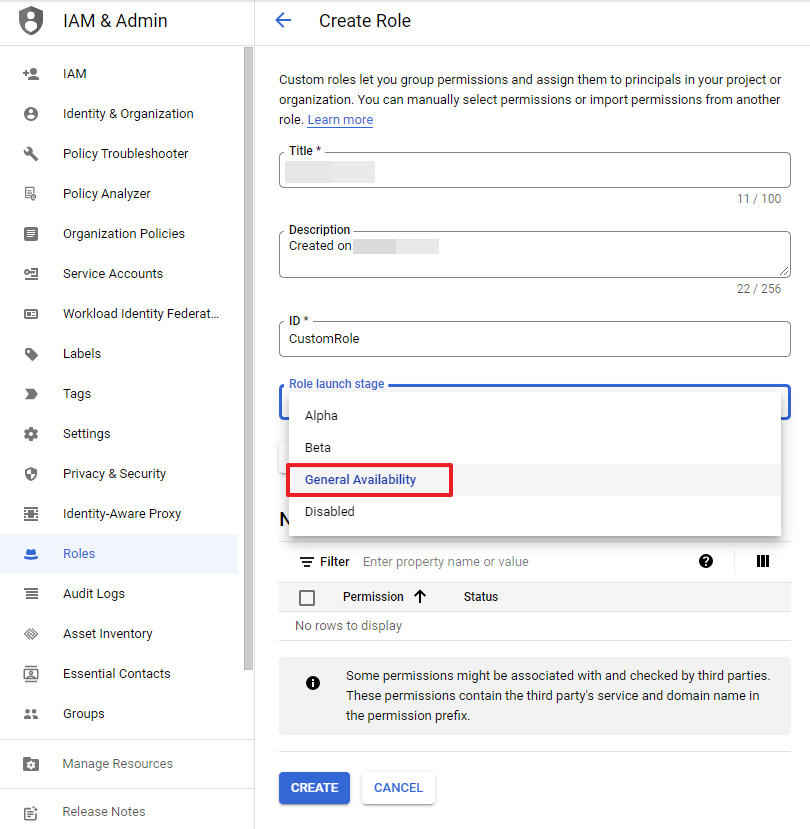
④ Click the [ADD PERMISSIONS] button and select Compute Admin from the Filter permissions by role drop-down list. And then search and select compute.instances.start and compute.instances.stop from the permissions list. Click the [ADD] button.
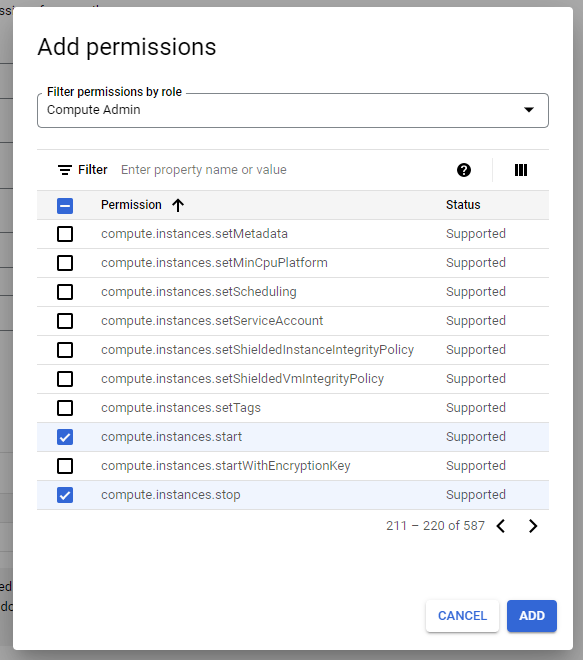
⑤ Click [CREATE] to complete creating a role.
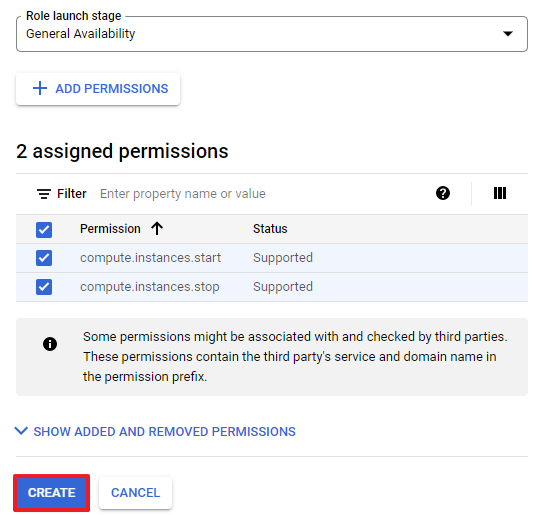
⑥ Now, go to IAM & Admin > IAM page to edit the current permissions. To edit the principal (service account) permission linked to the Resource Scheduler menu, click the pencil icon on the right.
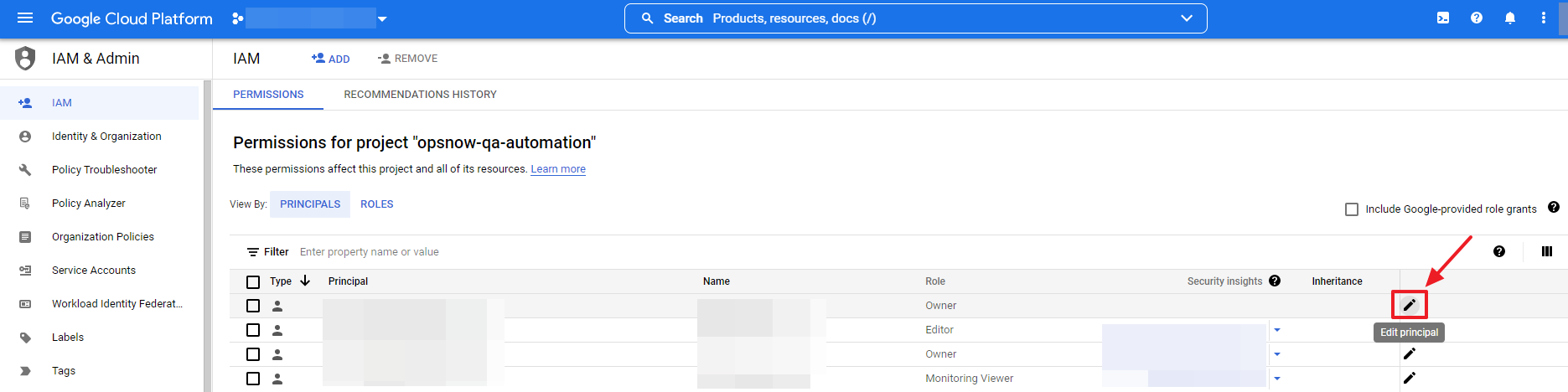
⑦ Click [ADD ANOTHER ROLE] and select Custom for the Select a role field and then select the created Role.
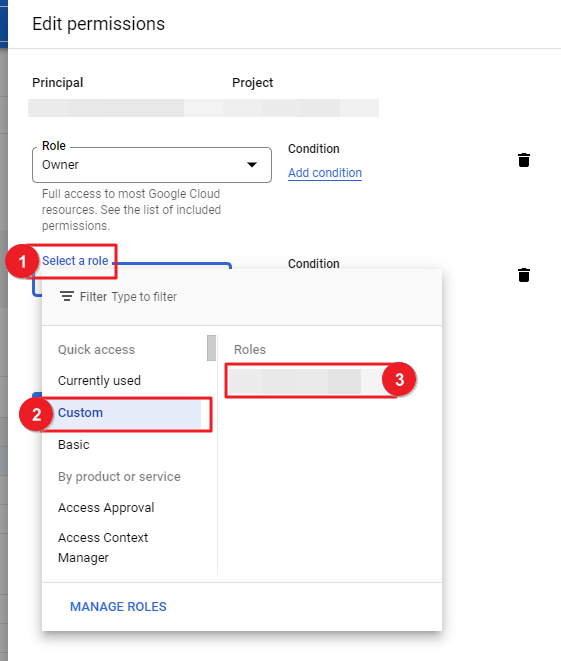
⑧ All required permission settings are now completed.
Create Resource Schedule
This section explains how to create a Schedule to start or stop the instances whenever you want.
① Go to Asset Management > Resource Scheduler > Schedule tab, and click Create.
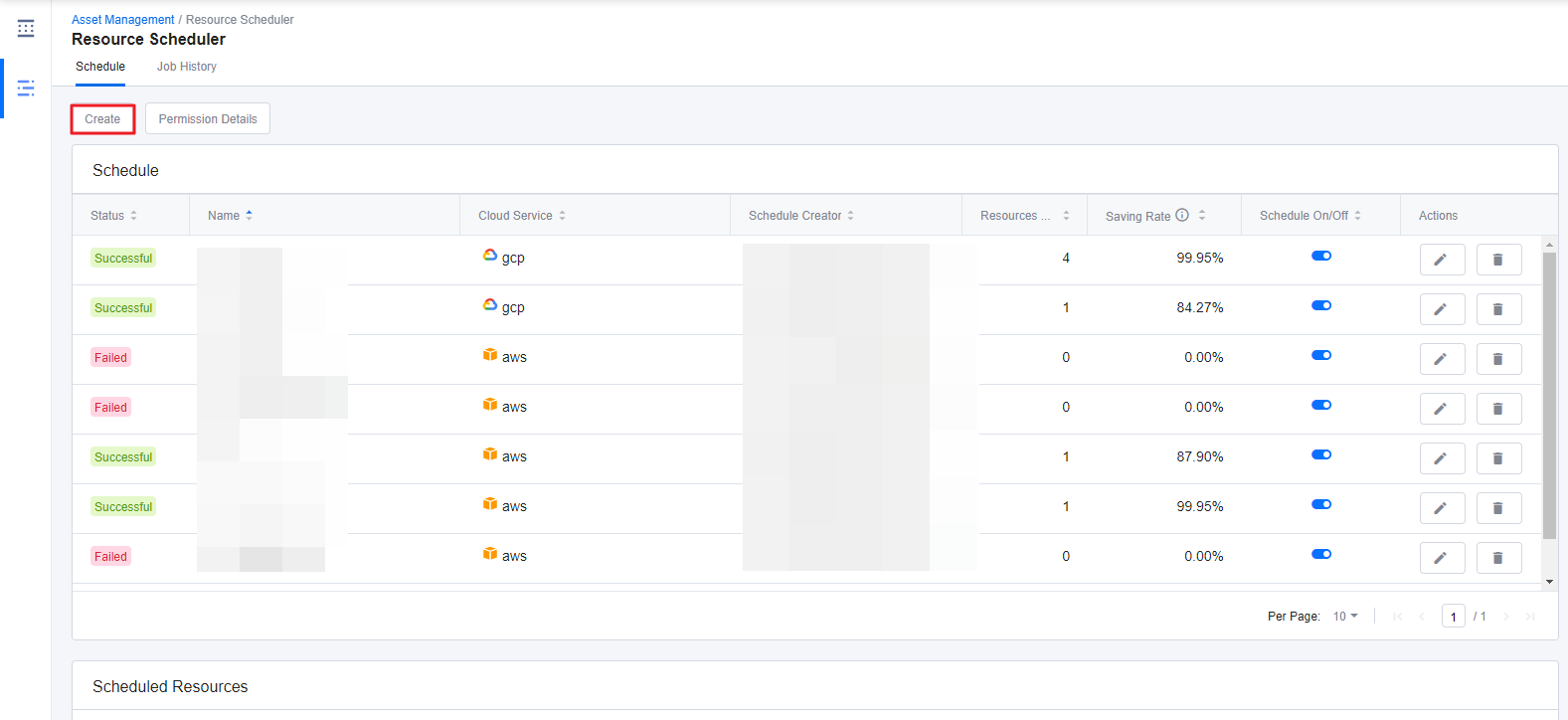
② Enter a Name, without any space, and select a Cloud Service Provider as well as a Resource Type for this schedule.
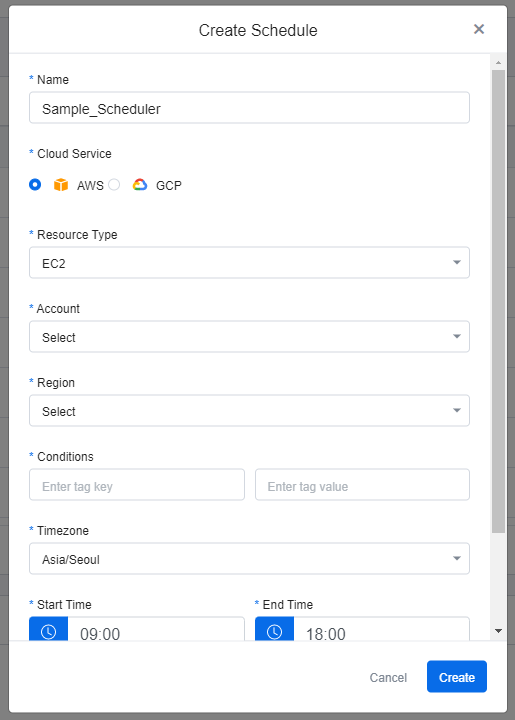
③ Fill in all items as they are required to create a schedule.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Account/Project | Registered accounts on the Cloud Accounts of the Service Portal are provided in the dropdown options. Select the cloud account alias. |
| Region | Select a region for the resource. |
| Conditions | Enter value and key, which are the conditions for this schedule. For AWS resources, enter tag key and tag value. For GCP resources, enter label key and label value. Only the resources matching the given key and value are subject to this schedule. The AWS tags can be applied in the Service Portal > Tag Assistant. |
| Timezone | Select a timezone. |
| Start and End Time | Enter the start and end time for the Scheduler. You can either enter the time directly or click the Clock icon to select the time. When you are setting the time for the schedule, you can only enter the time in H:mm form. You cannot enter any other special characters or letters here. |
| Days | Select one or more days that you want the Schedule to run. |
💡 Go to Tag Assistant Guide for more information.
④ Click Create to create a new Schedule.
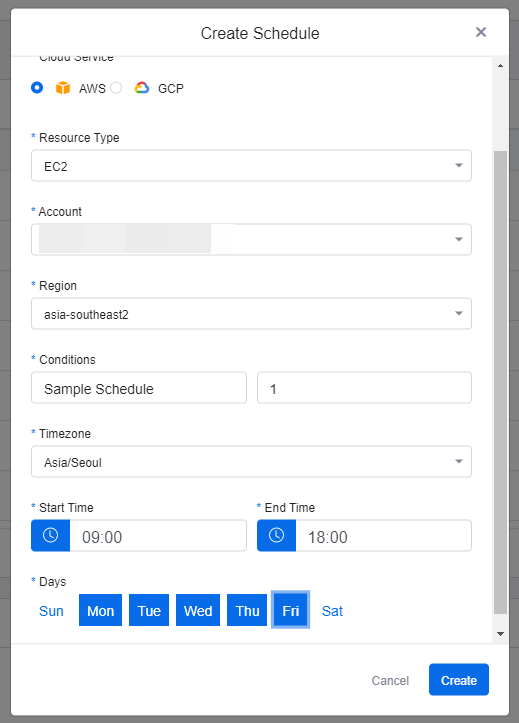
View Scheduled Resources
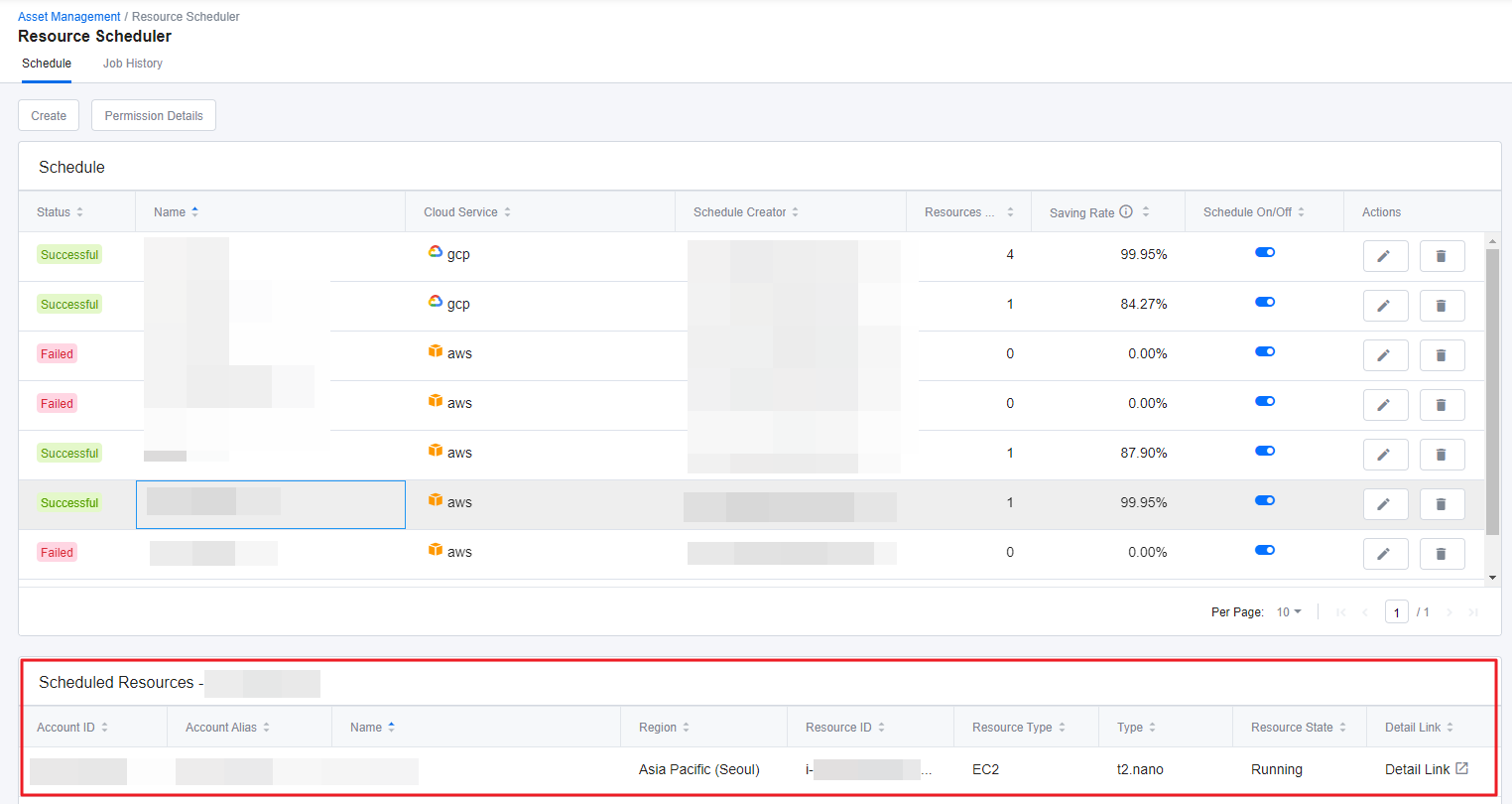
This section explains how to view the created schedules and the scheduled resources.
① Click a schedule from the list on the Schedule tab. If the number of scheduled resource is 0, then no resources are shown in the Scheduled Resources table.
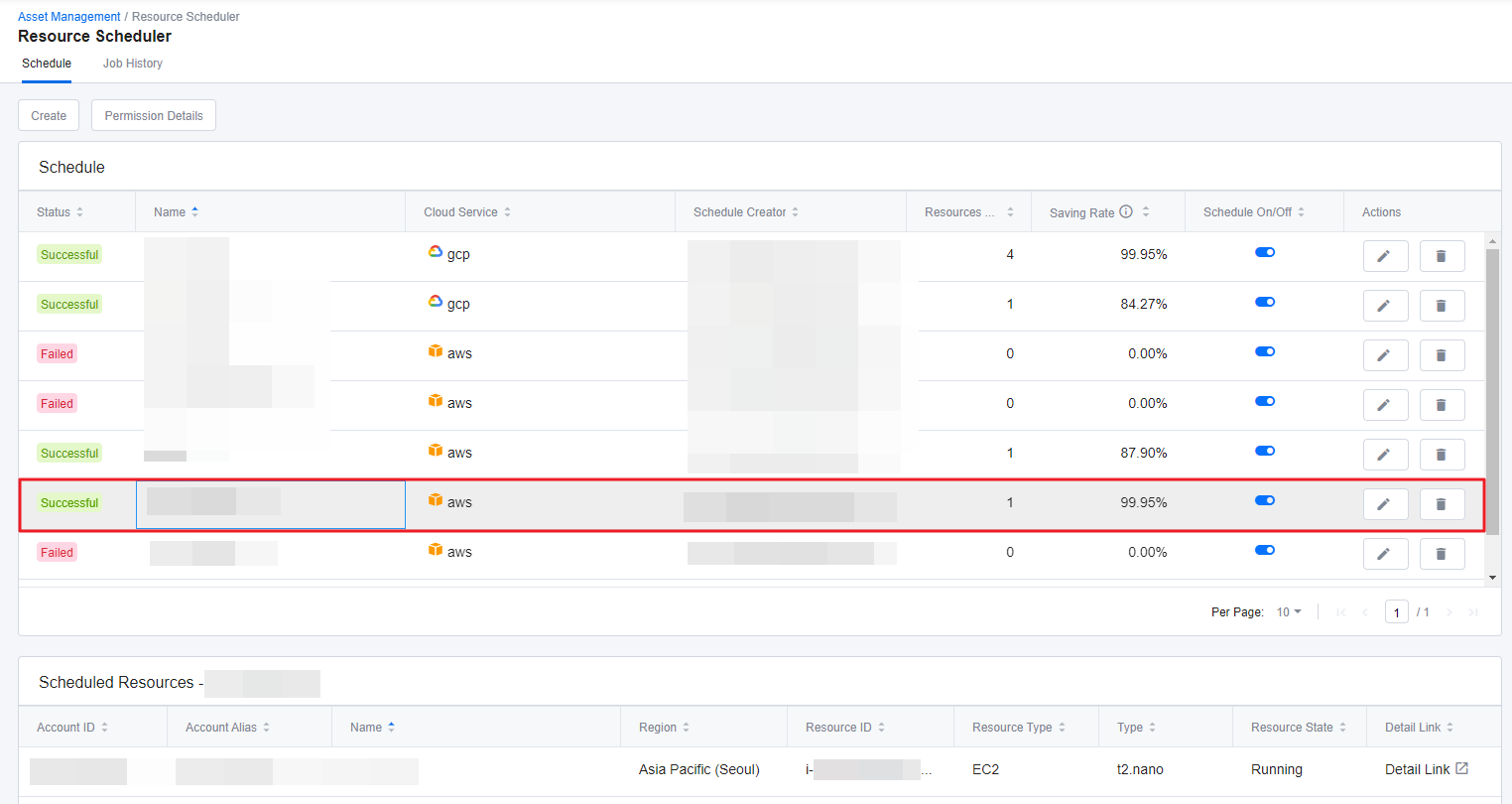
② You can view Account/Project ID, Account/Project Alias, Schedule Name, Region, Resource ID, Resource Type, Instance Type, and the resources’ current State under the Scheduled Resources table. If you want to view more details about the resource, click Detail Link.
View Schedule History
This section explains how to view the history of previously executed schedules.
① Go to Job History tab.
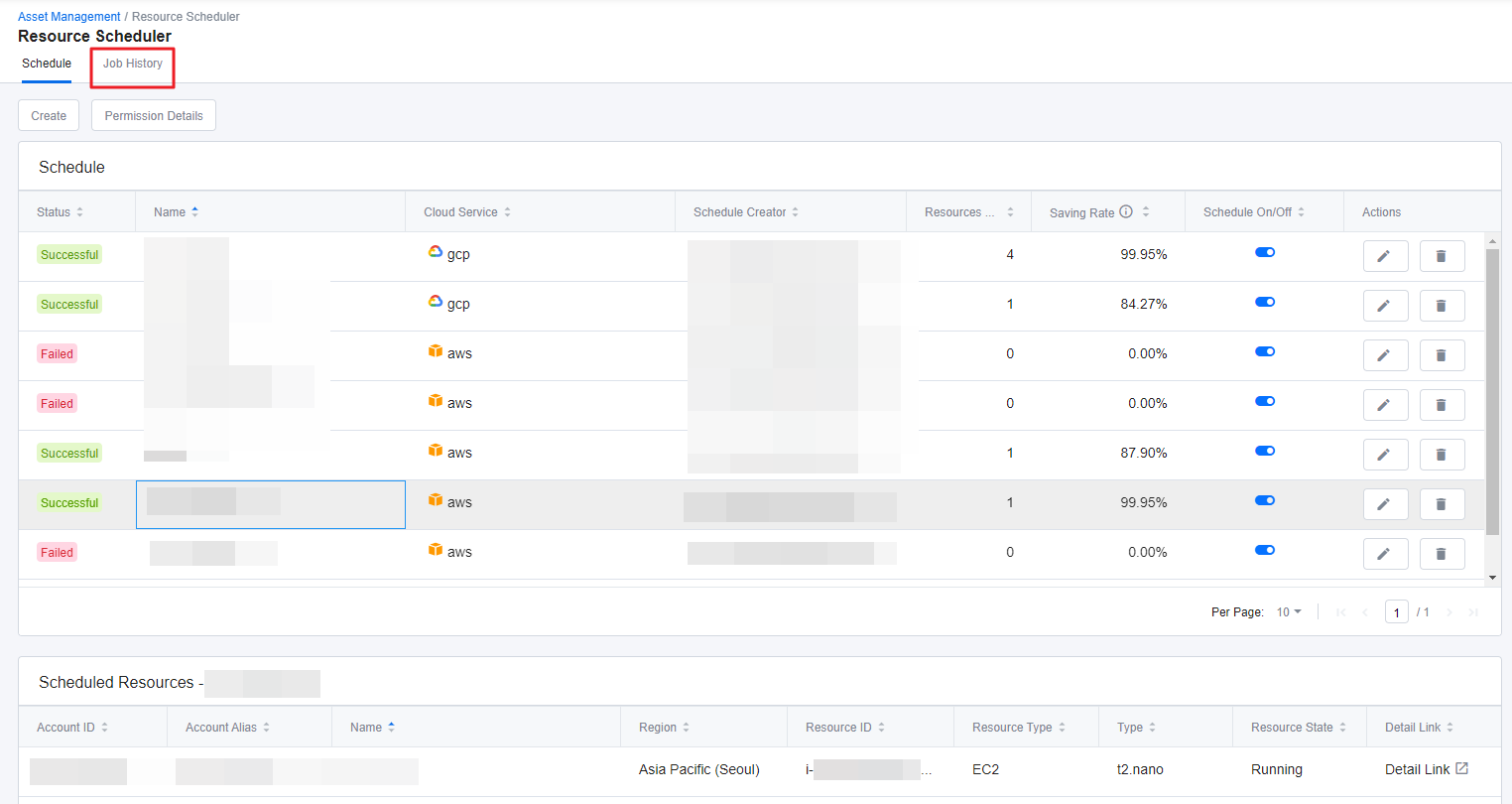
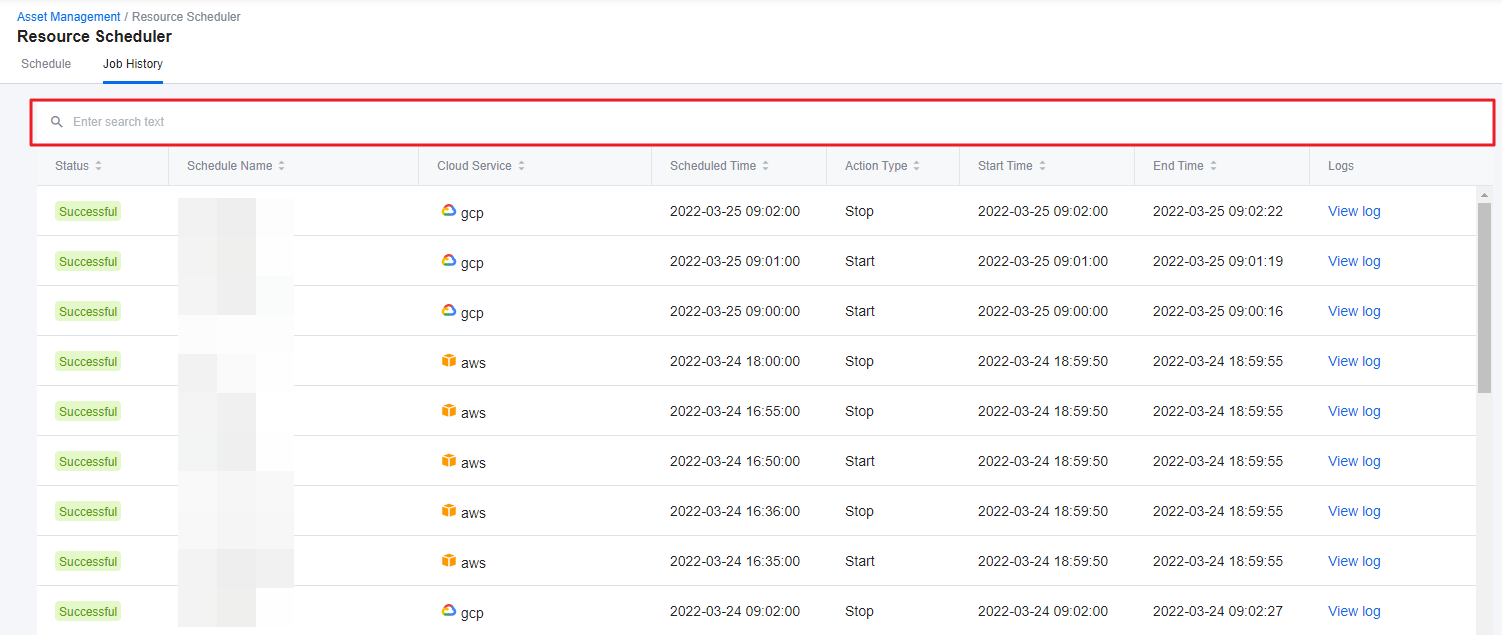
② You can view all of the executed schedules when the resource was Started or Stopped, and you can also search for specific job history from the top of the page.
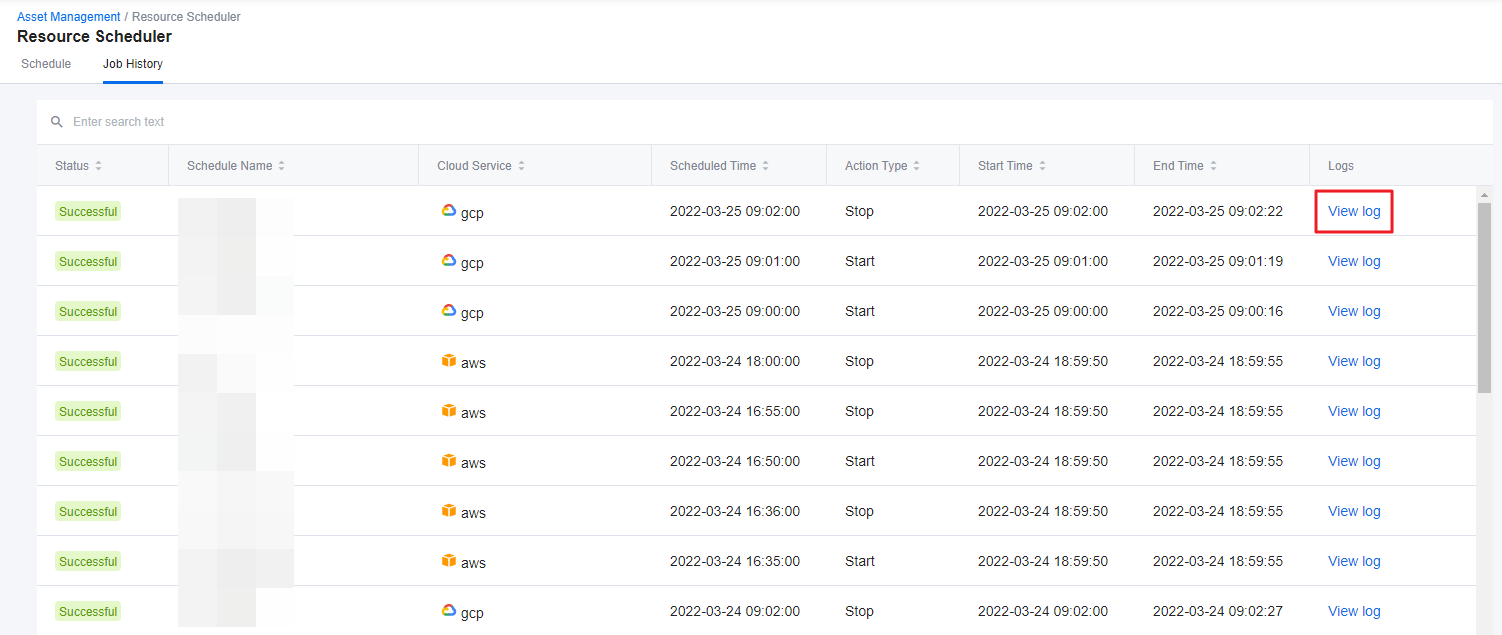
③ Click View log to see refined and summarized version of the job log.
Turn On and Off Schedule
This section explains how to turn on or off the Scheduler.
① Select a resource schedule from the Schedule tab and click the On/Off toggle switch.
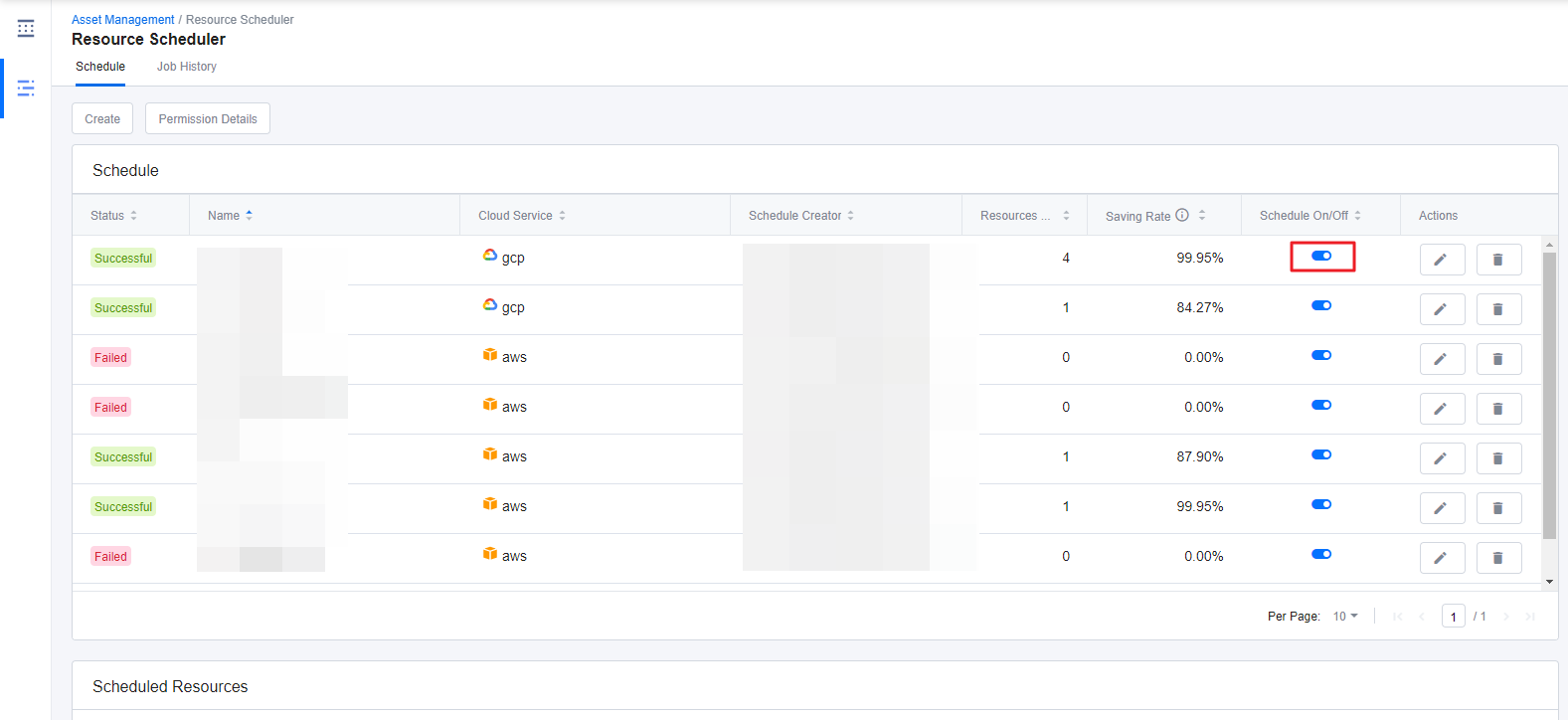
② When the schedule is running or on, it displays blue color, and when it is not, it displays gray color, meaning the schedule is currently off.
Modify Resource Schedule
This section explains how to modify a created resource schedule. Only the Schedule Creator who created the schedule can modify it.
① Select the schedule that you want to modify and click the [Pencil] icon.
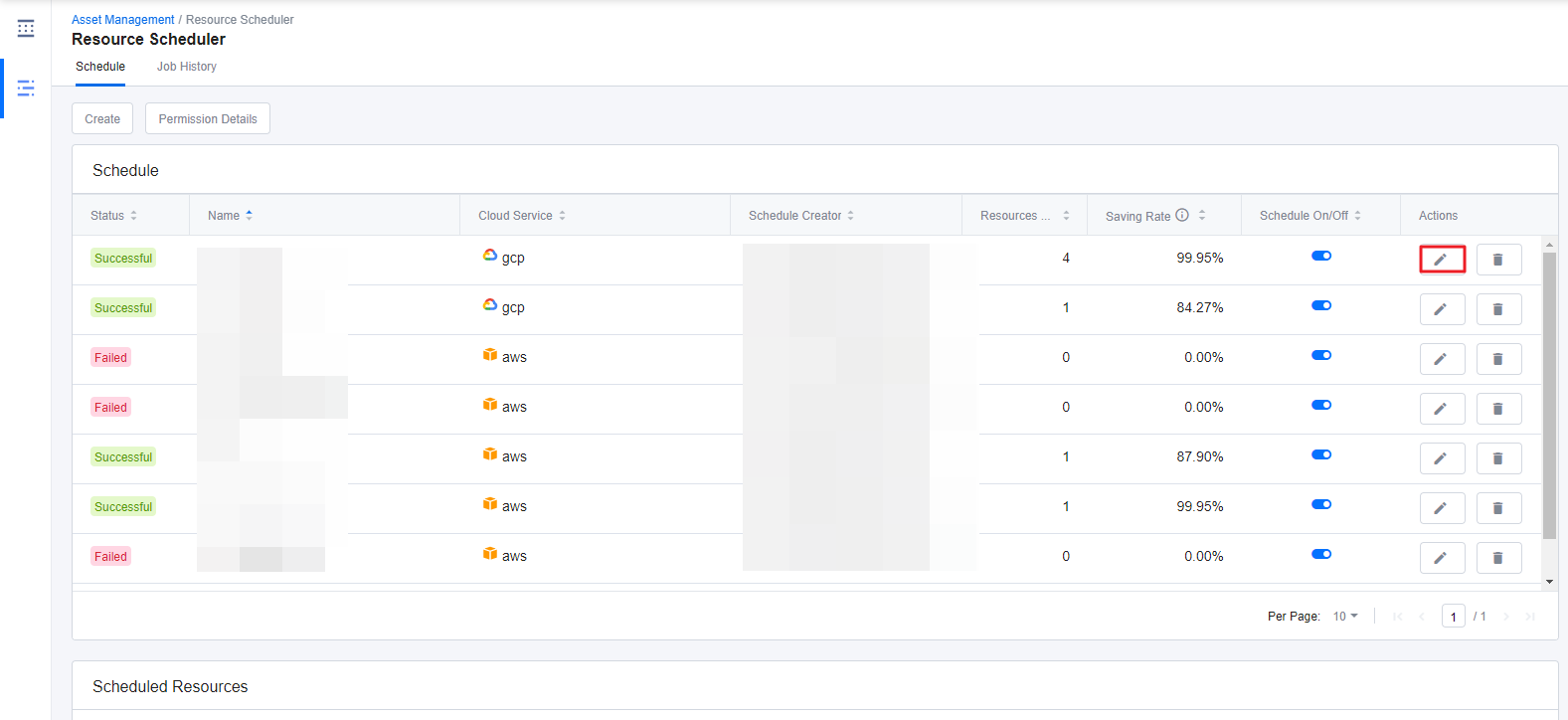
② Modify Schedule window that looks exactly the same as the Create Schedule appears. Make changes and click [Save] on the lower right corner.
Delete Resource Schedule
This section explains how to delete a created resource schedule. Only the Schedule Creator who created the schedule can delete it.
① Select the schedule that you want to delete and click the [Trash bin] icon.
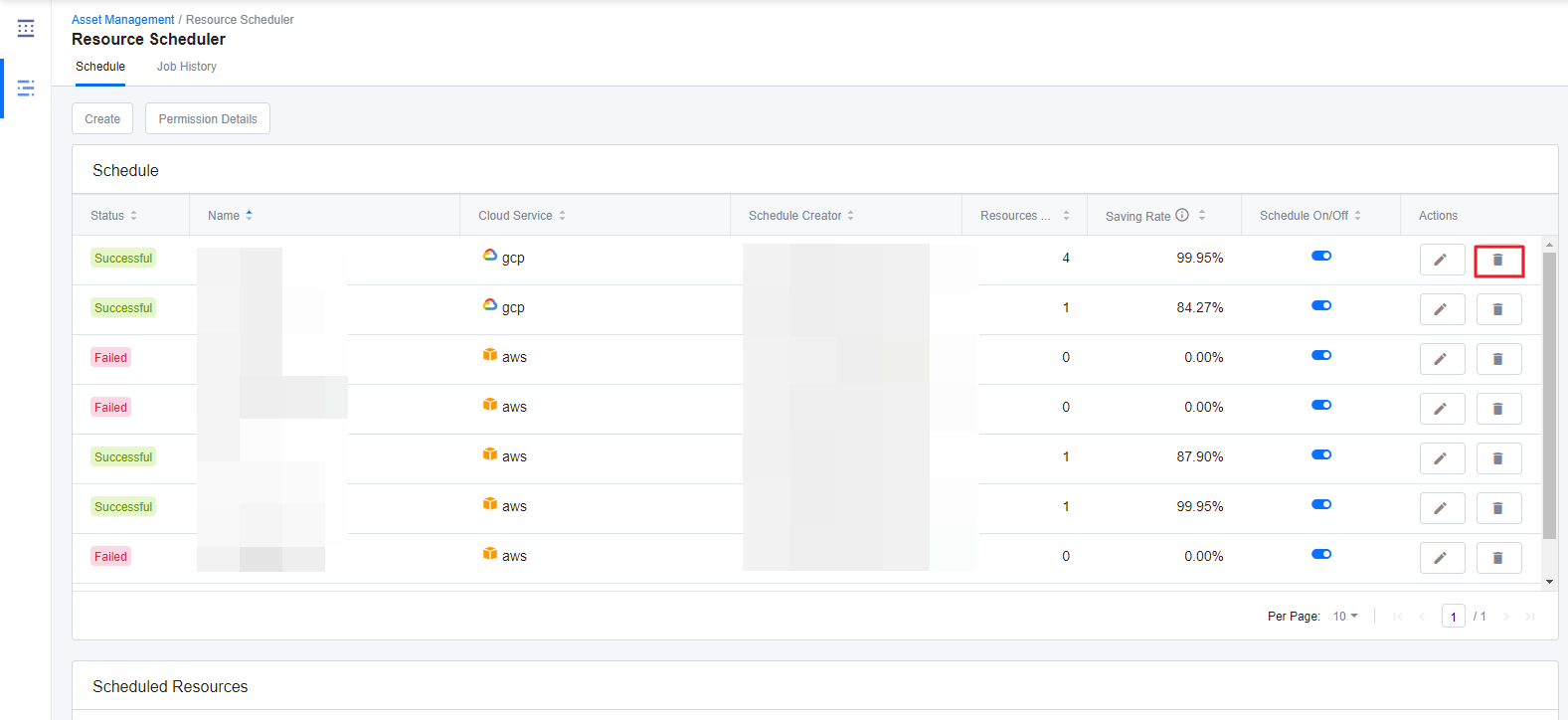
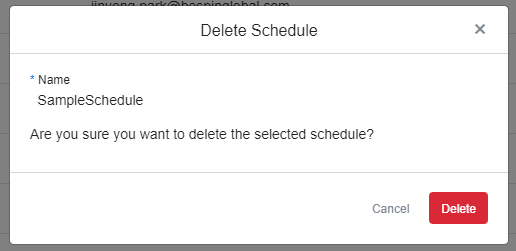
② A window appears to confirm the delete action. Click [Delete] to go ahead and delete the schedule.
Tag Assistant
Asset Management > Tag Assistant
Tags enable you to categorize your resources in different ways, for example, by purpose, owner, or environment. You can add tags to resources like account, region, and product, and can quickly identify and filter a specific resource based on tags that you’ve assigned to it. Tag Assistant is the right tool for you to add tags to resources easily.
Tag Assistant allows you to add and delete tags on resources directly in Service Portal instead of accessing AWS console to the job. In AWS Management Console, you need to log in with each account to edit tags for each product. Therefore, it is a time consuming process for tagging resources and can cause human error. Whereas Tag Assistant allows you to add or delete tags on multiple accounts, regions, and resources, and easily manage tag history as well.
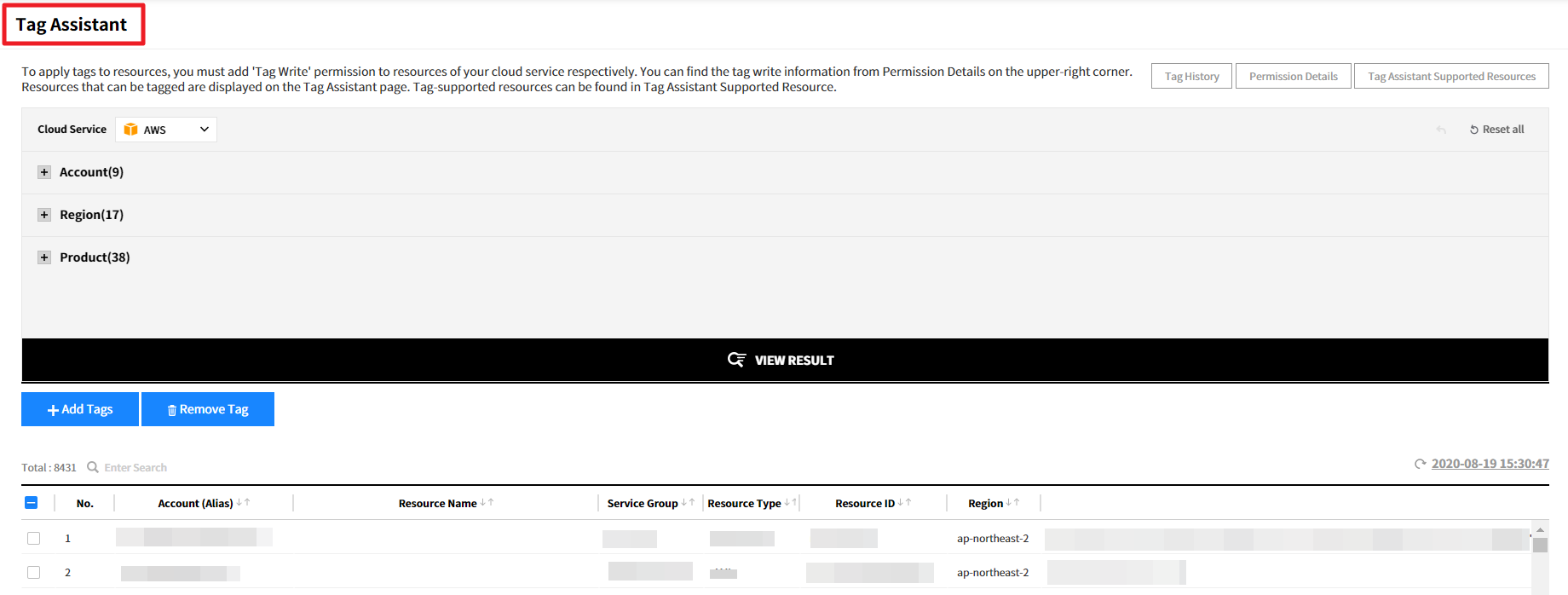
Add Permission - AWS
To use Tag Assistant, you need a Write Tag permission. To add the permission, copy the JSON policy statement provided by Permission Details of Tag Assistant and paste it in AWS Management Console. Before you get started working with Tag Assistant, be sure you have add Write Tag permission to accounts respectively.
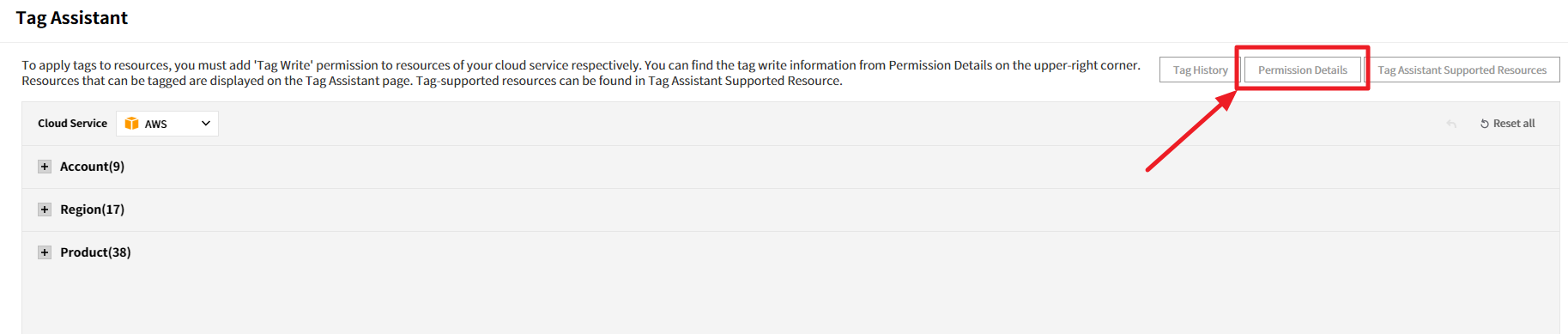
There are two ways to add permission.
There are two ways to add permission from: IAM Access Key or Cross-Account Access. To add permission, choose one of the methods and proceed depending on whether you used IAM Access Key or Cross-Account Access when you register cloud accounts.
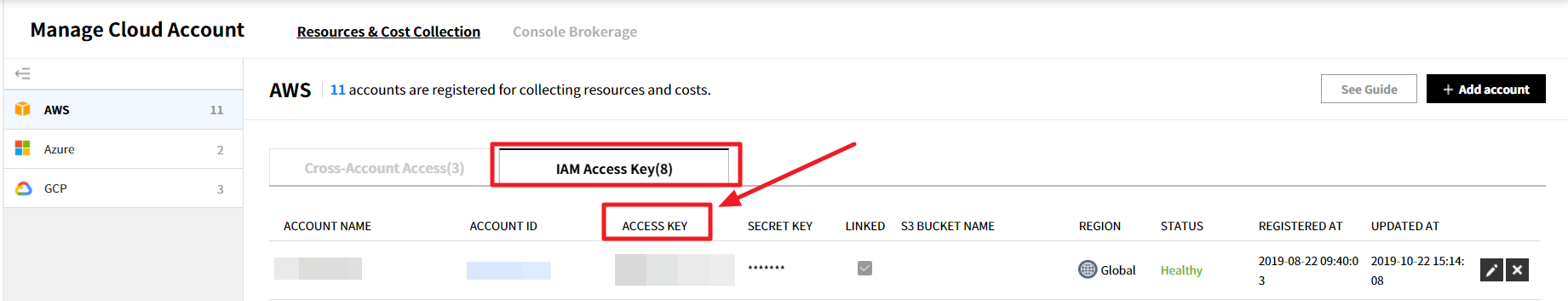
IAM Access Key
① Copy an ACCESS KEY of an account you want to grant permission from Service Portal > Cloud Account > IAM Access Key tab.
② Click Users in the left pane of the IAM menu in the AWS Management Console.
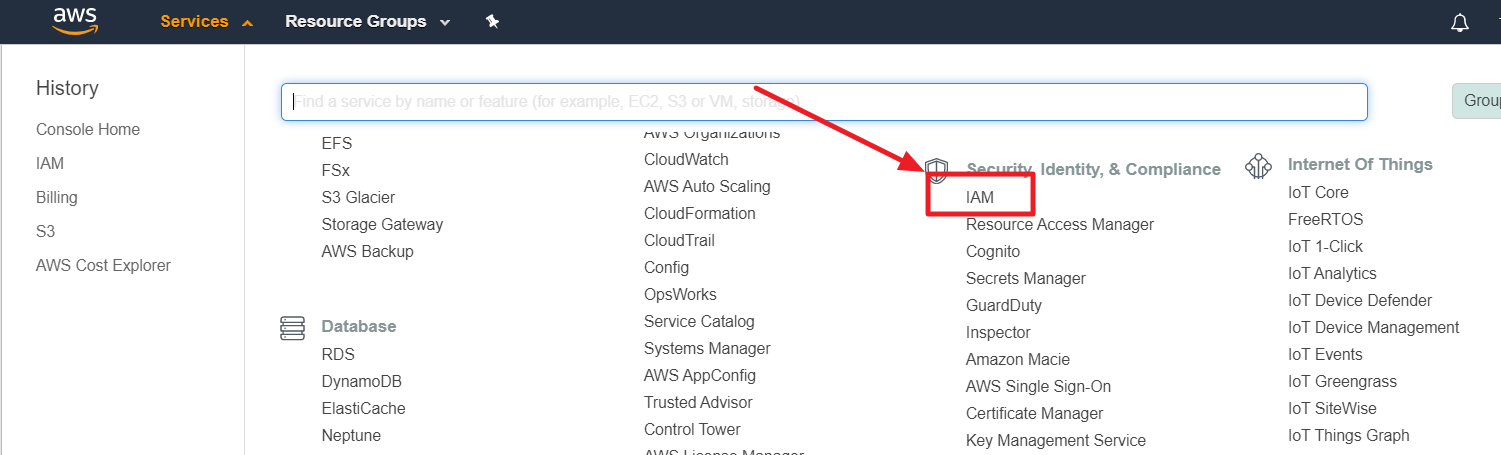
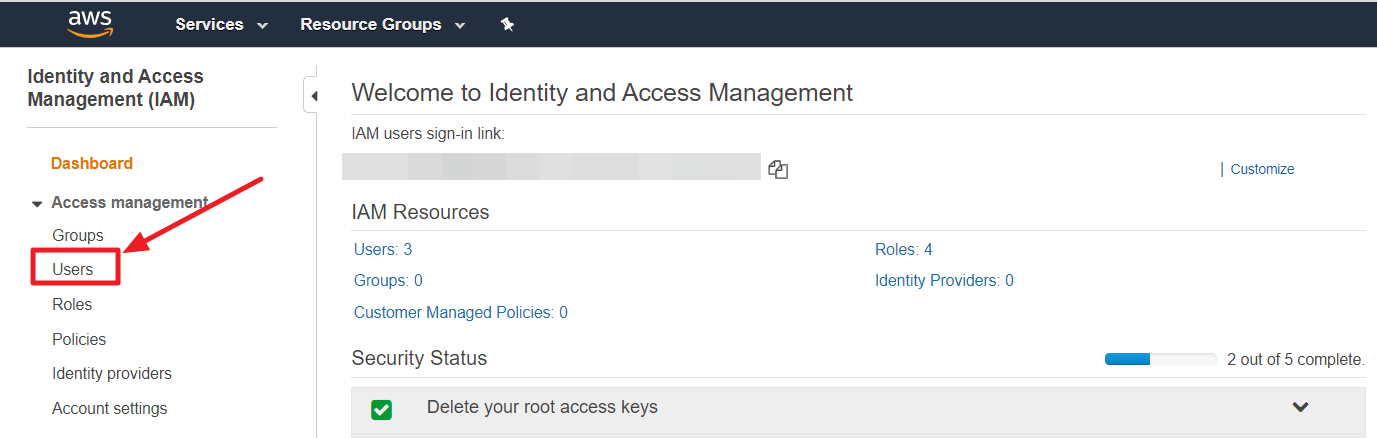
③ Search a user by using the ACCESS KEY copied from Service Portal.
④ Select a user from the list and click the [Add Permissions].
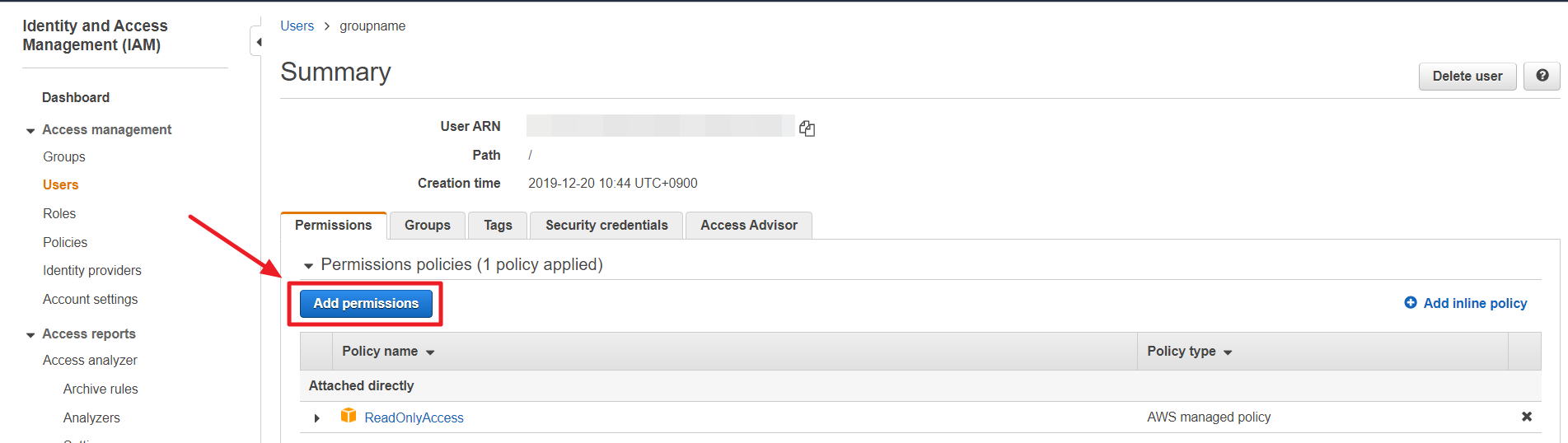
⑤ In Grant Permission page, select Attach existing policies directly.
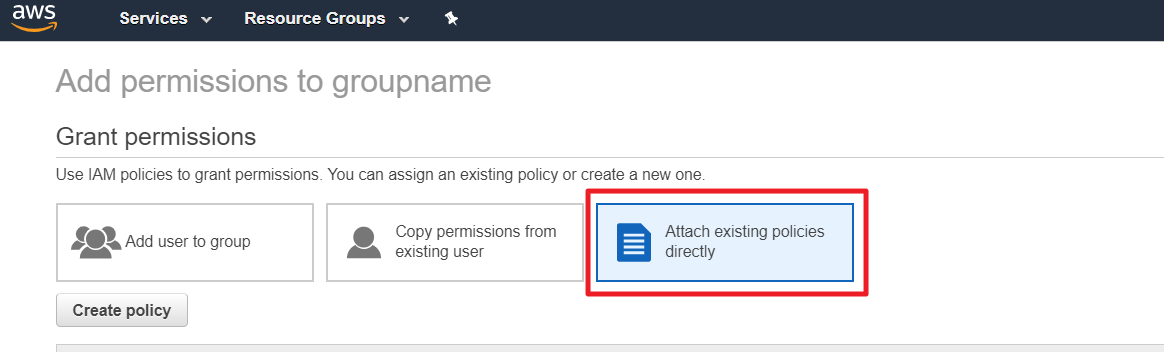
⑥ Click [Create policy] button and select JSON tab.
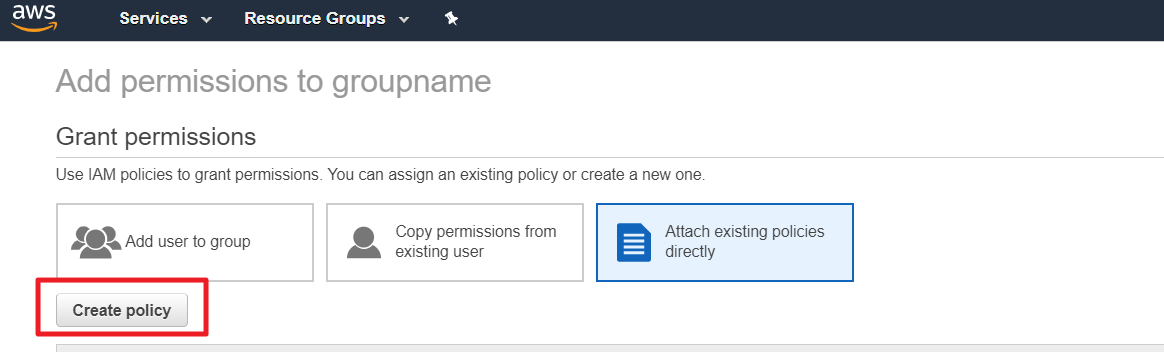
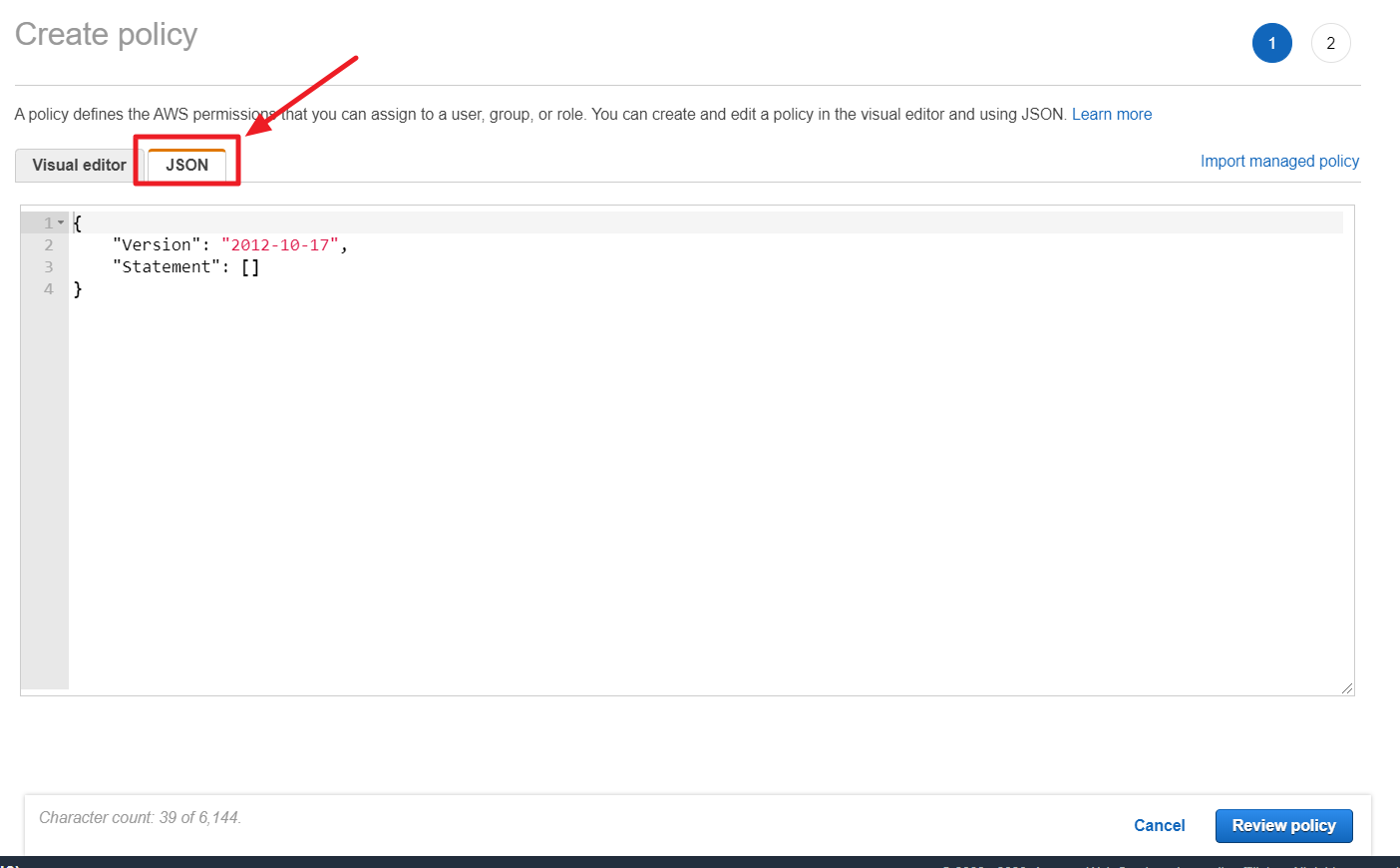
⑦ In Tag Assistant console, click the [Permission Details] and then copy the JSON policy statement from the pop-up window.

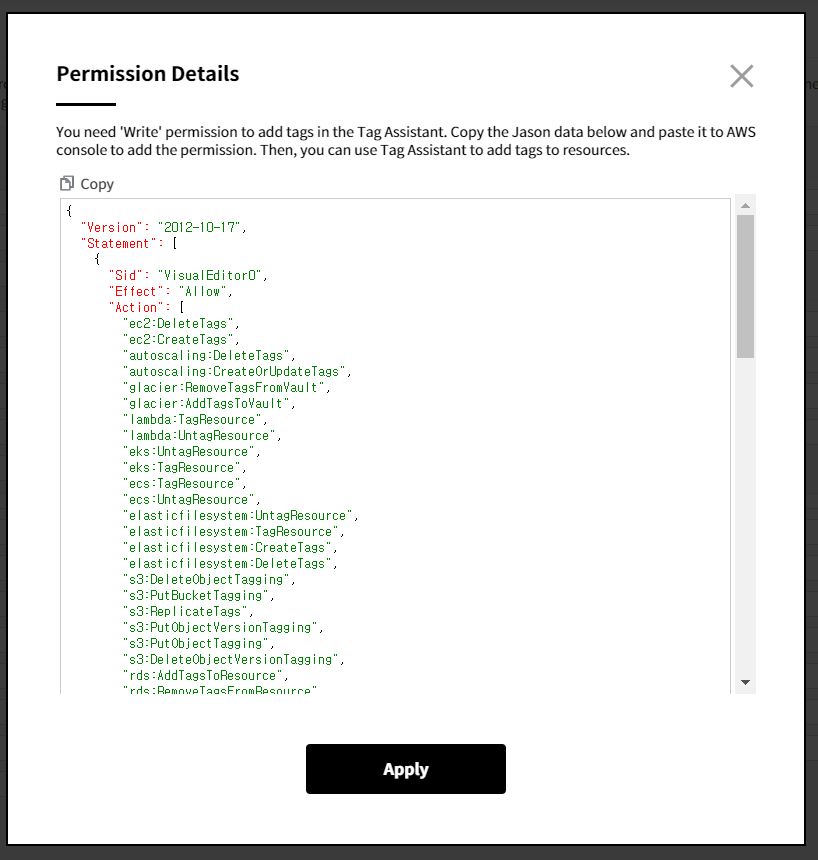
⑧ Paste the copied JSON data to the JSON tab in the AWS Console and then click the [Review Policy] button.
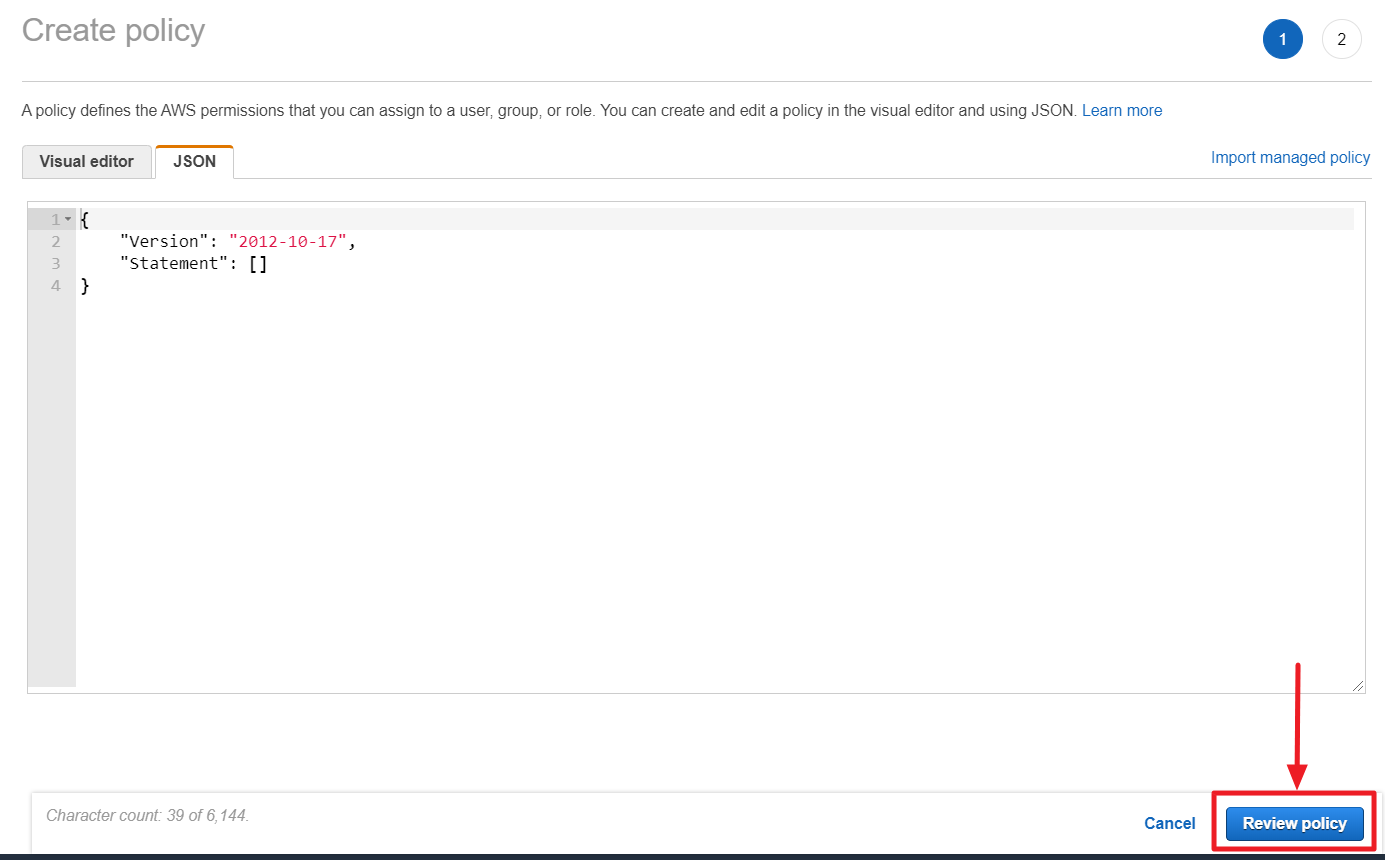
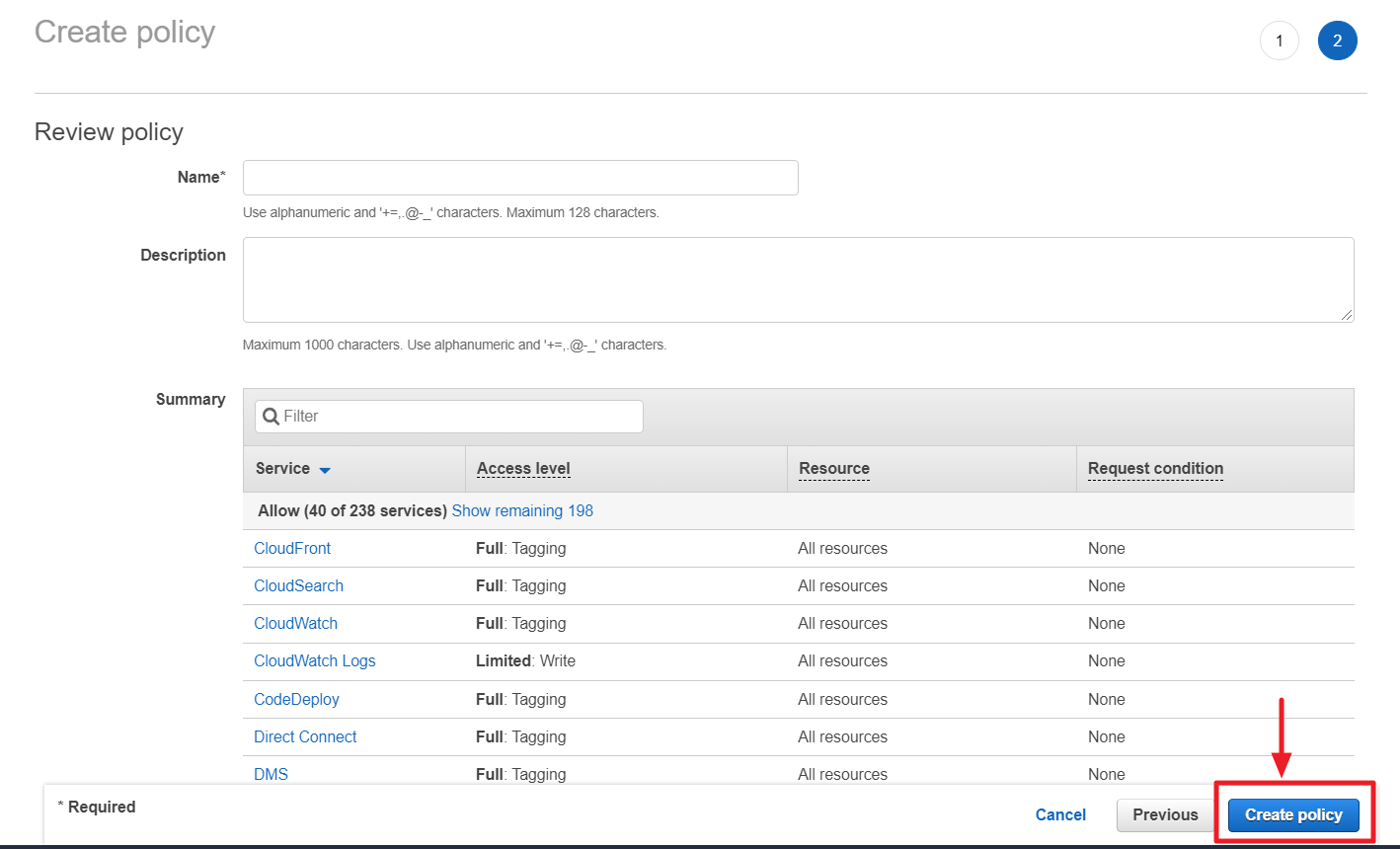
⑨ Click [Create policy] button after entering required values like name and description.
Cross-Account Access
① Copy a ROLE NAME of an account you want to grant permission from Service Portal > Cloud Account > Cross-Account Access tab.
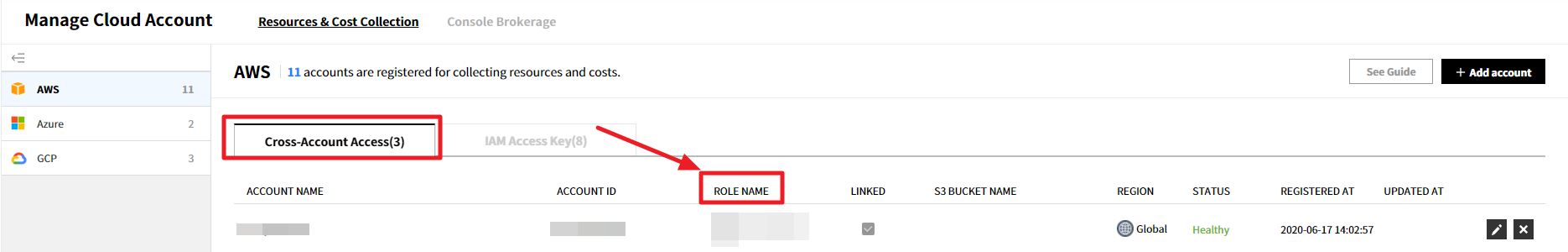
② Click Roles in the left pane of the IAM menu in the AWS Management Console.

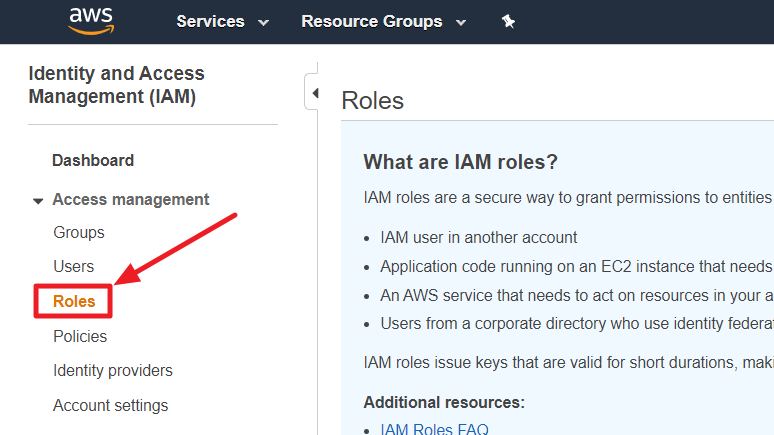
③ Search a user by using the ROLE NAME copied from Service Portal.
④ Select a role from the list and click the [Attach policies].
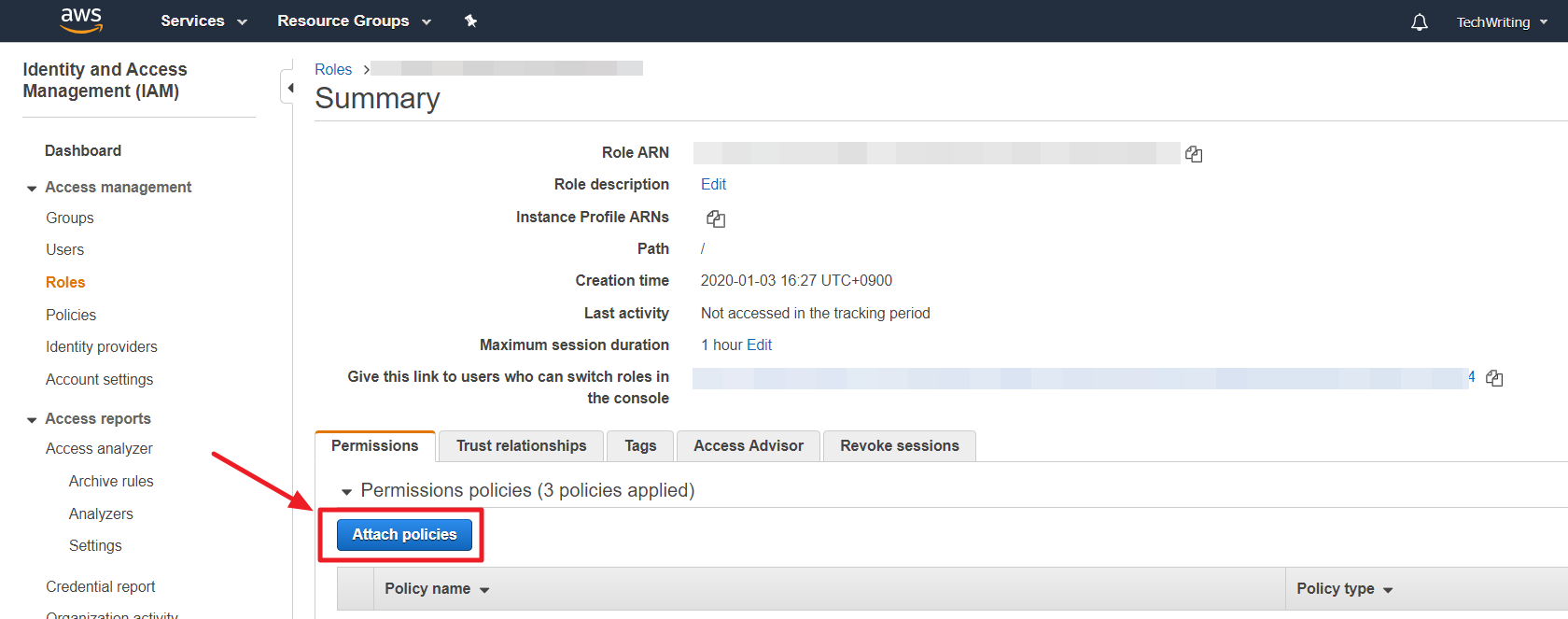
⑤ In Attach Permission page, select [Create policy].
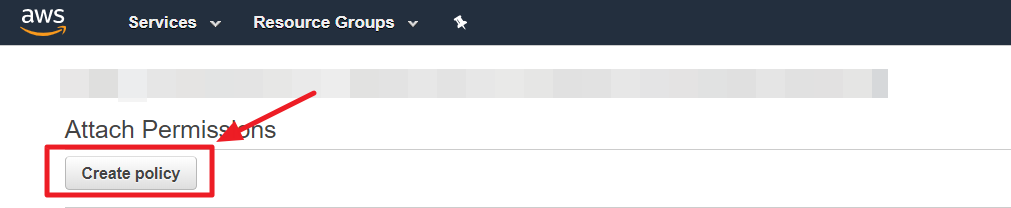
⑥ In Create Policy page, choose JSON tab.
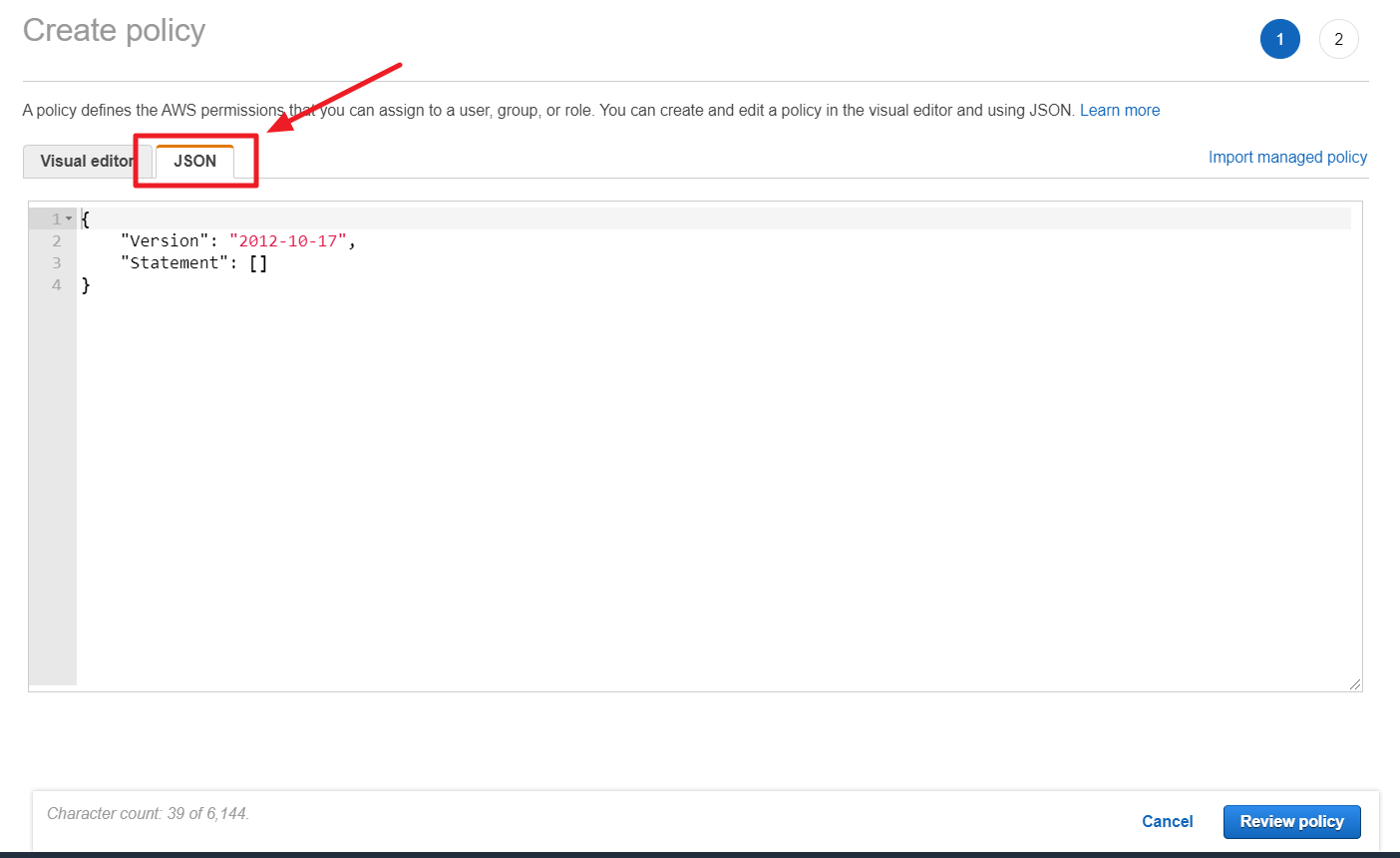
⑦ In Tag Assistant console, click the [Permission Details] and then copy the JSON policy statement from the pop-up window.


⑧ Paste the copied JSON data to the JSON tab in the AWS Console and click the [Review Policy] button.

⑨ Click [Create policy] button after entering required values like name and description.

Add Permission - GCP
To add labels to Google Cloud resources through Tag Assistant, you must add permissions on the Google Cloud console first.
① Select GCP for the cloud service and click [APPLY].
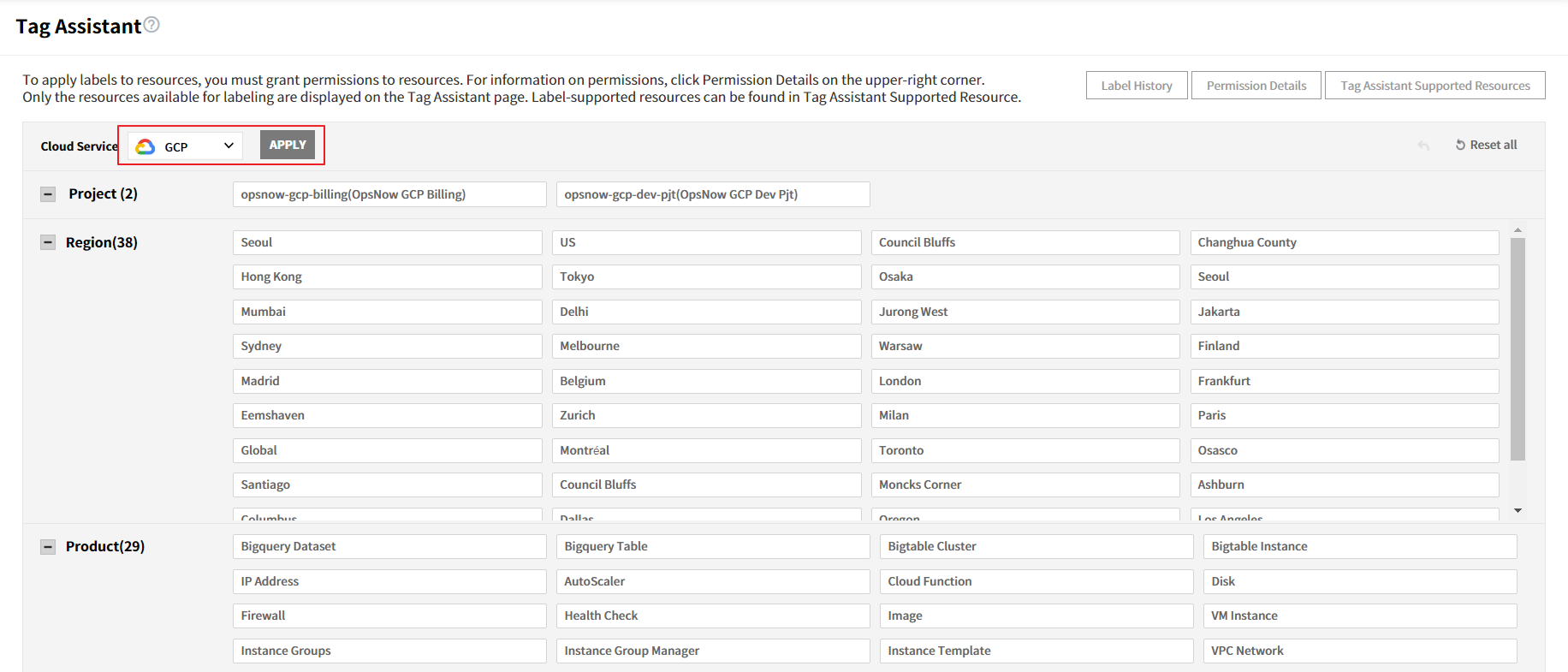
② Click [Permission Details] on top right and check permissions to add.
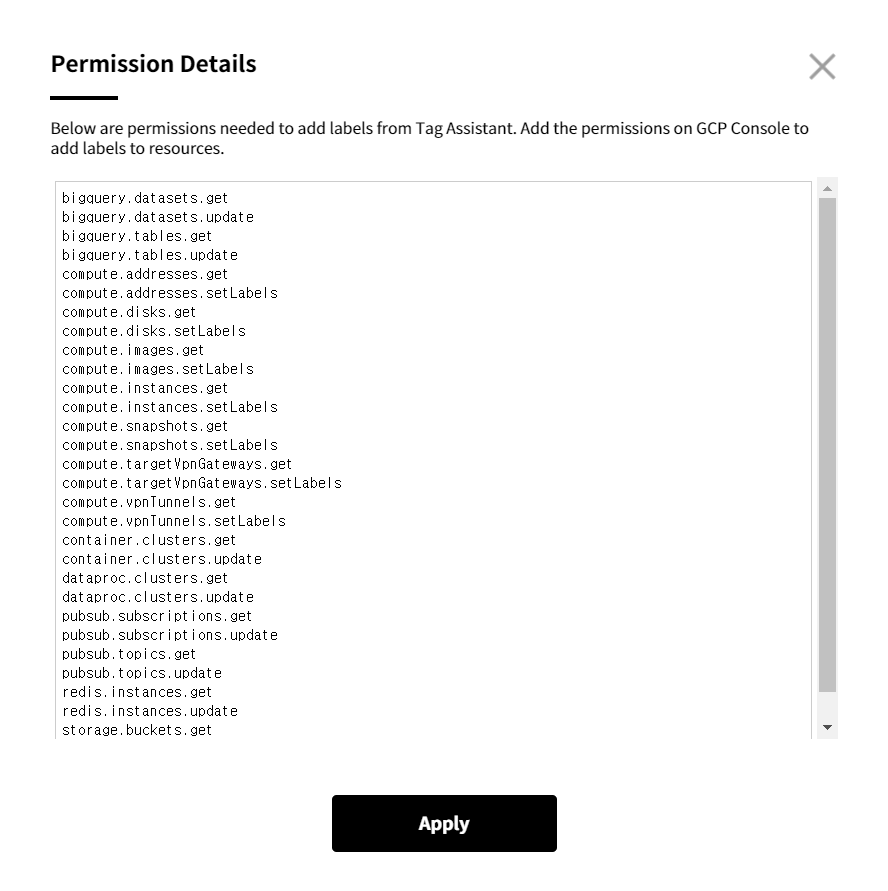
③ Log in to the Google Cloud console on a new window, go to IAM & Admin > Roles and click [CREATE ROLE].
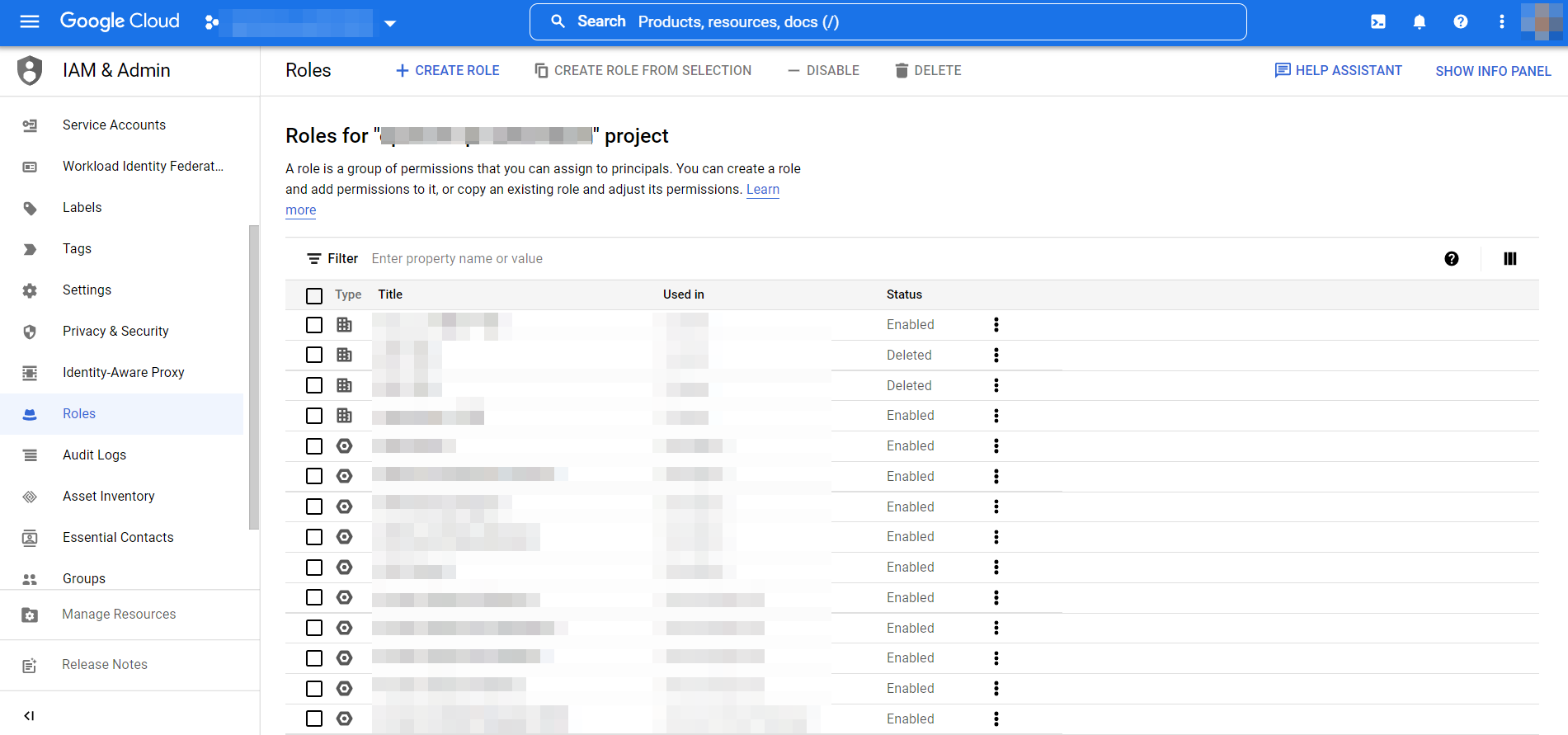
④ Enter a title and click [+ADD PERMISSIONS].
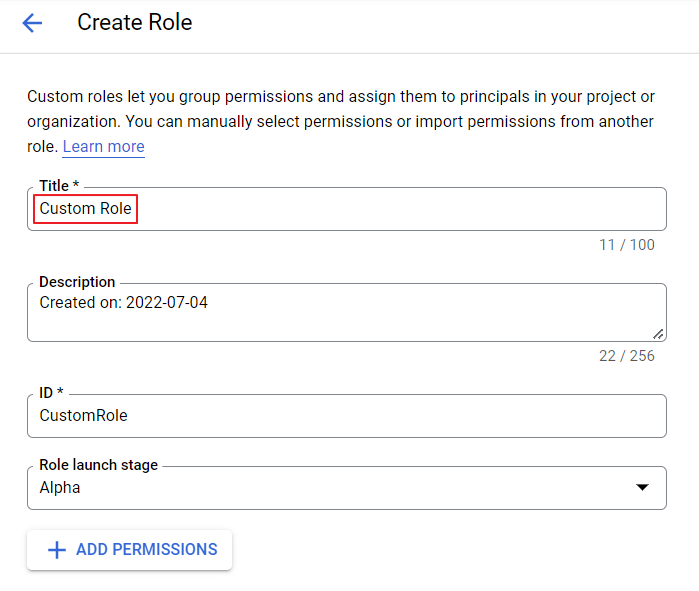
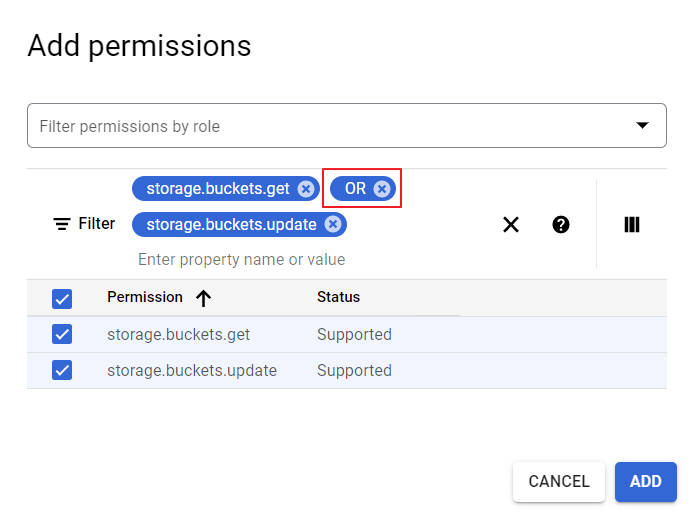
⑤ Enter permissions on the Permission Details page of Tag Assistant. Add them one by one without omission.
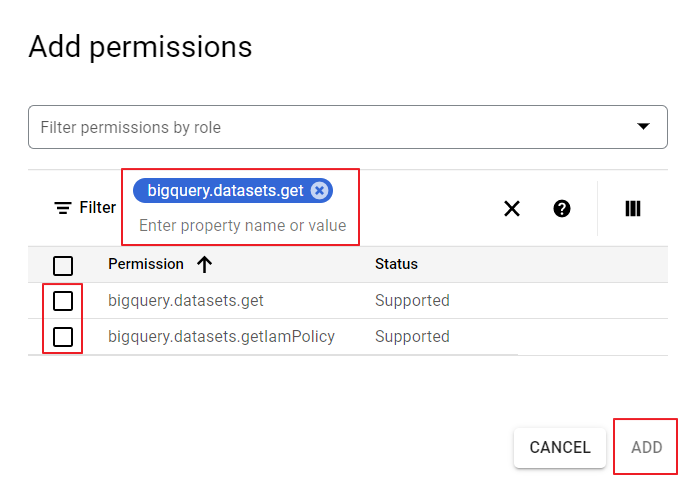
- Use OR as a classifier to have permissions displayed on the list below. If you copy and paste all permissions at once, the [Add] button is not activated and you will not be able to add them.
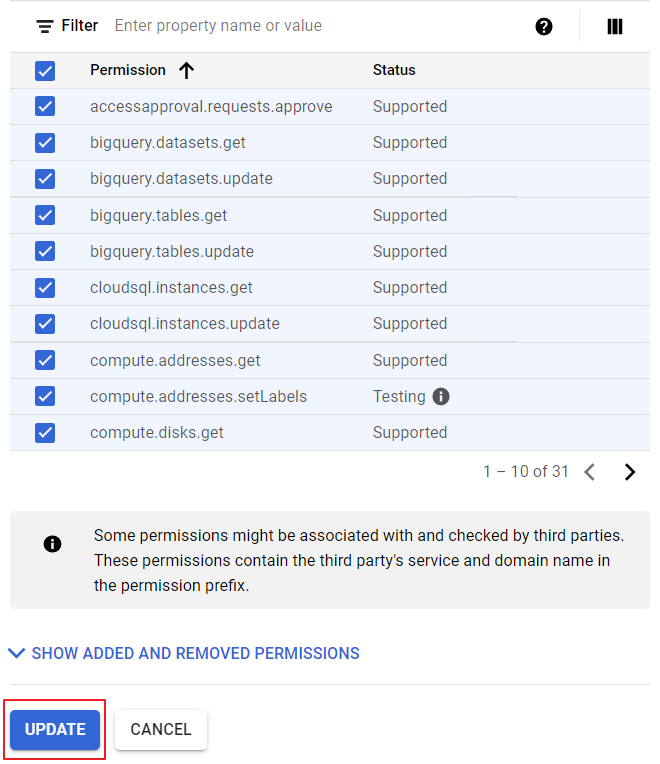
![]()
⑥ After adding all permissions, click [UPDATE] to create a role.
⑦ Click Service Accounts under the IAM & Admin tab and copy the Email address registered on OpsNow.
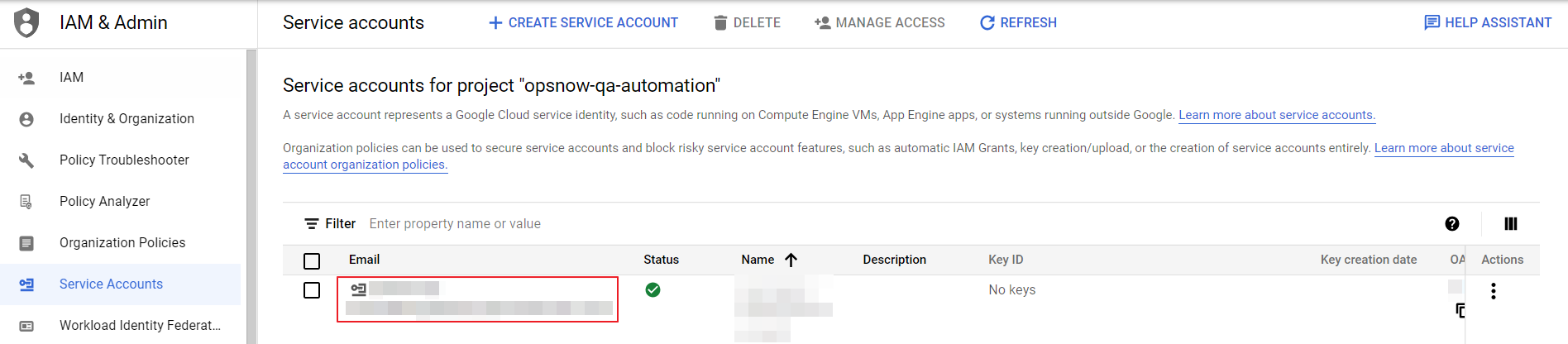
⑧ Click Manage Resources on bottom left, select the account registered on OpsNow and click [ADD PRINCIPAL] from the page unfolded on the right.
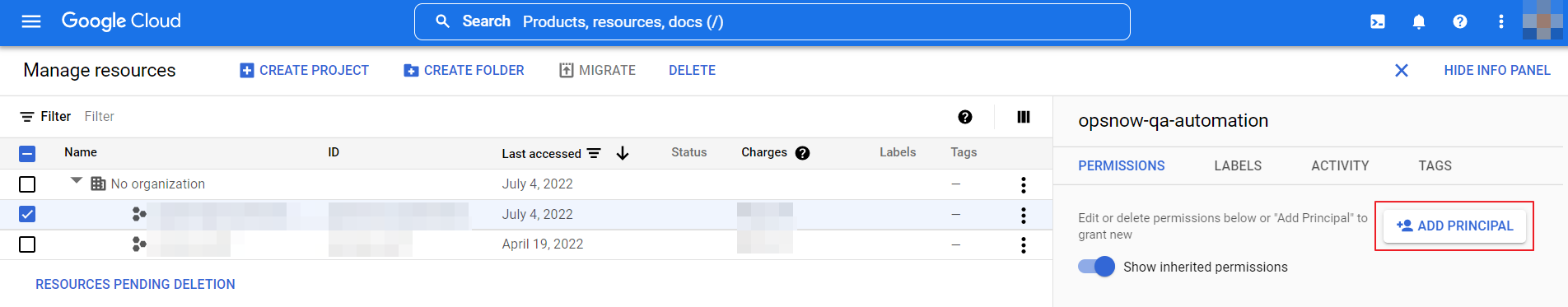
⑨ Paste the copied Email address in the New principals field, click the Select a role field below and select the role you created in Step 4-7 from the Custom filter.
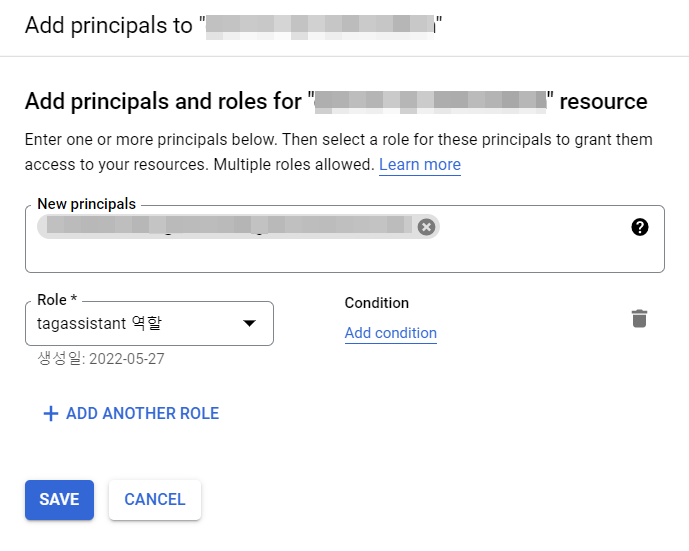
⑩ Click [Save] to have the permissions added.
Add and Remove Tags
Add Tags
① First, you can set the filter to display the resources you want on the list. On the Cloud Service dropdown menu, select a Cloud Service Provider and click [APPLY]. Currently, Tag Assistant supports AWS and GCP.
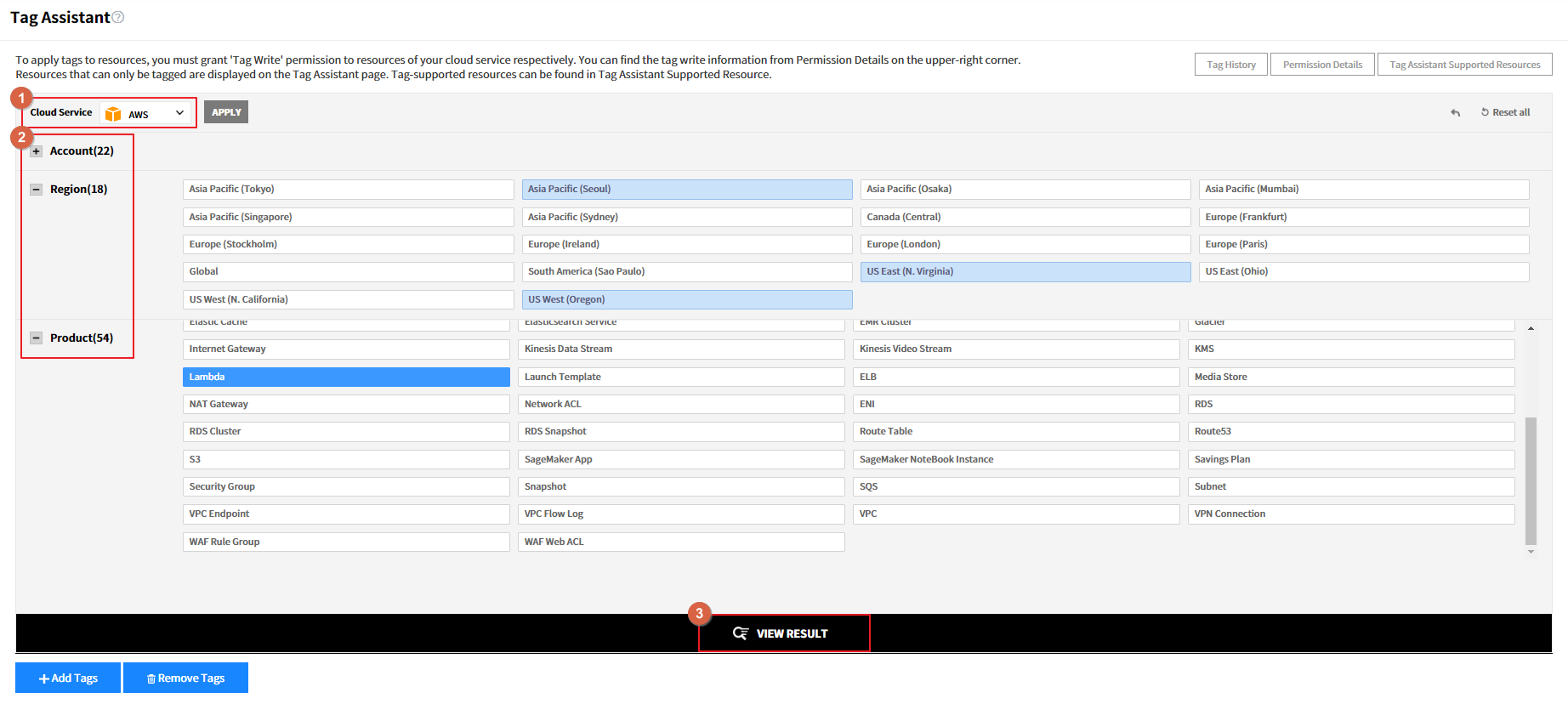
② After selecting a CSP, you can filter resources by account, region and product. If you click an item in 1 of the 3 categories, related items in other 2 categories are automatically selected and highlighted in sky blue.
③ Click [VIEW RESULT] to have your filtering condition be applied on the resource list below.
④ Go to the list and select one or more resources to add tags to and click the [+Add Tags] button.
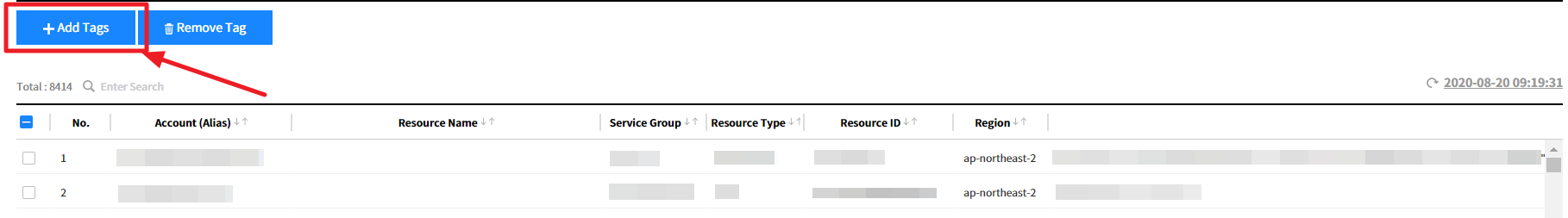
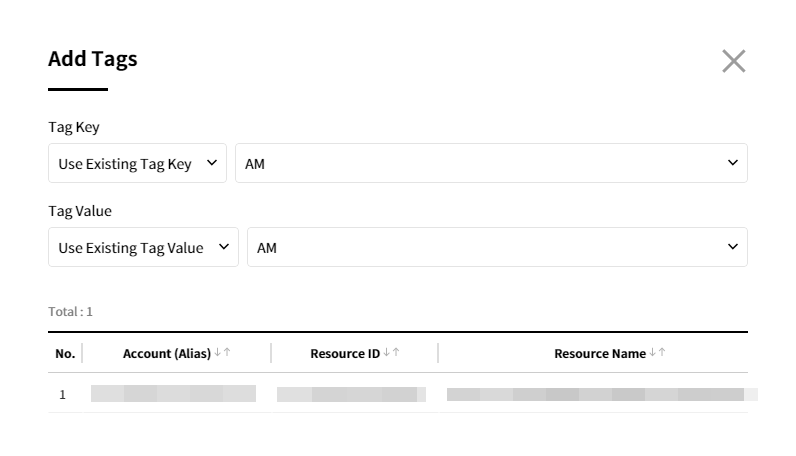
⑤ When the Add Tags pop-up appears, click the [Apply] button after selecting Tag Key and Tag Value. You can either add an existing tag key/value or a new tag key/value.
📌 Attention: Requirements for GCP tags
Unlike AWS, GCP resources have requirements for tag keys and values. Therefore, if you wish to add new tag keys and values to GCP resources, they must meet the following requirements.
• Each resource can have multiple tags, up to a maximum of 64.
• Keys have a minimum length of 1 character and a maximum length of 42 characters, and cannot be empty. Values can be empty, and have a maximum length of 42 characters.
• Keys and values can contain only lowercase alphabets, international characters (Korean, Chinese, Japanese, German, French, Spanish and Portuguese characters using UTF-8 enconding), numeric characters, underscores and hyphens.
• Keys must start with a lowercase alphabet or international character.
Remove Tags
① Select resources to delete tags from the list and click the [Remove Tags button].
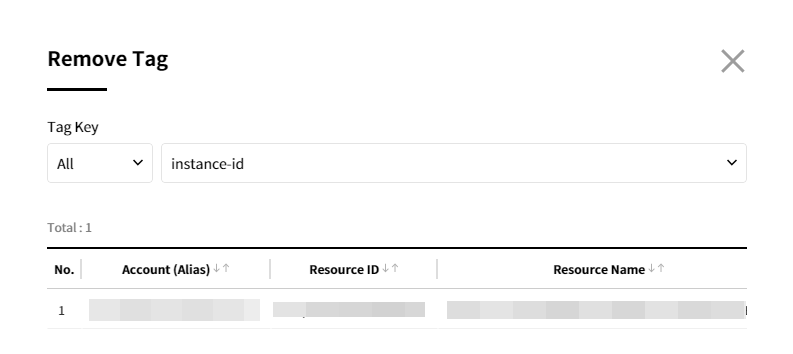
② When the Remove Tags pop-up appears, click the [Apply] button after selecting All or Common as a condition to delete tags.
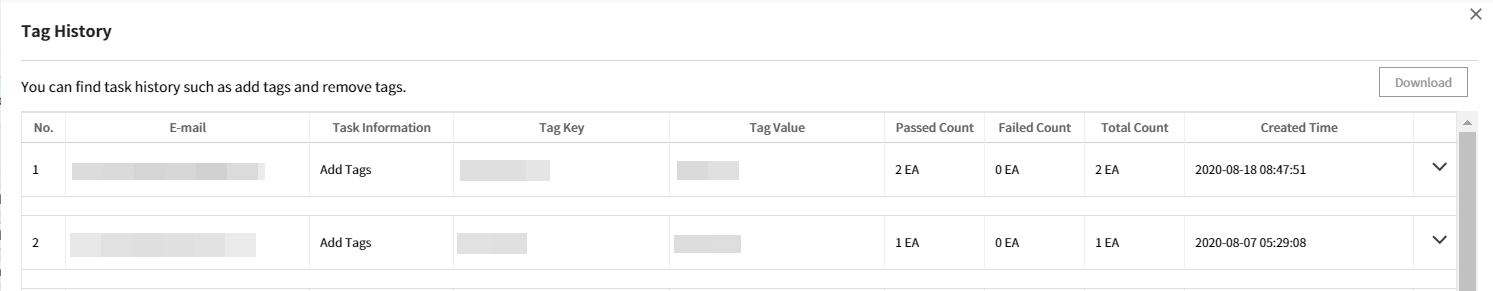
Tag History
Tag Assistant allows you to track when, where, what, and who added or deleted tags, and tagging resources was a success or failure. Click [Tag History button] on the right-corner to track all the logs, and the logs can be downloaded as Excel format as well.
Tag Assistant Supported Resources
You can view resources that are supported for tagging by Tag Assistant.